Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)

CEA Antibody
| Name |
Anti-Human Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) antibody |
| Catalog # |
R181c1 |
R182c8 |
R255k5 |
Platforms
Pairs |
Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) |
R255k5 (Capture)-R182c8 (Detection)
R181c1 (Capture)-R182c8 (Detection) |
| Description |
Mouse monoclonal antibody, cultured in vitro |
| Buffer |
1 x PBS, pH 7.4 |
| Purity |
Purity>95%, purified by Protein A/G chromatography |
| Storage |
Aliquot and store at -20°C or lower. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |

CEA Antibody Conjugates
CEA Antibody Conjugated Magnetic Beads
| Name |
Catalog # |
| CEA antibody conjugated magnetic beads |
B250y1 |
| B251y1 |
| B252y1 |

CEA Antigen
| Name |
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) antigen |
| Description |
Recombinant, C-terminal His-tagged, in vitro expressed from mammalian cells |
| Applications |
Calibrator and quality control product |
| Catalog # |
C1546 |
| Purity |
>90%, analyzed by R250-stained SDS-PAGE |
| Buffer |
1 x PBS����,pH 7.4 |
| Storage |
Aliquot and store at -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| SDS-PAGE |
Predicted MW around 72 kDa (tagged)
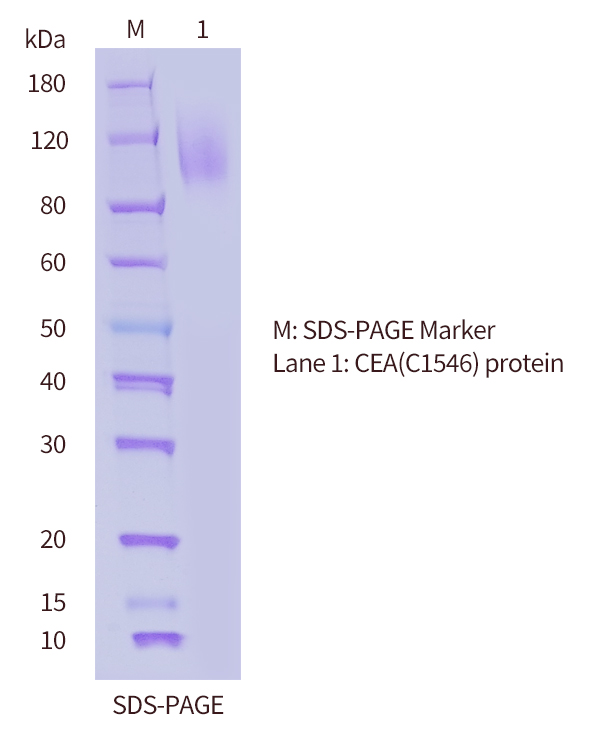
|

product_data
Updating

Introduction to Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), also known as CEACAM5 or CD66e, is a kind of adhesion molecule on the surface of immunoglobulin superfamily (Ig-SF). CEA contains 702 amino acids and has a molecular weight of approximately 150 kDa. The protein molecule consists of: N-terminal intrachain disulfide bond lacked Immunoglobulin variable-like (IgV-like) domain and six immunoglobulin type 2 constant region-like (IgC2-like) domains. CEA is highly glycosylated and contains many Glc-NAc-AsN bond type and ploy mannose type multiantennary carbohydrate chains.
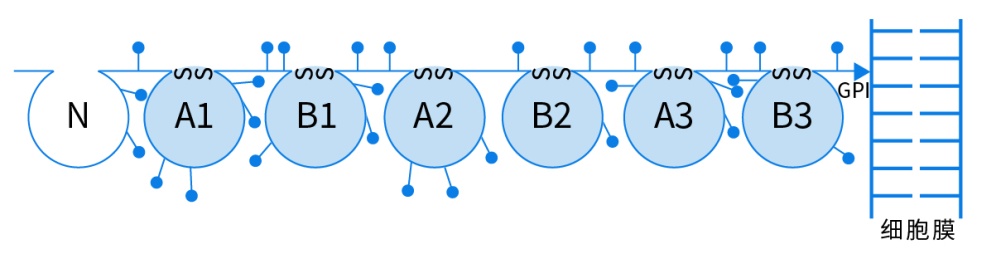
Figure 1. Molecular model of CEA based on cDNA structures
Note: Arrows indicate the connection GPI between CEA and cell membrane; N indicates the N-terminal IgV-like domain; A1-A3, B1-B3 indicate the IgC-like A and B domains; lollipop structures represent potential glycosylated sites.
Biological functions of Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
CEA has the function of inhibiting cell anoikis, inhibiting cell differentiation and preventing cell polarization. CEA also plays an important role in cell adhesion, intracellular signaling conduction and tumor progression.
A. Mediating cell adhesion
CEA can act as an adhesion molecule by mediating homogeneous and heterogeneous cell adhesion through its N-terminus when expressed on the surface of tumor cells. This may be related to the anti-parallel and parallel binding properties of CEA immunoglobulin superfamily (lg-SF) single-chain molecules. lg-SF single-chain molecules can bind with each other to form homo/hetero dimmers and higher-order complexes.
B. Inhibition of cell anoikis
CEA is anchored to the lipid rafts of cell membrane and bound to the integrin receptor α5β1 via the structure of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI). α5β1 localizes the cytoskeleton to adhesion site after binding to the ligand fibronectin (FN). When CEA is overexpressed, CEA-GPI anchored lipid rafts aggregate, leading to the aggregation and activation of integrin a5. Then, PI3-K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways are activated and survival signal is transmitted from extracellular to intracellular, and CEA exerts its inhibitory function to anoikis. Thus, tumor cells can survive and proliferate out of the plane of monolayer in absence of basement membrane adhesion. In addition, inhibition of anoikis can also inhibit cell differentiation and further aggravate cancer.
Clinical significance of Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
CEA is a stable molecule selectively expressed by the epithelium, with limited expression in healthy tissues and high expression levels in tumors, and its expression level is positively correlated with cell differentiation status.
In healthy people, CEA is mainly produced by colonic goblet cells and exists in the outer mucus layer of the apical glycocalyx and is finally excreted with feces. So the content of CEA in blood of healthy human is very low. "WS/T 645.2-2018 Commonly used clinical immunology test items reference interval part 2: Serum AFP, CEA, CA19-9, CA15-3, CA125" pointed out that the reference interval of serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in Chinese adults is ≤5 ng/mL.
In cancer patients (eg. colorectal cancer), CEA expression is upregulated and overexpressed in the apical lumen of tumor cells. Thus, the normal cells lose their polarity, components from the plasma membrane are continuously shed from the surface and CEA-coated vesicles are formed, which pass through the lymphangion and blood vessels and finally enter the blood. Along with the development of tumors, the content of CEA in the blood increases. Currently, CEA is mainly used for postoperative monitoring of colon cancer in clinical, and CEA monitoring provides patients with a lead time for secondary surgery or other treatments. Generally, CEA is a broad-spectrum biomarker and be used for various cancers. However, unlike other typical carcinoembryonic antigens, CEA has relatively poor tumor specificity and it needs to be combined with other indicators in clinical diagnosis to improve the specificity and sensitivity of detection.
References
[1]S, Hammarstrom. The carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues[J]. Seminars in cancer biology, 1999, 9(2): 67-81.
[2]C Ordoez, RA Screaton, C Ilantzis, et al. Human carcinoembryonic antigen functions as a general inhibitor of anoikis[J]. Cancer Res, 2000, 60(13): 3419-3424.
[3]P Camacho-Leal, CP Stanners. The human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) GPI anchor mediates anoikis inhibition by inactivation of the intrinsic death pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2008, 27: 1545-1535

Related Products




 A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出在线|
国产精品日本无码久久一老A|
成人无号精品一区二区三区|
国产偷人爽久久久久久老妇APP|
男人吸奶日进去视频|
西西人体扒开大胆大尺度展露|
国产欧美日韩视频怡春院|
亚洲欧美精品SUV苍井优|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色字幕综合|
少妇无码吹潮久久精品AV|
玩弄丰满奶水的女邻居|
色偷偷资源亚洲在线|
BBW.妇女被内射|
免费男女羞羞的视频网站中文子暮|
9999色艺术中心|
国产成人免费精品|
亚洲欧洲日产国码中学|
中文一卡二卡三卡四卡免费|
国产在线观看91香蕉|
丰满丰满区一区二区二一|
丰满岳跪趴高撅肥臀尤物在线观看|
超碰97久久国产精品牛牛|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
无遮挡h肉动漫在线观看幽默|
久久香蕉超碰97國產精品|
国产精选 第1页-要看tv|
成人免费无码特级毛片A片|
久艾草国产成人综合在线视频|
亚洲欧洲日本无在线码播放|
男女久久久视频2019|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
国产色情AAA级AAA电影|
国产精品久人妻精品|
成年免费大片黄在线观看岛国|
蜜桃av鲁一鲁一鲁一鲁樱花影院|
国产清纯白嫩大学生正在播放|
国产又大又粗又硬又长A片小说|
国产十八熟妇AV成人一区|
小骚妇下面水多要插视频|
顶级欧美做受xxx000大乳|
影音先锋熟女少妇AV资源
|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫|
国产欧美丝袜另类第三区|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
国产AV国产精品白丝JK制服|
亚洲精品无码高潮喷水A片在线
|
WWW成人国产高清内射|
无码人妻欧美丰满熟妇区毛片
|
色欲精品国产AV久久久|
欧美视频 偷窥自拍视频|
国产A∨无码专区亚洲A∨麻豆|
A片试看120分钟做受视频红杏|
国产夜色精品一区二区|
好男人在线视频神马影视WWW|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
97色伦午夜国产亚洲精品 |
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
免费网站观看av片|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产丝袜|
久久精品国产免费中文|
青青草在免费线观曰本|
性生生活大片又黄又|
影音先锋资源AV看片站|
最近2018中文字幕视频免费看|
午夜熟女插插XX免费视频|
亚洲精品久久久午夜福利电影网|
被男人添B超爽视频免费|
免费A级毛片黄A片高清在线播放
|
动漫美女H黄动漫在线观看|
欧美国产在线播放欧美|
国产精品色哟哟网站高清|
久久久国产人妻精品|
77成年轻人电影网网站|
国产精品福利在线播放|
欧洲一卡2卡三卡4卡乱码毛1|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
国产一区精选播放022|
国产亚洲精久久久久久无码妖精|
性一交一乱一美A片图片|
国产清纯白嫩大学生正在播放|
色综合亚洲色综合久久网张柏芝|
国产麻豆剧传媒精品国产AV|
国产一区二三区无码免费|
饥渴难耐的浪荡艳妇在线观看
|
99RE6国产精品99RE在线|
少妇又色又爽又紧的A片|
五月婷婷丁香花综合网|
亚洲乱码一卡二卡四卡乱码新区
|
中文字幕视频一区亚洲欧美|
4484在线观看视频|
末成年美女黄网站色大片连接|
巨大乳女人做爰视频在线|
8090碰在线视频97|
高潮A片揉搓乳尖乱颤视频
|
2019爱久久视频在线12|
av大片在线网站|
天天做天天添天天谢|
国产成熟妇人高潮A片|
小粉嫩精品A片在线视看|
中文日韩欧美亚洲|
少妇把腿扒开让我添69式漫画|
风韵人妻丰满熟妇老熟女|
超级青草碰碰免费视频|
亚洲高清无在码在线电影|
精品卡一卡二卡三免费使用|
欧美成人A片免费无码毛片|
又色又爽的无遮挡免费网址|
91香蕉视频污在线观看|
肉浦团在线观看快播|
亚洲综合AV色婷婷五月蜜臀|
欧美日韩综合无码中文字幕|
欧美乱熟人妻色情影视|
国产又色又爽又刺激的A片|
欧美精品一区二区久久丰满湿润|
一区二区三区A片无码视频不卡|
国产aaav淫片|
欧美粗大特黄AAA片|
草莓AV福利网站导航|
国产午夜精品AV一区二区麻豆|
国产在线观看不卡|
五月色婷婷亚洲男人的天堂
|
欧洲精品无码一区二区三区的视频空间|
av免费无码专区|
91久久无码一区人妻A片蜜桃|
97高潮就出奶水多还在哺乳|
无码人妻久久久午夜一区二区三区|
成人亚洲黄片欧美日韩|
国产V片在线播放免费观看大全|
精品日产乱码卡一卡2卡|
最近韩国日本MV免费观看免费|
A片扒开双腿猛进入免费观|
无遮挡拍拍拍免费观看|
老熟女肥臀AV老熟女A片|
久久久精品免费视频|
黄片欧美一区二区三区|
精品人妻无码一区二区三区手机板|
成年女人免费影院播放|
四虎视频成人版黄A片|
真人做爰视频在40分钟左右|
免费无码又黄又爽又刺激|
免费番肉动漫在线观看|
中日韩AV亚洲高潮无码|
青娱乐国产视频在线分类|
99久久亚洲精品日本无码|
又硬又粗进去爽A片免费|
人妻无码AV中文字久久|
人人妻人人澡人人爽人人老司机|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
肥熟女视频一区二区三区国|
中文字幕乱码免费视频|
亚洲精品中文幕一区二区|
国产粉嫩小泬在线观看泬|
韩国精品福利一区二区|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
无码av在线不卡在线观看|
人妻无码AV中文系统久久免费|
粉嫩av一区二区三区|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
亚洲欧美人高清精品a不卡|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
久了re热在线视频播放6|
嫩草AV久久伊人妇女超级A|
中文字幕 亚洲 有码 在线|
久热这里只精品99re8久|
国产V片在线播放免费观看大全|
国产视频适合在网上看的和出水了|
日韩色情一区二区无码AV|
老妇高潮潮喷到猛进猛出|
美女被免费网站在线视频app|
2019国产精品青青草原|
成人av片无码免费天天看|
强开小婷嫩苞又嫩又紧视频|
亚洲50熟女性视频免费|
无码免费一区二区三区日本A片|
亚洲国产精品一区二区第一页|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
添女人荫蒂全部过程AV|
人妻丰满熟妇av无码久久洗澡|
国产丰满农村妇女一区区|
cijilu在线视频|
泰国两熟女春梦邂逅猛男|
国产欧美日产综合动漫在线观看网站视频
|
99超级碰碰成人香蕉网|
亚洲成人视频一区二区|
中文字幕亚洲精品久久AV|
欧洲精品不卡1卡2卡三卡四卡|
欧美亚洲综合免费|
国产高潮抽搐在线观看
|
1000部免费视频观看|
精品亚洲A∨无码国产一品在线|
色偷偷WWW.8888在线观看|
东京热456大交乱高清视频|
91av国产超碰在线|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
国产精品一区二区 尿失禁|
产福利一区在线观看精品尤物|
越南女子杂交内射BBWBBW|
极品媚黑91黑人在线播放|
又湿又深又爽的A片视频|
国产传媒18精品A片一区|
麻豆AV无码精品一区二区|
亚洲最大天码AV在线观看|
2020最新国产自产精品|
国外人成人色视频在线
|
337p日本欧洲亚洲大胆色噜噜 |
大片国产片日本观看免费视频|
日产一区日产2区日产三区|
极品少妇粉嫩小泬啪啪AV|
日韩色情一区二区无码AV|
影音先锋天堂网资源av|
亚洲乱码AV中文一区二区|
久久视频精品38在线播放|
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA
|
在线毛片片免费观看|
黄 色一 片 级 日本|
一个人看的www的视频中文|
AV国产精品私拍在线观看|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频|
又硬又粗进去好爽A片春色视频
|
丰满熟女人妻中文字幕免费|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
免费无码AV色情在线|
圆产精品久久久久久久久久久新郎
|
男生J桶进女人P又色又爽又黄|
精品亚州aⅤ无码一区|
人妻中文字幕乱人伦在线|
久久久久综合网久久|
A片扒开双腿进入做视频|
www.成人.com|
欧美亚洲色倩在线观看|
国产高潮A片羞羞视频涩涩|
国产内射大片99|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
狠狠色老熟妇老熟女|
国产AV无码熟妇人妻麻豆|
国产yw8825免费观看网站|
丰满少妇大力进入A片中文|
国产精品久久久久久亚洲小说|
不充会员的爽爽影院|
嗯啊开小嫩苞HHH...嗯啊|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
国产在线观看91香蕉|
国产精品乱码久久久久久软件|
天天做天天躁天天躁|
麻豆精品一卡2卡三卡4卡免费观看
|
拍真实国产伦偷精品|
99精品欧美一区蜜桃在线 |
最新国产精品好看的国产精品|
欧洲老妇60一70|
av在线观看网站免费|
国产一区国产二区在线|
亚洲乱码一卡二卡四卡乱码新区
|
性一交一伦一A片免费看|
麻豆果冻传媒在线观看|
久久偷看各类WC女厕嘘嘘偷窃|
www国产亚洲精品久久网站|
免费A片看黄网站WWW|
欧乱色国产精品兔费视频|
2020中文在线一区二区三区|
国语激情对白 VIDEOS|
无码少妇一区二区三区动漫免费看|
久久精品国产亚洲AV高清色三区|
区产品乱码芒果精品综合|
97久久久精品综合88久久|
成人三级理论电影|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片漫|
狂处让老二爽18p|
摸添揉捏胸还添下面视频|
国产成人精品一区二三区熟女在线|
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩18禁|
CAO死你好紧好爽好湿视频男男|
91精品久久久久久综合五月天|
久久精品成人无码A片小说|
99久久精品免费国产一区二区三区
|
2017能在线观看的网站|
91久久综合精品国产丝袜长腿|
国产成人精品男人的天堂网站|
福利午夜视频在线|
欧美粗大特黄AAA片|
亚洲在线一人香蕉免|
国产精品aⅴ久久久久久鸭绿欲|
丰满熟女人妻一区二区三|
成年视频网站在线观看777|
成年人免费在线看黄|
YY6080午夜福利无码理论|
久久五月天激情五月天|
欧美精品久久96人妻无码|
在线看欧洲一卡二卡三卡残暴|
麻豆av一区二区三区|
女人添荫蒂舒服了A片|
最新一本到2019线观看|
亚洲 欧美 制服 另类 无码|
久久久老司机精品网站福利|
亚洲熟妇AV日韩熟妇在线|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片小说|
91精品一区二区在线观看|
色情A片成人免费观看视频|
www色情免费观看日本|
a级毛片无码免费真人久久国|
毛片内射久久久一区|
边啃奶头边躁狠狠躁AV|
大陆老熟女嗷嗷叫AV在线|
从后面挺进去激情视频|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩在线
69一区二三区好的精华
|
中国国语对白高潮A片|
国产成人精品一区二区免费|
污污内射久久一区二区欧美日韩|
成人做爰WWW免费看视频日本
|
无敌神马影院视频观看高清免费|
亚洲av制服自拍诱惑|
男生女生看片视频免费的|
中文无码第3页不卡av|
SM情趣鞭打尿失禁强制高潮女|
日本无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放|
天天影视欲香欲色成人网|
2019天天拍天天爱天天拍|
麻豆星空精东天美MV第一页|
国产亚洲精品AAAAAAA片|
久久久精品国产SM最大网站|
精品成人无码A片观看香草视频|
日韩精品AV一二三区在线|
日韩美女自卫慰黄网站|
黄WWW禁止男女萝卜|
亚洲精品无码一区二区色戒|
羞羞视频网站在线观看18岁无遮挡|
陈红下面又紧又小好爽|
丰满丰满区一区二区二一|
久久成人麻豆精品一牛影视太久|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
强行糟蹋人妻HD中文|
爽灬好舒服灬别拔出来视频人|
日韩插啊免费视频在线观看|
最近中文2019在线观看|
佳佳黑高跟极致踩踏调教视频|
九九影院免费还看视频|
张柏芝精品一区二区三区在线观看|
99久久免费只有精品国产高潮
|
影音先锋中文无码一区|
日本妇人成熟A片一区-老狼|
亚洲国产欧美日韩另类精品一区二区在线
|
安徽妇槡BBBB搡BBBB|
国产精品一区二区不卡蜜臀在线
|
国产国语特级 a毛片|
公交车上双乳被老汉揉搓玩|
人妻少妇精品无码一区二区三区
|
一区二区超碰免费在线观看|
91精品国产高清久久久久久l|
欧美人妻精品久久久久久|
日本无码MV免费视频在线|
国产玉足榨精视频在线观看|
2014手机免费基地旧版懂得|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区不卡|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
青草亚洲国产欧美一区二区|
人妻无码AV中文系统久久免费|
国产偷自久久精品久久|
成人亚洲免费影视|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
91大香蕉国产一区|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片|
91一区二区三区四区五区|
男女无遮挡猛进猛出免费观看视频|
少妇人妻av中文系列久久
|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片漫|
91高清综合一区天天干夜夜操|
chinese国产hdsex水滴|
69无人区乱码一二三四区别|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
最近日本字幕MV在线观看|
亚州日韩精品AV片无码中文|
污污免费看锕锕锕锕锕锕锕|
精品国内片67194|
欧美特级另类xxx|
欧美日韩免费在线|
粗大挺进亲女H小蕾的嫩苞第几集|
AV8888AV色情观看在线|
A片高潮抽搐揉捏奶头视频在线看|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
羞羞影院午夜男女爽爽影院网站|
国产精品高潮呻吟AV久久床戏|
一级黄日本C爱视频|
日本一本道2018无号码|
大陆国产aⅴ国语精品对白|
激情内射亚洲一区二区三区爱妻|
高清国产不卡视频|
亚洲国产成人久久精品导航|
chinese国产hdsex水滴|
欧洲一级毛卡片免费不卡|
中文字幕 亚洲 有码 在线|
91av视频免费在线观看|
欧美特级特黄AAAAA片|
色噜噜狠狠一区二区三区|
成在人线av无码免观看麻豆|
日本一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡高清视频下载
|
又大又紧18P少妇在线观看|
精品无码国产污污污免费|
91国产丝袜在线播放|
少妇被躁到高潮A片免费|
亚洲一区二区三区国产|
成人国产在线观看|
99精品福利视频|
成人无码在线视频区|
又大又黄又爽免费看A片|
影音先锋av在资源天堂|
好大好爽好深舒服死了A片|
少妇又色又爽又紧的A片|
美女被c视频在线观看|
日本A一片中国A一片|
欧美人妻WWW无码国产黄漫|
四川少妇搡BBB搡BBB爽爽爽小说|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
男生女生看片视频免费的|
人妻精品久久无码专区色视蜜臀|
欧洲成人4卡5卡6卡7卡|
军人同性CHINESE69猛男|
欧美区日韩区国产区|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
男女在线观看啪网站|
国产爆初菊一区视频|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
国偷自产aV一区二区三区|
亚洲AV无码乱线观看性色|
日韩好片一区二区在线看|
露营野外帐篷奶头舔齐根没入小说
|
国产欧美又粗又猛又爽|
男插女一起爽的免费樱花小视频|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片秋霞|
午夜精品A片一区二区三区|
亚洲区色情区激情区小说公|
国产国产乱老熟女视频网站97|
国产精品免费AⅤ片在线观看男女|
a亚洲Va欧美va国产综合 |
国产69精品久久久久999小说|
又大又爽又黄A片免费|
中文字幕高清免费日韩视频在线
|
亚洲少妇久久久久|
又黄又粗暴的gif动态图|
国产亚洲精品A片久久久|
色情A片成人免费观看视频|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
10000拍拍18勿入免费看动漫
|
一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡在线|
色老头在线视频免费观看|
亚洲国产成人久久精品导航
|
91中文字字幕人人国产3|
国产女仆美女主播一区二区|
五月综合激情婷婷六月色窝|
成人高清精品视频|
一本道中文字幕av无码|
视频一区二区三区蜜桃麻豆|
亚洲AV成人噜噜无码网站A片|
国产婬A片999片免费网站|
黄色网址在线免费观看|
日本做爰A片AAAA|
欧乱色国产精品兔费视频|
久久久精品国产SM调教网站|
日产乱码一二三区别免费麻豆|
午夜福利精品视频|
很黄又污又色情又爽又猛|
国产精品日本无码久久一|
五十路近親相姦中出し親子|
99国产精品免费一区二区
|
午夜无码熟熟妇丰满人妻|
欧美性猛交aa一级|
精品AAAA巨乳|
91精品国产高清久久久久久l|
无码精品人妻一区二区三刘亦菲|
欧美日韩一级婬片A片吞精怀直播|
又黄又爽又无遮挡在线观看免费|
国产色欲婬乱视频网站免费|
8090碰在线视频97|
亚洲多毛妓女毛茸茸的|
亚洲av免费分钟观看|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
久久久天堂国产精品女人|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
麻花豆传媒剧国产MV入口|
40分钟超爽大片黄|
欧乱色国产精品兔费视频|
日本高清色情高清日本|
午夜欧美日本一区二区三区|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
欧美精品一区二区久久丰满湿润|
亚洲精品国产国语|
亚洲精品久久久久久久蜜桃臀
|
国产亚洲av资源在线观看|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
亚洲女厕所小便bbb|
自怕偷自怕亚洲精品|
三级片中文字幕一区二区|
久久久国产精品无码人妻|
成人a级特黄毛片|
国产精品一区二区亚瑟不卡|
香蕉视频在线看污污|
五月天精品视频在线观看|
99久久人妻无码精品系列性欧美|
成年网站免费视频网站|
亚洲巨乳巨臀在线一区二区BBW|
国色天香精品卡一卡二卡三二百|
中文字幕丰满孑伦无码专区|
边吃奶边狠狠躁日韩A片|
欧美日韩精品电影一区|
教室停电H嗯啊好硬好湿攻守|
女人体a级1963免费|
国产av一区二区三区精华液|
亚洲国产欧美日本视频|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
国产超级a天堂直播在线观看
|
无码中文字幕AV久久专区
|
影音先锋av最新资源网|
99久久人妻无码精品系列蜜桃
|
又大又黄又爽免费看A片|
艾草在线精品视频播放|
九九综合VA免费看|
五月丁香综合啪啪成人|
西西4444www无码大胆|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师|
欧美搡BBBBB摔BBBBB|
国产精品日本无码久久一老A|
邻居少妇被爽到高潮A片|
百度国产精品网友自拍|
四虎视频成人版黄A片|
在线观看的av免费网站|
嫩草欧美曰韩国产大片|
最近中文字幕免费MV视频|
触手侵犯の奶水授乳羞羞漫画动漫|
羞羞影院午夜男女爽爽免费|
丰满少妇大力进入A片中文|
国产清纯美女爆白浆视频|
wuyueqingsetian|
宅男色影视亚洲人在线|
国产精品女A片爽爽免费按摩|
五月丁香激色婷五月天|
无码久久久久久中文字幕视频|
最近中文2019在线观看|
欧美又硬又粗进去好爽A片|
国产亚洲欧美日韩色|
男女作爱在线观看免费网站|
亚洲精品久久久WWW小说|
久久tv中文字幕首页|
日本A片特黄久久免费观看|
欧美叉叉叉BBB网站|
中文字幕乱妇无码AV在线|
免费gv在线观看网址|
另类女人ZOZO人禽交|
a97se亚洲国产综合自在线|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
欧洲一卡二卡三卡|
欧洲一卡2卡三卡4卡网站国色天香|
特级A欧美做爰AAAAA片|
欧美性生交大片免费看|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
91精品国产自产91精品资源|
性色AV爽歪歪啪啪A片|
中国国语对白高潮A片|
久久精品成人无码A片小说|
韩国精品无码少妇在线观看网站|
精品国产一区二区三区久久影院|
亚洲国产aⅴ精品无码|
搡的我好爽视频免费观看|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心
|
国产精品人妻无码免费久久久|
国产又粗又长又大精品A片|
91九色熟女欧美日韩欧美|
国产JJZZJJZZ视频免费看|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区不卡|
亚洲av无码成人精品区在线播放|
亚洲国产卡1卡2卡34卡|
亚洲-av-无限看|
女性爽爽影院免费观看|
大片免免费观看视频播放器在线观看
|
日韩成人伦理在线|
精品亚洲成A人7777在线观看|
免费网站观看av片|
高清成人欧美一区二区三区 |
国产精品人妻黑人借宿电影|
精品卡一卡二卡三免费使用|
欧美成人精精品一区二区三区
|
色婷婷婷丁香亚洲|
亚洲精品一区二区无码夜色|
精品国产亚洲一区二区三区|
国产成人午夜极速观看|
特黄特色大片免费播放器9|
亚洲熟女乱综合一区二区在线
|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
中文无码妇乱子伦视频国产精品亚洲LV粉色
|
又硬又粗进去爽A片免费无码|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片99A|
97成人精品一区二区三区狼人|
黄色网址视频在线播放|
第4色影院午夜在线观看|
91福利视频合集|
亚洲AV爽爽香蕉久久影|
欧美日韩无套内射另类|
91日韩精品在线观看|
色情无码WWW视频无码区小黄鸭|
亚洲AV无码久久蜜桃杨思敏|
伊人狠狠色丁香婷婷综合男同|
少妇的丰满2中文字幕|
适合一男一女看的爱情视频|
强开小婷嫩苞又嫩又紧视频|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区竹菊影视
|
在线精品亚洲观看不卡欧|
国产真实交换配乱婬98视频|
色噜噜2017最新综合|
中文字幕日韩人妻|
最近中文字幕视频完整版在线看|
一道本av免费不卡播放|
圆产精品久久久久久久久久久新郎|
男女又黄又刺激B片免费网站|
蜜桃视频在线观看网站|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
91福利华人在线观看|
国产成人av在线影院 |
粉嫩无套白浆第一次jk|
青青草国产97免费观看|
国产网友自拍在线视频|
国内偷拍亚洲欧洲2018|
影音先锋av色噜噜影院|
午夜福利精品视频|
成人在线观看国产一区|
琪琪电影网www888dvdc|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
百度国产精品网友自拍|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
国产视频久久久久久久一区二区三区|
丰满放荡岳乱蜜桃AV|
塔尔萨之王免费观看西瓜|
拍拍拍无遮挡高清视频在线网站|
成人小视频在线观看 |
少妇的丰满2中文字幕|
99久久婷婷国产综合精品青草欧美成人
|
成人A片产无码免费视频奶头鸭度|
国产成人精品综合久久久久|
久艹视频在线免费观看|
狠狠色很很鲁在线视频|
av天堂影音先锋在线|
中文字幕在线看成电影乱码|
久久中文字幕人妻AV熟女|
99超级碰碰成人香蕉网|
色欲人妻AAAAAAA无码|
色婷婷丁香A片区毛片区女人区|
爱我几何完整版在线观看|
日本乱人伦片中文三区|
亚洲精品婷婷无码成人A片在线
|
免费又黄又爽又色的绿巨人|
国产亚洲精品AV麻豆狂野|
国产极品粉嫩福利姬萌白酱|
成人国产精品视频大全|
亚州日韩精品AV片无码中文|
老头把我添高潮了A片故视频|
国产人妖视频一区二区|
欧美黑人一区二区三区免费A片
|
曰本女人牲交视频视频试看|
啊轻点灬大JI巴又大又粗A片|
亚洲欧洲日韩极速播放|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
av影音先锋天堂网|
50岁的牲欲强老熟女|
国产精品人妻一区二区三区A|
师尊胯羞坐抬臀抖吟迎合视频
|
第四色播日韩AV第一页|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
久久国产精品成人电影院|
影音先锋电影网站色|
看亚洲一级黄色片|
国产欧美日韩另类精彩视频|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片动漫
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA
|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
免播放器无码av网址|
A片好大好紧好爽视频|
四平青年之喋血曼谷免费观看完整|
午夜神马福利电影不卡|
欧美性活一级视频|
亚洲日韩精品一二三四区|
www.啪啪.com|
19不插片免费视频|
WWW射我里面在线观看|
国产亚洲麻豆精品AA片在线观看|
国产在线精品视频二区|
免费人做人爱的视频完整|
久久久国产一区二区三区|
成人特级毛片WWW免费版|
好爽快点我受不了了国产|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
人妻中文无码就熟专区欧美|
一级片视频网站免费看|
中文字乱码电影在线播放|
综合天天久久一区三区乱码|
国产色情精品一区二区唱戏|
最近中文字幕MV免费高清下载|
99久久婷婷国产综合精品青草欧美成人
|
激情综合成人五月天|
最近日本MV字幕免费高清视频|
老司机无码精品A|
极品少妇高潮啪啪无码吴梦梦|
男女啪啪永久免费观看网站|
国产欧美一区二区三区在线看蜜臀|
少妇A级裸片AAAAA八戒|
亚洲欧美日韩国产|
成人黄色网站在线播放|
cijilu在线视频|
在线观看的av免费网站|
青草青草久热精品视频在线百度云|
高潮肉欲少妇A片在线看|
国产一级淫片在线观看|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
AV亚洲欧洲日产国码无码苍井空|
欧美日韩一区二区视频免费观看
|
久久精品国产一区二区三区四区|
丰满女教师中文字幕4|
色欲av亚洲情无码av蜜桃|
大陆老熟女嗷嗷叫AV在线|
99视频这里只有精品国产|
又黄又爽吃奶视频在线观看|
久久精品AV一区二区三|
一本到在线高清观看
|
XXX一区二日本视频|
国产又爽又大又黄A片美女裸体|
精品无人区一码卡二卡三|
影音先锋av网站大全|
成人国产精品无码一区二区三区|
婷婷综合色五月久丁香|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师|
影音先锋av丝袜天堂|
国产成人免费精品|
欲女熟妇国产一区二区|
色妞色视频一区二区三区四区|
国产一级婬小说A级|
男人猛躁进女人毛片A片|
精品国产亚洲一区二区三区|
国产亚洲一卡2卡3卡4卡老狼
|
苍井空三年级片网站|
一本道不卡中中文无码|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
高中女学生破苞视频免费|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
大片国产片日本观看免费视频|
综合天天久久一区三区乱码|
日本乱人伦片中文三区|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
国产人伦激情在线观看三级
|
成年美女黄网站色大免费视频|
亚洲精品无码苍井空A片|
亚洲jizzjizz中国妇女|
先锋影音av资源站av|
91精品人妻人人做人踫人人爽
|
99久久人妻无码精品系列蜜桃|
91av在线免费观看|
亚洲国产一卡2卡3卡4卡5公司|
女人A级毛片19毛水真多|
18禁止进入黄大全在线|
九九九免费观看视频|
三级久久高清欧美|
一本久到久久亚洲综合|
jijzzizz老师出水喷水多毛|
亚洲AV综合AV一区二区综合|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出AVV
|
91精品一区二区三区无码吞精|
朝桐光日韩一区二区三区|
无人一码二码三码4码免费|
日韩欧美高清在线观看|
国产激情无码久久久久久
|
富婆偷人对白在线观看|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放|
人妻饥渴偷公乱中文字幕|
亲胸揉胸膜下刺激视频在线观看
|
人妻互换HD无码中文在线|
好男人WWW神马社区在线观看|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片软|
秘书下面太紧拔不出来怎么办|
亚洲高清无在码在线电影|
CHINESE叫床对白VIDEOS|
无码精品AV久久久奶水|
掀开奶罩边躁狠狠躁苏玥视频|
亚洲最大天码AV在线观看|
国产精品VA无码区二区|
黄网站色视频大全免费观看|
国产精品久人妻精品老妇|
欧美日韩不卡一区视频在现|
女人与牲囗牲恔视频免费|
亚洲午夜精品AV无码少妇|
变态另类av手机版天堂|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片WWW|
中文字幕电影乱码在线观看|
少妇夹得好紧太爽了A片|
成人久久18秘免费网站|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片动漫软件|
996这里只有精品|
国产色拍拍视频在线|
精品欧美久久三级|
最近最好的中文字幕2019免费|
国产做A爰片久久毛片A片蜜臀|
成在人线av无码免观看麻豆|
国产精品午夜无码AV在线播放
|
那种视频在线观看亚洲|
91精品高清91久久久久久|
欧美丰满少妇a毛片直播|
亚洲-av-无限看|
91精品福利视频|
久爱精品视频在线视频|
蜜月a 免费一区二区三区|
很黄又污又色情又爽又猛|
日韩免费视频一区|
无忧传媒MV国产在线观看|
无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩18禁|
免费亚洲成人久久精品|
手机看片1204免费视频观看|
国产爆初菊一区视频|
免费gv在线观看网址|
97亚洲狠狠色综合久久|
2020最新中文字幕在线|
男人天天在线视频|
а∨天堂在线中文免费不卡|
男女久久久视频2019|
亚洲在线国产日韩欧美|
国产做A爰片久久毛片A片蜜臀|
国产sm激情首页视频在线观看|
午夜无码熟熟妇丰满人妻|
免费番肉动漫在线观看|
9l国产精品久久久久|
宝贝你真湿真紧好爽h视频男男|
国内久经典AAAAA片|
最近中文字幕在线资源3|
青青草免费线观综合网|
陈红下面又紧又小好爽|
成人WWW色情在线观看|
亚洲综合久久无码一区|
少妇高潮喷水惨叫一区|
亚洲精品口国自一产A片|
搡BBBB搡BBB搡18免费观看|
国内露脸少妇精品视频|
免费人成网站在线高清|
特级做A爰片毛片A片免费|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片动漫软件|
9国产熟女视频在线观看|
国产又色又香又爽视频|
搡BBB上海少妇搡BBB3|
国产美女做爰A片免费|
乱换玩3p视频在线视频|
亚洲精品无码一区二区色戒|
国产麻豆剧果冻传媒视频免费|
好吊色欧美一区二区三区视频|
精品久久久久久久无码伊人|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
国产99视频精品免费视频6|
久久国产精品无码观看|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
亚洲男人天堂2022|
最新黄色网址在线观看|
午夜成人亚洲理伦片在线观看|
亚洲综合久久无码一区|
亚洲精品久久久鸭子
|
久热这里只精品99re8久|
国产亲子乱XXXXinin|
麻豆产国品一二三产品区别|
色情五月亚洲中文字幕|
国产精品一级A精品特黄A|
欧美肥胖裸熟妇的毛发布|
91国内免费在线视频 |
青青青爽在线视频观看|
中文人妻熟女波多野结衣|
免费视频在线播放啪|
男生肌肌桶女人屁股|
高清国产激情视频在线观看|
国产精品爽黄69天堂A|
aⅴ国产系列欧美亚洲|
真人做爰视频在40分钟左右|
FREECHINESE东北女人真爽|
a篇片在线观看快播|
国产精品偷窥女厕视频|
黄色网址成人在线观看|
国产69精品久久久久久久久久久久|
午夜亚洲乱码伦小说区69堂
|
亚洲国产精品色情777777|
日产乱码卡一卡2卡三卡四福利|
看毛片看1级片看超级超级片|
美女18禁永久免费观看网站|
91香蕉在线国产 |
小小视频在线观看www|
丝袜熟女脚交足在线一区|
不充会员的爽爽影院
|
国产肥熟女老太老妇A片|
国产日韓无码一区二区三区|
动漫AV纯肉无码AV电影网|
免费gv在线观看网址|
极品少妇粉嫩小泬啪啪AV|
最近更新中文字幕2019国语在线|
亚洲AV无码一区二区A片成人|
国产精品一区二区免费|
蜜臀AV色欲无码A片一区|
美女被免费网站在线视频app|
一级A女人高潮毛片免费男|
丰满人妻在公车被猛烈进入电影|
WWW国产精品内射老熟女|
成人午夜特黄AAAAA片男男|
av手机在线观看网站不卡|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩在线|
色YEYE在线视频观看网站|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
国产成人精品电影不卡|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
99视频在线观看这里只有精品
|
精品人妻无码一区二区三区50|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
人人妻人人澡人人人爽人人DVD|
顶级欧美做受xxx000大乳|
色偷拍亚洲国产大姐|
国产JK白丝喷白浆精品视频|
精品无码国产AV一区二区|
最近中文字幕高清字幕在线视频 |
国产做爰完整版在线观看|
偷拍亚洲制服另类无码专区|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
巨爆乳肉感一区二区三区视频|
很黄又污又色情又爽又猛|
欧美肉体视频一进一出在线|
亚洲AV久久无码精品国产网站|
亚洲精品久久99久久一二三区|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产|
91精品国产午夜福利蜜臀|
996这里只有精品|
真人女性生图片高清黑毛|
亚洲AV综合AV一区二区综合
|
99 精品视频网站|
丝袜熟女脚交足在线一区|
欧美亚洲综合免费|
久久免费精品视频互動交流|
在线观看日韩一区二区视频|
2019年秋霞鲁丝片84|
久久伊人精品毛片|
不卡在线播放一区|
成人网站在线观看免费|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片小说|
蜜臀久久AV无码牛牛影视|
国产中文字幕一区|
国产AV无码熟妇人妻麻豆|
亚洲一区欧洲一区|
99超级碰碰成人香蕉网|
丰满少妇被猛烈进入毛片|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频|
少妇无套内谢久久久久|
小柔在公厕被灌满jing液|
精品精品国产欧美在线|
成人亚洲黄片欧美日韩|
中午日产幕无线码8区|
青青草在现线久观看2019|
日本三级香港三级三级人!妇久|
闷骚的小少妇全程露脸|
成年人视频网站免费|
2018国产偷拍免费视|
无遮挡啪啪摇乳动态图GIF|
欧美又大又粗又硬又色A片|
高潮无遮挡成人A片在线看|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片软|
一区二区三区免费看A片|
歪歪爽蜜臀AV久久精品人人槡|
AV国産精品毛片一区二区|
91嫩草国产在线无码观看 |
宝贝你真湿真紧好爽h视频男男|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出在线|
欧美FREE性黑寡妇|
国产av网站中文字幕|
欧美牲交A欧美牲交VDO|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
国产精品自产拍在线观看55亚洲|
亚洲50熟女性视频免费|
亚洲AV成人影视综合网|
影888午夜理论不卡|
www国产亚洲精品久久网站|
国产亚洲麻豆精品AA片在线观看
|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫|
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
试看多人做人爱的视频|
男女狂进狂出动态图GIF|
亚洲无人区一码二码三码区别|
少妇中文综合欧美|
国产精品久久久久久99人妻绯闻|
大肉大捧一进一出好爽MBA|
高潮无遮挡成人A片在线看|
女人另类牲交ZOZOZO|
小雪的13又嫩又紧又多视频|
999国产精品欧美一区二区 |
www.黄色免费网站|
日本公妇里乱片A片在线播放保姆|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
se97se成人亚洲网站|
成年人免费在线看黄|
日本成人一区二区三区|
97在线观看视频公开免费|
国产AV麻豆一区二区|
少妇bbb搡bbb搡bbb|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
亚洲成人视频一区二区|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
91精品久久人人妻人人爽人人|
亚洲无码黄色片网站|
丰满多毛少妇做爰视频爽爽和R|
无码人妻AⅤ一区二区三区A片一
|
久久tv中文字幕首页|
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
亚洲精品中文字幕制|
成av人电影在线观看|
超碰97成人免费在线观看|
日日摸夜夜添夜夜添亚洲女人|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片软件|
专干老肥熟女视频网站300部|
亚洲人成人无码.WWW石榴|
国产人妻99精品无码一区二区三区
|
免费费很色视频大片|
欧美黑人添添高潮A片视频|
特黄A又粗又大黄又爽A片|
双性猛男被脔到怀孕txt|
国语激情对白 VIDEOS|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
欧美91精品国产玩人妻|
亲胸揉胸膜下刺激视频在线观看|
中文字幕暖暖永久在线视频
|
亚洲一卡2卡3卡4卡国色天香app
|
国产学生粉嫩无套进入在线小说
|
国产又粗又猛又黄又爽A片|
国产一级特黄高清免费视频|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片秋霞|
免费岛国片在线播放|
a级黄色大片在线观看视频男男|
中文字幕亚洲精品久久AV|
99精品国产亚洲|
国产亚洲国产精品欧美|
少妇人妻偷人精品无码视频新浪|
欧美日韩精品亚洲一区二区|
一本大道一卡二卡入口|
se97se成人亚洲网站|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
欧美乱熟人妻色情影视|
色欲天香天天影视综合|
羞羞漫画破解无线书币|
高清无码国内自拍视频|
国产强被迫伦姧在线观|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
8050午夜二级|
九九视频在线观看视频6|
精品AAAA巨乳|
日韩免费精品视频一区二区三区|
国产精品人妻无码99999|
99国产精品免费一区二区|
欧美性猛交99久久久久99按摩|
天天噜av在线观看|
中文字幕人妻熟女在线|
欧美精品久久久久久无码人妻|
国产欧美日韩专区发布|
特级A欧美做爰AAAAA片
|
在线精品视频raPPer|
色欲AV亚洲午夜精品无码|
大帝a∨无码视频在线播放 |
国产午夜高潮熟女精品AV|
久热久热aV在线青青|
成年网站免费视频网站|
国产精品女A色欲AV色欲老师|
日韩色情一区二区无码AV|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
曰本一本道a东京热播|
欧美荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
色欲AV巨乳无码一区二区|
最近中文字幕大全免费版在线|
无码影片成人网站在线观看|
色情狠久久AV五月综合五月|
亚洲AV一宅男色影视|
国产精成人品2018|
91免费精品国产拍在线|
成人看片黄a在线看|
青青青爽在线视频观看|
亚洲欧美日韩中文在线制服
|
极品吹潮视频大喷潮tv|
最近高清中文在线字幕观看|
成人在无码AV在线观看一|
国产九九精品视频免费播放4互動交流
|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
播五月开心婷婷欧美综合|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区|
丰满少妇被猛烈进入毛片|
欧美特级另类xxx|
91性爱在线视频|
久久午夜无码鲁丝片午夜精品|
日本二本道dvd视频|
久久视频这里有精品21|
天天影视网网色色欲|
国产福利酱国产一区二区|
天堂AV国产夫妇精品自在线|
少妇做爰免费理伦电影|
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
国产精品白丝AV网站|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合尤物|
91精品日韩欧美国产|
2017秋霞在线观看免费大奶子|
91精品国产高清久久久久久l|
亚洲日本精品国产第一区二区|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
97亚洲狠狠色综合久久|
免费无码婬片AAAA片直播表情|
国产中的精品AV一区二区|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站一丁|
秋霞国产日韩91视频|
欧洲精品一卡2卡三卡4卡影视|
久久人人槡人妻人人玩夜色AV|
图片区视频区小说区|
国产精品人成视频免费软件|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
久久中文字幕人妻AV熟女|
天天鲁在视频在线观看|
国产三级激情av|
最近中文字幕MV手机免费高清|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
玩50岁四川熟女A片|
日韩在线看片免费观看软件
|
免费看国产成人无码A片|
免费全部黄A片免费播放软件|
久久免费视频播放中文|
最近日本MV字幕免费观看视频|
色偷偷超碰av男人天堂|
SM情趣鞭打尿失禁强制高潮女|
好爽快点我受不了了国产|
欧美成人A片欲伦艳|
日韩美女欧美精品|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
人妻性爱午夜不卡视频|
有人有片视频吗 免费的|
91大香蕉国产一区|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片软件|
国产一级特黄高清大片多人P一信息网|
国产精品96久久久久久|
女人18毛多水多A片视频|
国产亚洲精品A片久久久|
无码潮喷A片无码高潮漫画
|
先锋影音av最新资源|
免看黄29分钟继续看|
妇搡BBBB精品一区二区|
午夜亚洲一区二区亚洲福利|
黄网站免费永久在线观看下载|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
久艹视频在线免费观看|
日韩人妻精品久久日|
同性男男黄H片在线播放网站|
7777精品伊人久久久大香|
国产看真人毛片爱做A片|
亚洲熟妇男女啪啪视频|
国产高中生三级视频|
香蕉久久国产AV一区二区|
色噜噜2017最新综合|
快播可以看的a网站|
一区二区三区内射美女|
成年美女拍拍视频免费|
国产浓毛大BBWBBW|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
亚洲男人的天堂A片我要看|
四川少妇搡BBB搡BBB爽爽爽小说|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
欧美又大又长又粗又爽A片|
香蕉尹人综合在线观看|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
2019国产精品青青草原|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站仙踪林|
免费啪视频在线看视频|
无码天堂亚洲国产AV久久|
亚洲色欲色欲综合网站|
女人另类牲交ZOZOZO|
奶真大水真多小荡货AV|
国产精品583一区二区免费看|
男生J桶进女人P又色又爽又黄
|
91视频精品在线观看 |
五月丁香综合啪啪成人小说|
内射白嫩少妇超碰|
肉浦团在线观看快播|
国产又粗又长又硬又猛A片|
亚洲久热无码av无码中文字幕|
亚洲无遮挡无码A片在线|
成人国产一区二区精品小说|
成人网站在线进入爽爽爽|
1区2区3区4区产品乱码99|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区竹菊影视
|
AV久久无码AV喷水高潮|
天堂中文www资源在线|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
陈红下面又紧又小好爽|
最近中文字幕视频完整版在线看|
国产色综合色产在线视频|
美女校花被调教出奶水|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
欧美叉叉叉BBB网站|
亚洲国产精品日本无码小说|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片男男
|
91精品一区二区精品视频|
国产精品成人A片在线果冻|
用舌头去添高潮无码AV在线观看|
天堂最新版在线中文|
粉嫩小泬WWW免费视频网站下载|
国产人妻换人妻仑乱电影
|
97高清国语自产拍久久|
亚洲一品AV片观看五月色婷婷|
87福利午夜福利视频|
粗大的内捧猛烈进出视频网|
免费无套内谢少妇毛片A片软件|
草草影院永久线路CCYY|
玖玖爱这里只有精品视频|
国产91精品人妻一区二|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
欧美日韩精品亚洲一区二区|
A欧美爰片久久毛片A片|
风韵丰满优存少妇在线观看|
91久久精品无码一区二区毛片
|
WWW成人国产高清内射|
欧美日韩综合无码中文字幕
|
最近高清中文在线国语视频|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
嫩草AV久久伊人妇女超级A|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
国产一区日韩一区二区三区|
国产偷拍在线不卡偷拍|
亚洲无人区码一码二码三码的特点|
3atv精品不卡视频|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
WWW国产精品内射老熟女|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
男女又色又爽又爽视频|
女人爽得直叫免费视频|
精品综合日本国产|
国产欧美网站亚洲成人免费
|
无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩18禁|
色99久久久久高潮综合影院|
又黄又湿免费高清视频|
jlzzzjizzzjlzzz亚洲|
女人在厨房被添高潮全过程A片|
91超碰人妻人人人|
欧美一区二区高清|
玩50岁四川熟女A片|
国产精品A一区二区三区腾讯导航|
日韩精品AV一二三区在线|
午夜精品A片一区二区三区|
久久久久老熟女久久百度淫荡视频|
午夜人妻理论片天堂影院|
无码人妻AⅤ一区二区三区A片一|
98在线精品在线视频|
熟女丰满老熟女熟妇|
又硬又粗进去爽A片免费无码安娜|
最近免费视频中文2019完整版|
多毛熟女HDVido多毛的简介|
日本三级人妻一级二级三级|
成人午夜爽A片免费视频|
护士又紧又深又湿又爽|
欧美群伦性艳史黄94|
国产精品久久久久久爽爽爽床戏|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片WWW|
中文字幕乱码亚洲精品一区|
天天久久尤物视频综合|
乡下妇乱子伦小说|
网址在线观看你懂我意思吧免费的
|
中文在线无码高潮潮喷在线|
夫目前犯人妻av中文字幕|
好爽好紧好大的免费视频国产|
饥渴难耐的浪荡艳妇在线观看|
国产成人无码网站m3u8|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
国产中的精品AV一区二区|
人妻熟女狠狠涩蜜桃|
亚洲福利在线观看|
99国产精品久久人妻无码|
www.xxx-av.com|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
成人做爰69片免费看网站|
思思99在线视频|
美女翘臀强进入系列在线观看|
未满小14洗澡无码视频网站|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片小说|
大陆国产aⅴ国语精品对白|
国产精选 第1页-要看tv|
成人无码A片视频播放|
被男人添B超爽视频免费|
欧美群交在线播放1|
97SE亚洲精品一区|
国产成人永久免费无码观看|
国产在线精品免费AAA片|
草莓视频APP下载黄色安装|
日本五月婷婷手机在线观看|
成人性三级国产在线观看|
99爱免费视频在线看|
91精品久久久久久综合五月天|
女人与牲囗牲恔视频免费|
囯产少妇BBBBBB高潮喷水一|
久久激情成人国产|
国产成人永久免费无码观看|
麻婆豆腐传媒一区二区三区|
先锋影音源资2019|
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
国产V日产∨综合V精品视频麻豆
|
精品無碼人妻一區二區三區品|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色蜜臀v1.5|
国产50岁熟妇露脸|
夜来香AV在线观看|
亚洲一区二区三区国产|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
青青草免费线观综合网|
最新一区二区三区在线影院
|
一边添奶一边添p好爽视频|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
妞干网无缓冲这里只有精品|
97人妻熟女成人免费视频|
91无码人妻一区二区|
久久91精品国产91久|
chinese中国人自拍在线|
亚洲图片综合图区20p|
亚洲多毛妓女毛茸茸的|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
AA片在线观看视频在线播放|
不卡人妻无码AV中文系列APP
|
大香焦在线伊人74|
扒开双腿吃奶呻吟做受视频|
日本69色视频在线观看
|
在线看片免费观看视频|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
亚洲美女综合香蕉片|
欧洲熟妇大荫蒂高潮A片视频|
在线精品亚洲观看不卡欧|
最新国产专区不卡|
日韩视频一区二区有码无码|
成人A片激情免费视频|
国产sm激情首页视频在线观看|
国产熟妇高潮叫床视频播放|
亚洲精品鲁一鲁一区二区三区|
影音先锋av熟女资源网|
影音先锋av在资源天堂|
最新av网站免费在线观看|
999国产精品欧美一区二区 |
台湾四级露性器在线观看|
久久久久亚洲Av无码专区桃色|
色婷婷丁香A片区毛片区女人区|
91麻豆产精品久久久久久粉嫩|
小柔在公厕被灌满jing液|
亚洲国产精品成人久久久软件
|
日本不卡码在线网站|
又大又硬又粗做大爽A片|
欧美整片sss第一页视频|
国产对白精品刺激一区二区|
影音先锋亚洲AV少妇熟女|
精品国产乱码久久久久乱码|
在线最新无码经典无码|
在线观看日本污污ww网站|
成人国产精品影院|
久章草在线视频播放国产|
又爽又高潮的BB视频免费看|
色情免费100部A片看片|
性一交一乱一欲A片|
国产精品1区2区3区|
国产成人不卡AV在线观看|
一女被两男吃奶添下A片V|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
亚洲精品无码高潮喷水A片软|
91州精品一区二区三区|
无码性午夜视频在线观看|
亚洲精品久久久午夜福利电影网|
免费人妻无码不卡中出|
国产真实露脸乱子伦|
4484在线观看视频|
狠狠狠地在啪线香蕉|
多毛熟女HDVido多毛的简介
|
在线午夜福利视频免费|
把腿张开被添得死去活来在线|
男人使劲躁女人过程A片|
男人猛躁进女人毛片A片|
男生肌肌桶女人屁股|
小小视频在线观看www|
午夜精品久久久久久久久日韩欧美|
老太交70years性行为|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
免费无码AV片在线观看潮喷|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片软件
欧洲一卡2卡三卡4卡乱码毛1
|
区产品乱码芒果精品综合|
A片娇妻被交换粗又大又硬
|
五十路近親相姦中出し親子
|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
成人亚洲免费影视|
超碰97久久国产精品牛牛|
青青青视频免费观看2018|
成人AV网站A天堂|
少妇又色又爽又紧的A片|
麻花豆传媒剧国产MV入口|
在线午夜电影63网导航|
精品丰满人妻AV久久久|
啦啦啦中文日本免费高清百度
|
成人啪啪免费无码网站|
无码色情影片视频在线看免费
|
色狠狠色噜噜AV天堂五区|
丰满人妻熟妇乱又伦精品劲|
亚洲一区欧洲一区|
69激情露脸视频|
亚洲视频一区在线|
55大东北熟女啪啪嗷嗷叫|
岛国色情A片无码视频免费看|
不卡久久精品国产亚洲av麻豆|
精品午夜伦理一区|
久久精品视频在线直播6|
影888午夜理论不卡|
SM情趣鞭打尿失禁强制高潮女|
秘书下面太紧拔不出来怎么办
|
三人荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
精品无码国产AV一区二区|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
亚洲人成电影网站在线观看|
巜漂亮的女邻居又紧又爽三级|
91亚洲狠狠色综合久久久久久久
|
朝桐光日韩一区二区三区|
免费一级特黄3大片视频|
最近中文字幕大全免费版在线|
免费一级做a爰片久久毛片潮喷|
好久被狂躁A片视频无码免费视频|
亚洲成α∧人片在线播放无码|
女生奖励自己的声音素材高清版|
日日摸天天添天天添无码蜜臀|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
成年女人免费影院播放|
欧美成人无码A片在线视频QQ群|
国产精品一区二区三区四区五区|
yy6080午夜色情理伦片在线|
国产成人免费爽爽爽视频|
一道本av免费不卡播放|
99久久精品免费观看国产色综合|
亚洲精品gv天堂无码男同娇喘|
欧美亚洲国产小说图片图专区|
国产JK白丝喷白浆精品视频|
无人区AV在线观看|
六月丁香婷婷综合网激情网|
亚洲人成在线播放无码|
92久久精品一区二区|
老女人熟女人妻国产|
日韩高清特级特黄毛片|
自怕偷自怕亚洲精品|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说
999精品国产人妻无码梦乃爱华
|
av一本久道久久综合久久鬼色|
成人A片激情免费视频|
久久精品AV一区二区三|
国产妇少水多毛多高潮A片小说|
99精品欧美一区 |
一级一级特黄女人精品毛片视频|
影音先锋每日最新AV资源网|
综合久久一区二区三区|
男女一对一免费视频|
欧美阿v天堂视频在99线|
嫩BBB槡BBBB槡BBBB18|
性色aV一区二区天美传媒|
亚洲无码黄色片网站|
精品综合久久久久久98|
高清国产在线视频导航 |
欧美人妻精品久久久久久|
亚洲国产一卡2卡3卡4卡5公司|
亚洲AV无码乱线观看性色|
爽爽影院免费观看视频|
女人体a级1963免费|
羞羞漫画破解无线书币|
国产精品色吧国产精品
|
朋友娇妻的滋味中文字幕A片|
51久久国产露脸精品国产|
啊轻点灬大JI巴又大又粗A片|
久久视频这里只精品10|
阴部内射好爽性视频成人|
亚洲乱码一卡二卡四卡乱码新区
|
国产亚洲老牛精品视频|
99国产观看免费视频|
99久久免费只有精品国产高潮
|
久久婷婷五月综合色丁香花|
成av人电影在线观看|
国产特黄级AAAAA片免|
成人精品一區二區激情 |
欧美成人无码A区在线观看免费|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者
|
国产成人精品一区二区免费|
chinese老仑乱|
久久久精品国产AV麻豆|
插插射啊爱视频日A级|
92国产精品综合在线|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小|
92人妻国产一区二区三区|
日韩色情无码免费A片|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套
|
国产清纯美女爆白浆视频|
内谢XXXXX8老|
久久精品视频在线直播6|
免费看毛片的网址|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在|
日韩电影一区二区三区|
94久久国产乱子伦精品免费 |
55夜色66成年视频观看免费|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
天美传媒小甜豆完整视频在线观看|
中文字幕人妻熟女在线|
国产无遮挡A片无码免费软件|
国产一级片内射30岁老熟女
|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578
|
国产经典噜噜在线无码一二三区|
成人av在线播放观看|
少妇高潮呻吟A片免费看软件|
日本亚洲精品无码专区国产|
人妻免费视频公开上传|
性色AV爽歪歪啪啪A片|
麻花豆传媒剧国产入口|
男人天堂2018新在线版|
丰满大姐免费视频16MIN|
国产寡妇乱子伦一区二区三区。|
性色AV一区二区三区咪爱四虎|
亚洲自偷自偷在线制服|
国产成人精品777|
99精品热线在线观看免费视频|
99re视频在线|
荫蒂添的好舒服A片免费|
国产色综合色产在线视频|
国产一级婬小说A级|
国产AV麻豆一区二区|
亚洲一区欧洲一区|
国产十八熟妇AV成人一区
|
久久久久亚洲AV无码AV男人|
人妻丰满熟妇av无码久久洗澡|
黄污色污国产高清无码在线观看|
国产成a人亚洲精品在线观看|
成人乱码一区二区三区A片
|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
国产午夜男女爽爽爽爽爽|
国精品人妻无码一区二区三区性色|
91在线精品你懂的|
歪歪爽蜜臀AV久久精品人人槡|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色蜜臀v1.5|
黑人二十厘米进入A片|
伊人久久丁香色婷婷啪啪|
亚洲av片不卡无码久东京搔|
内射高潮享受视频在线观看|
在线观看免费av网站|
国产偷国产偷亚州清高APP|
99久久99热这里只有精品|
午夜无码影院在线|
又爽又高潮的BB视频免费看|
最新国产精品自拍不卡|
精品免费国产一区二区三区四区五
|
国产av一区二区三区精华液
|
青青草免费线观综合网|
亚洲是图 夜夜撸|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
国产偷国产偷亚州清高APP|
狠狠噜天天噜日日噜久久久电影|
久久人人爽人人爽人人片AV不|
又黄又湿免费高清视频|
国产精品美女WWW爽爽爽视频|
好吊视频一区二区三区|
日本无码国产在线婷婷直播|
波多野结衣亚洲一二三|
男人J桶进女人下部无遮挡A片|
男人都懂的www网站免费观看|
草莓视频成年人 |
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
岳的大肥屁熟妇五十路99|
欧美疯狂三P群体交乱免费视频
|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
97国产露脸精品国产麻豆|
久久久精品理论A级A片|
男女啪啪永久免费观看网站|
日韩色情无免费高清在线视频|
50岁老熟女高潮喷水|
粗大猛烈进出高潮免费视频日本|
少妇搡BBBB搡BBBB毛多多|
国产精品视频一区二区三区不卡|
YY6080午夜福利无码理论
|
又色又爽又高潮免费视频观看|
亚洲日韩国产AV无码无码精品|
国产精品日本无码久久一老A|
久久人人爽人人人爽成人AV
|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片免费|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放
|
一本加勒比HEZYO东京热高清播放|
波多野结衣AV在线观看|
丰满少妇又爽又紧又丰满在线观看|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
精品深夜AV无码一区二区老年|
久久免费看少妇高潮A片小说图片|
免费观看欧美成人AA片爱我多深|
成年妇女观看在线视频|
无套内射无矿码免费看黄|
亚洲精品伦理熟女国产一区二区|
好爽好深好猛好舒服视频上|
好大好爽快点大JI巴视频|
欧美精品久久96人妻无码|
泰国两熟女春梦邂逅猛男|
色情WWW成人片WWW222|
少妇午夜精品福利一区二区三区蜜桃
|
五月丁香国产在线视频|
老师办公室娇喘浪吟女学生漫画|
拔萝卜视频免费看高清|
欧美性A片又大又长|
欧洲老妇60一70|
国产精品人成在线观看1一|
无广告观看久久精品99久久香蕉国产全集
|
宅男宅女做a天堂|
色99久久久久高潮综合影院|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
欧美人妻无码A级视频|
日韩高清一区二区三区不卡|
成人国产精品无码一区二区三区|
四平青年之喋血曼谷免费观看完整|
久久女婷五月综合|
高潮肉欲少妇A片在线看|
vr专区自拍无码中文字幕精品|
亚洲国产精品无码乱码三区红酒|
亚洲AV久久无码精品国产网站|
99视频久九热精品|
99国产精品免费一区二区|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
国产精品系列在线一区|
免费看少妇高潮A片特黄
|
日韩一区二区三区免费视频|
糖心LOGO在线观看视频|
成年人视频网站免费|
中文字幕欧美人乱人精品A片|
成片免费观看视频大全|
日本无码MV免费视频在线|
亚洲尤码不卡AV麻豆|
成年妇女观看在线视频|
影音先锋影院中文无码|
小柔在教室伦流澡到高潮视频|
龙欲h粗喘强占公妇H|
野花视频免费观看2019|
亚洲国产精品无码乱码三区红酒|
久久99热人妻偷产国产|
免费高清在线国产视频|
梦寻桃花源免费观看|
无码免费一区二区三区日本A片|
最近的中文字幕在线MV|
欧美性狂猛AAAAAA|
成AV免费大片黄在线观看|
真实国产乱子伦对白视频37P|
人妻中文字幕av无码专区|
中文字幕丰满孑伦无码精品|
四虎影成人Av在线观看|
国产后式a一视频|
国产高清色情在线观看APP|
91丝袜白浆高潮潮喷在线观看|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
美女裸身无档视频免费|
秋霞成人国产理论A片|
亚洲AV无码乱码国产麻豆穿越|
天天影视亚洲综合网|
poronovideos人初重口|
国产清纯91天堂在线观看|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片|
成人WWW色情在线观看|
欧美牲交A欧美牲交VDO|
www.成人.com|
人妻熟女狠狠涩蜜桃|
恋夜影院支持安卓视频美女|
www.日日夜夜撸|
在线永久免费观看黄网站|
草莓视频成年人 |
亚洲AV嫩草AV极品A片|
a在线视频播放免费视频完整版|
末成年毛片在线播放|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
2022一本久道久久综合狂躁|
乌克兰女人大白屁股ASS|
老头把我添高潮了A片视频|
东北旺仔系列xvideos|
AV国産精品毛片一区二区|
屁屁影院最新地址入口|
蜜臀AV99无码精品国产专区|
特极西西444WWW大胆无码|
公交车上扒开嫩J挺进去|
动漫熟女制服一区二区 |
99精产国品一二三产品香蕉|
国产国语特级 a毛片|
91超碰人妻人人人|
色欲av亚洲情无码av蜜桃|
成人自拍网站在线观看|
欧美群交在线播放1|
精品综合日本国产|
成在人线av无码免观看麻豆|
午夜精品人妻无码一区二区三区
|
国产一级特黄a大片99|
男人猛躁进女人毛片A片|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片|
成人激情综合网影院在线观看|
亚洲天天一色综合AV|
少妇成熟A片无码专区小说
|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
91久久人澡人人添人人爽|
无码人妻久久一区二区三区免费|
色情成人影音先锋电影|
欧美又粗又大又黄A片在|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
国产吧在线视频中文字幕|
精品卡1卡二卡三卡乱码|
国产三区在线成人AV|
亚洲国产货青视觉盛宴|
亚洲天堂av一本道无码|
91亚洲狠狠色综合久久久久久久
|
91在线精品你懂的|
日韩雏女无套内射11P|
玩弄了裸睡少妇人妻野战|
五月丁香六月婷婷网线视频|
囯产精品一区二区三区线|
丰满岳跪趴高撅肥臀|
奇米影视第四色av首页|
免费高清在线国产视频|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
男生肌肌桶女人屁股|
无套内射无矿码免费看黄|
久久无码人妻一区二区三区|
搡8O老女人老妇人老熟|
五月丁香综合啪啪成人小说|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
粉嫩小又紧水又多A片|
国产精品人妻黑人借宿电影|
99精品国产综合久久麻豆|
色情成人影音先锋电影|
风韵人妻丰满熟妇老熟女|
无遮挡啪啪摇乳动态图GIF|
huan色大片电影百度影音|
蜜臀久久AV无码牛牛影视|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
亚洲无码在线观看免费|
天美传媒小甜豆免费观看|
国产成人精品不卡久久久|
天天看片视频免费观看|
拔萝卜视频免费看高清|
丰满人妻老熟妇伦人精品|
中文字幕乱码 电影在线观看|
国内自拍真实伦在线视频|
日韩无码一区二区三区四区|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
内射干少妇亚洲69XXX|
亚洲人成小说网站色|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说色噜噜|
成人免费无码特级毛片A片|
欧美黑人精品三级网站|
国产高潮A片羞羞视频涩涩|
全黄做爰100分钟视频|
丁香五月综合缴情在线观看|
极品吹潮视频大喷潮tv|
日本成人一区二区三区|
亚洲区色情区激情区小说公|
japanesevideo喷潮|
亚洲AV成人影视综合网|
秋霞成人国产理论A片|
久久久久久久999|
精品无人区一码卡二卡三|
亲胸揉胸膜下刺激视频在线观看|
香蕉久久av一区二区三区|
国产亚洲精品久久777777|
欧美又黄又粗暴免费视频|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
成人毛片100免费观看|
国产三级激情av|
成人做爰WWW免费看视频日本|
XXX波多野结衣苍井空|
a在线视频播放免费视频完整版|
很很鲁在线视频播放影院|
欧美又色又爽又黄的A片18禁|
亚洲欧美第一精品网站|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
新婚人妻不戴套国产精品
|
白丝校花被狂揉大胸羞羞动漫|
欧美成人精精品一区二区三区|
快播可以看的a网站|
2020最新国产自产精品|
免费看毛片的网址|
最新国语对白超清偷拍|
女教师杨雪的性荡生活|
人妻无码AV一区二区三区|
最新欧美精品一区二区视频|
亚洲精品中文幕一区二区|
91一区二区三区四区五区|
99精品久久久久久久久久综合|
国产爆初菊一区视频|
免费无套内谢少妇毛片A片软件|
亚洲乱码AV中文一区二区|
人妻精品久久无码专区色视蜜臀|
www成人国产在线观看网站|
五月婷婷在线人妻精品视频|
久久AV无码乱码A片无码|
中文字幕高清免费日韩视频在线
|
免费啪视频在线看视频|
亚洲精品无码苍井空A片|
国产V日产∨综合V精品视频麻豆
|
午夜熟女插插XX免费视频|
免费无码又黄又爽又刺激|
中文字字幕在线中文乱码2019|
国产乱人伦无无码视频|
婷婷四月开心色房播播|
人妻内射一区二区在线视频|
先锋影音源资2019|
无人区卡一卡二卡老狼网站|
97在线观看视频公开免费|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
色AV亚洲AV永久无码精品软件
|
偷拍自偷 亚洲 欧美20P|
欧美黑人一区二区三区免费A片
|
人插女人免费视频久久|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
亚洲欧美国产高清|
亚洲成年人免费网站|
日本老头4569gay|
有人有片视频吗 免费的|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产丝袜|
日韩MV欧美MV中文无码|
男人和女人香蕉网线看|
丰满人妻老熟妇伦人精品|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片漫|
美国一级大黄一区免费无码|
8x8国产人妻精品一区二区|
无人区AV在线观看|
久久视频在线视频观看 99|
91日韩精品在线观看|
欧美性猛交XXXXX拉换交大3|
成 人影片 免费观看10分钟|
成人国产精品久久久久久亚洲|
人妻AV无码一区二区三区蜜臀|
亚洲精品国产国语|
欧美激情一区二区三区四区|
国产色综合色产在线视频|
asian极品呦女xx农村|
影音先锋av网站大全|
在线观看高清黄网站免费|
国产又色又爽又刺激的A片|
天黑黑影院免费观看视频在线播放|
成人免费激情毛片|
女人另类牲交ZOZOZO|
成人三级理论电影|
亚洲国产精品一区二区第一页|
成A人亚洲精V品无码樱花国产|
真人女人无遮挡内谢免费视频%|
亚洲中文字幕熟女久久
|
激情自拍另类亚洲|
视频一区国产第一页|
午夜夫妻试看120国产|
欧美日韩综合无码中文字幕|
少妇又大又粗又硬啪啪|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
91桃色污无限免费看|
国产真实乱子伦清晰对白|
久久久精品国产SM调教网站|
免费又黄又爽又色的绿巨人|
17c人妻无码一区二区三区|
激情综合成人五月天|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
国产精品久久久AV色欲A|
久久99AV无色码人妻蜜|
国产精品久久人妻互换毛片|
欧美一级黃色A片免费看蜜桃|
99操在线观看国产视频|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
国产成+人欧美+综合在线观看|
欧美ideosgratis暴力|
亚洲中文字幕在线观看|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
2020美女视频黄频大全视频|
成人黄色国产视频|
大陆极品少妇内射AAAAA|
影音先锋资源av天堂|
国产无遮挡又黄又爽又色又刺激|
一本道免费高清视频ccd|
y1111111丰满少妇毛片|
小柔跪趴撅着给人玩弄H视频|
拍在线2018国产爽在|
色偷拍亚洲国产大姐|
日本一卡2卡三卡4卡无卡免费网站|
www.日韩av.com|
不卡在线播放一区|
国内精品视频在线播放一区|
日韩人体做爰大胆337P|
亚洲AV无码乱线观看性色|
高中女学生破苞视频免费
|
一面亲上边一面膜带揉胸|
精品人妻一区二区A片|
好大好爽快点大JI巴视频
|
成人无码免费A片免费看软件|
色偷拍亚洲国产大姐|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
国产厨房一区二区三区
|
麻豆星空精东天美MV第一页|
亚洲AV无码一区二区A片成人|
免费永久在线观看黄网站|
中文字幕欧美一区|
亚洲A片无码秘色多多|
成人无码www免费视频欧美|
男生J桶进女人P又色又爽又黄
|
8x8x福利在钱视频|
国产一区二区三区四区精品AV|
av三级国产a级水|
色情.WWW成人天堂|
办公室的超薄丝袜人妻献身 |
久久精品久久精品久久精品|
国产成人精品不卡久久久|
亚洲成α∧人片在线播放无码|
亚洲人美女肛交真人全程|
草莓视频中文字幕|
国产人成视频在线观看|
999国产精品欧美一区二区 |
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
999在线免费视频|
欧美全黄a一级一区二区三区视频
欧美日韩国产精选福利片
|
99久久精品免费国产一区二区三区
|
在线观看黄A片免费AV软件|
y1111111丰满少妇毛片|
中文字幕欧美人乱人精品A片|
亚洲成年人免费网站|
成人无码www免费视频欧美|
亚洲乱码AV中文一区二区|
小SAO货张开腿CAO死你A片|
亚洲国产精品一区二区三区在线观看|
HEZYO加勒比久久爱综合|
2017男人天堂手机在线|
国产精品aⅴ久久久久久鸭绿欲
|
日日躁夜夜躁夜夜揉人人视频|
亚洲99精品A片久久久久久|
av免费无码专区|
国产综合久久久777777|
最近最好的中文字幕2019免费|
免费黄色录像一集AV一集片|
欧美日韩精品一区二区三区不卡|
国产中文字字幕乱码无限|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
丁香花视频资源在线观看|
99爱免费视频在线看|
男人天堂2018在线观看97|
国色天香精品卡一卡二卡三二百|
丰满成熟少妇A级毛片|
色狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片55|
美女翘臀强进入系列在线观看|
国产又色又粗又黄又爽免费|
人妻激情偷乱一区二区三区|
国产真实交换配乱婬98视频|
亚洲久悠悠色悠在线播放|
欧美特级特黄a大片免费|
午夜色情A片成人免费视频下载|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在线观看|
欧美激情一区二区三区不卡|
色噜噜狠狠一区二区三区|
又硬又粗进去好爽A片春色视频|
欧美肉动漫一区二区三区无码|
国产强被迫伦姧在线观|
最好免费观看高清视频直播小说|
亚洲精品伦理熟女国产一区二区|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
777片理伦片在线观看|
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
国产免费进入一区二区|
中文字幕一区二区三区视|
色情成人免费视频激情在线观看|
99久久精品免费观看国产色综合|
网站情侣色情网网站|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
日韩免费视频一区|
好看的国产精彩视频|
果冻传媒国产仙踪林|
成年人午夜激情黄色视频|
国产熟女真实乱精品视频|
av综合网男人的天堂|
黄片长版看嘛 直播片|
特黄做愛又硬又大A片视频|
无码人妻欧美丰满熟妇区毛片|
亚洲成AV人片一区二区梦乃|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
日韓最新视頻一區二區三|
多人做人爱免费视频试看|
AV久久无码AV喷水高潮|
欧美一道本一区二区三区|
又大又硬又粗做大爽A片|
爆乳JK美女脱内衣裸体网站
|
久久婷婷五月综合色精品|
少妇内射高潮福利炮|
嫩BBB搡BBBB榛BBBB|
免费无码AV色情在线|
亚洲精品无码苍井空A片|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片88|
美女内射毛片在线看|
亚洲国产熟妇无码日韩|
国产成人av免费手机麻豆 |
国产91对白刺激露脸在线观看|
亚洲欧美一区二区三区久久|
久久人人做人人妻人人玩精品AV|
91桃色污无限免费看|
师尊胯羞坐抬臀抖吟迎合视频|
成人免费又大又爽A片视频|
亚洲不卡在线观看|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
天天做天天躁天天躁|
男人天堂网2018最新地址|
国产精品VA无码区二区|
亚洲一区在线电影|
2022一本久道久久综合狂躁
|
精品国语自产拍在线观看|
国产精品丝袜一区二区|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
欧美成人无码A区在线观看免费|
欧美无人区码卡二卡3卡4|
日本亚洲精品无码专区国产|
国语对白农村老太婆BBw|
无码影片成人网站在线观看|
最新av网站免费在线观看
|
午夜精品成人一区二区视频|
一区二区三区免费版在线|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
麻豆精品一区二区综合AV|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
综合久久一区二区三区|
亚洲 暴爽 AV人人爽日日碰|
农村嫖妓一区二区三区|
亚洲AV无码一区二区A片成人|
国产精品久久久久久久AV大片|
免费一级做a爰片久久毛片潮喷|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
亚洲精品美女av在线|
大香伊在人线国产中国|
性一交一乱一美A片69|
男女又黄又刺激B片免费网站|
日本一本道2018无号码|
AV8888AV色情观看在线|
欧美一级黃色A片免费看蜜桃|
91在线精品你懂的|
国产女13黄A片AAA片视频|
不卡久久精品国产亚洲av麻豆|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套|
亚洲精品美女av在线|
国产精选 第1页-要看tv|
精品一卡二卡三卡四卡网站|
精品国产乱码久久久久久下载|
2015影音先锋色撸撸|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
欧美日韩精品一区二区三区高清视频
|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫
|
色婷婷激婷婷深爱五月小蛇|
青娱乐国产视频在线分类|
欧洲亚洲精品A片久久99果冻
|
99麻豆久久久国产精品免费|
AV免费网站在线观看
|
成人黄色小视频在线观看|
狠狠色老熟妇老熟女|
乱伦小说与照片电影一区二区三区|
色情无码永久免费网站APP|
亚洲一区美女视频|
欧美AAAA级A片又粗又硬|
免费A级毛片黄A片高清在线播放
|
日韩高清特级特黄毛片|
69无人区乱码一二三四区别|
9久热这里只有国产中文精品国产|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在线观看|
av三级国产a级水|
精品日韩一卡2卡三卡4卡乱码
|
窝窝午夜看片http|
国产熟妇久久精品亚洲熟女图片|
欧洲精品无码一区二区三区的视频空间|
人人妻人人澡人人爽人人老司机|
成人免费大片黄在线观下载|
很很鲁在线视频播放影院|
欧美整片sss第一页视频|
国产精品人妻无码免费久久久|
亚洲精品国偷拍电影自产在线|
精品久久久久久久无码伊人
|
男女狂进狂出动态图GIF|
不卡精品国产夜色|
国产国语高清在线视频二区|
亚洲国产欧美日本视频|
亚洲图色中文字幕|
国产1988精品A片|
欲妇荡岳丰满少妇A片|
91精品福利尤物|
亚洲福利在线观看|
亚洲欧美日韩国产精品一区二区|
国产啪精品视频免费制服丝袜
|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
国产又色又爽又刺激的A片|
a国产在线v的不卡视频视频免费 |
99久久精品免费看国产免费粉嫩|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站仙踪林|
99精品免费在线视频|
无码潮喷A片无码高潮软件|
国产高清色情在线观看APP|
荫蒂添的好舒服A片免费|
狠狠噜天天噜日日噜久久久电影
|
中文日韩欧美亚洲|
中文人妻熟女波多野结衣|
日韩A片中文字幕视频免费|
欧美阿v天堂视频在99线|
乳荡麻麻肉欲500合集|
国产精品高潮呻吟AV久久床戏
|
成人精品视频99在线观看免费|
丁香啪啪综合成人亚洲|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
国产精品大陆在线观看|
奴色虐aV一区二区三区|
久久伊人久久大香线蕉一区|
亚洲最大成人综合网720P|
成av人电影在线观看|
国产成人精品综合久久久久
|
欧美一级特黄aaaaaa在线看首页|
亚洲无码视频免费观看|
国产精品久久久久国产A级|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
巨爆乳肉感一区二区三区视频|
精品日产1区2卡三卡麻豆|
三上悠亚网站在线观看一区二区|
18国产成人在线|
欧美亚洲国产精品久久第一页|
美女禁止的网站免费|
欧美顶级又粗又大又黑A片黑寡妇
欧美性色欧美性A片色欲
|
最新欧美精品一区二区视频|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片小说|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色字幕综合|
国产十八熟妇AV成人一区|
未满小14洗澡无码视频网站|
中文字幕精品无码一区二区|
久久精品视频在线直播6
|
一本色道88久久亚洲精品|
日日摸天天添天天添无码蜜臀|
se97se成人亚洲网站|
201一本道在线在线观看|
成人免费视频caoporn|
亚洲夜夜夜无代码|
一区二区三区在线视频观看|
91精品一区二区三区无码吞精|
入室强伦轩人妻HD|
中文无码妇乱子伦视频国产精品亚洲LV粉色
|
同性男男黄H片在线播放网站|
国产亚洲欧洲人人网|
成 人 黄 色 视 频网址大全|
国产女人乱人伦精品一区二区|
变态Sm天堂无码专区|
香蕉AV777XXX色综合一区|
爱爱好爽好大好紧视频|
2019四虎最新地址免费观看
|
成年人视频网站免费|
两老头把我添高潮了A片苏晴|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片漫画|
狼狼躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
婷婷五月色综合人妻|
黄色小网站在线观看|
久久久久亚洲Av无码专区桃色|
国语对白白浆69XX|
国产精品无码人妻在线|
免费无码AV片在线观看潮喷|
最近免费视频中文2019完整版|
骚片AV蜜桃精品一区|
美女老黄一区二区|
久亚洲AV无码专区A片|
搡女人真爽免费视频大全|
国产无遮挡又黄又爽又色又刺激|
在线观看日韩一区二区视频|
国产乱码一卡一卡2卡三卡四|
成人特级裸体AAA毛片 |
女人十八毛片水真多啊|
丁香啪啪综合成人亚洲|
国产精品久久丫毛片A片软件|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
来啊mm影院亚洲mm影院|
九九九免费观看视频|
人妻性奴波多野结衣无码|
清纯漂亮小美女准备啪啪|
乌克兰美女18xxoo在线|
99国精产品一区二区三区A片|
免费无码婬片AAAA片直播表情|
亚洲精品AV一区午夜福利|
欧美产品与亚洲日韩视频|
精品国产人妻国语|
国产午夜男女爽爽爽爽爽|
国产色欲婬乱视频网站免费
|
国产xxxxxx久色视频在|
欧美精品色婷婷五月综合|
成人av网址一区二区|
欧美一区二区三区不卡免费|
国产做爰又粗又大免费看|
最近韩国日本MV免费观看免费|
美女翘臀强进入系列在线观看|
亚洲国产精品无码乱码三区红酒|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
很黄很黄地在床视频女|
粗大的内捧猛烈进出视频网|
91九色熟女欧美日韩欧美
|
国产又爽又黄又不遮挡视频|
女人一级A片免费播放|
97无码欧美熟妇人妻蜜桃天美|
亚洲综合AV色婷婷五月蜜臀|
国产无码在线观看黄色|
影音先锋2018av网址|
国内偷拍亚洲欧洲2018|
亚洲成人视频一区二区|
77成年轻人电影网网站|
国产又色又爽又黄的|
10周岁女全身裸无遮挡网站|
免费人做人爱的视频完整|
国产精品583一区二区免费看|
中文字幕日韩一区二区不卡|
J8又粗又硬又大又爽又长A片|
成人免费网站又大又黄又粗
|
欲妇荡岳丰满少妇A片24小时|
天美传媒小甜豆完整视频在线观看
|
亚欧成人毛片一区二区三区四区|
日产一区日产2区日产三区|
国产又粗又猛又爽在线视频|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
欧美特级另类xxx|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
亚洲精品国产一区二区三|
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
国产又粗又长又硬又猛A片|
亚洲一区在线电影|
成 人 黄 色 视 频网址大全|
国产 亚洲 综合 在线观看|
女人爽到高潮潮喷叫床69|
国产婬A片999片免费网站|
影音先锋中文无码一区|
91精品一区二区三区无码吞精|
熟妇人妻系列AV无码一区二区|
五月色播先锋在线丁香|
91性爱在线视频|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
琪琪电影午夜理论片YY6080|
泰国两熟女春梦邂逅猛男|
18禁止进入黄大全在线|
苍井空激烈的120|
男人用嘴添女人免费视频A片|
18勿入网站免费永久|
久久久久亚洲AV无码专区首护士|
99精品视频久久精品|
五月色丁香婷婷网蜜臀AV|
97精品国产高清在线看入口|
在线午夜福利视频免费|
猫咪av最新永久网址无码|
丝袜脚夹住上下摩擦榨精|
日本爽爽爽爽爽爽在线观看免
|
蜜臀色欲AV无人A片一区|
成人小视频在线观看 |
91AV在线视频网址|
日韩一区二区三区无码影院
|
老湿地在线观看一区二区三区
|
欧美黑人一区二区三区免费A片
|
国产免费进入一区二区|
99在线观视频免费观看|
亚洲一区二区三区电影在线|
欧美亚洲综合在线|
欧美乱大交AAAA片IF|
亚洲AV无码男男A片在线观看|
日本一本道2018无号码|
边啃奶头边躁狠狠躁AV|
超久久人人爱免费|
波多野结衣亚洲一二三
|
色YEYE网址在线观看|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
日韩一级无码中文字幕|
试看免看一级a一片|
午夜dj在线观看免费完整高清神马|
影音先锋2017av资源|
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA
|
小14萝视频裸体视频|
欧美又大又长又粗又爽A片|
偷拍自偷 亚洲 欧美20P|
亚洲精品无码色情AV在线观看|
四虎成人午夜影视亚州精品|
中文字幕日韩精品有码视频|
国产福利视频一区二区|
A片爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽|
欧美一区二区三区成人A片|
欧美荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
日本爽爽爽爽爽爽免费视频|
免费网站观看av片|
成全影视在线观看国语|
欧美激情一级精品国产|
成人av在线播放观看|
国产内射大片99|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
影音先锋秋霞在线影院|
国产乱对白刺激视频|
欧美又黄又粗暴免费视频|
少妇高潮毛片色欲AVA片|
亚洲色噜噜狠狠站欲八|
成人精品视频99在线观看免费|
玩弄丰满奶水的女邻居|
性色AV爽歪歪啪啪A片|
先锋影音avt天堂影院|
亚洲AV又黄又爽超级A片软件|
午夜精品久久久内射近拍高清|
国产乱码免费卡1卡二卡3卡四卡|
边摸边吃奶边做爽视频免费|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
爱咲れいら无码一区二区|
10000拍拍18勿入免费看动漫|
男人的天堂在线无码高清|
777片理伦片在线观看|
欧美疯狂三P群体交乱免费视频|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
圆产精品久久久久久久久久久新郎|
50岁老熟女高潮喷水|
无码中文字幕热热久久|
91国产自产精品a|
国产乱妇无码大黄AA片|
日韩中文字幕资源站|
最近中文字幕免费MV视频|
性一交一乱一美A片图片|
欧美日韩不卡一区视频在现|
免费啪视频在线观看视频日本|
亚洲欧洲日本无在线码播放|
精品AAAA巨乳|
中国字字幕在线播放2019
|
宝贝你真湿真紧好爽h视频男男|
一本到在线高清观看|
成人乱码一区二区三区AV66|
免费人成网站在线高清|
五十六十老熟妇激情A片|
护士又紧又深又湿又爽|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套
|
亚洲日韩AV在线中日综合|
欧美无人区码卡二卡3卡4|
精品国产卡一卡2卡3卡|
国产真实乱子伦清晰对白|
亚洲成AV人片一区二区梦乃|
百度国产精品网友自拍|
亚洲av免费分钟观看|
92久久精品一区二区|
疯狂少妇2做爰中文字幕|
精品无码久久久久久国产牛牛影视
|
男女作爱在线观看免费网站|
粉嫩无套白浆第一次jk|
日产一线二线三线哺乳|
狂野猛交ⅩXXX吃奶免费视频|
国产又硬又粗进去好爽A片软件|
av黄在线观免费网站|
国产成人精品综合久久久久|
精品丰满人妻AV久久久|
91一级特黄大片 |
日产乱码一二三区别免费麻豆|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
91精品久久人人妻人人爽人人|
黑寡妇巨大粗爽毛片欧美|
影音先锋影院中文无码|
美女禁止的网站免费|
强硬进入岳A片69视频|
一区二区三区内射美女|
国产成人亚洲欧美一级在线|
免费番肉动漫在线观看|
人妻含泪让粗大挺进|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
色狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片55|
色综合久久88色综合天天6|
99精品国产福久|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片小说天美|
www.黄色免费网站|
91极品女神私人尤物在线播放|
影音先锋2017av资源|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
大片国产片日本观看免费视频|
午夜无码片在线观看影院|
欧洲内射XXX高清|
真人真实做爰30分钟试看|
国产精品久久久久久爽爽爽床戏|
男人天堂影院WWW94|
國產午夜亞洲精品一區二區|
A片免费观看一区二区三区|
欧美产品与亚洲日韩视频|
蜜月a 免费一区二区三区|
亚洲欧洲日韩极速播放|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
无码精品AV久久久奶水|
18精品久久久无码午夜福利 |
一本av高清一区二区三区|
狼狼躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
亚洲国产aⅴ精品无码|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合|
国产内射大片99|
成人A片产无码免费视频奶头鸭度
一女被两男吃奶添下A片V图
|
国产成人av在线影院 |
播五月开心婷婷欧美综合|
中文字幕人成乱码熟女免费69|
中国字字幕在线播放2019|
日本无码国产在线婷婷直播|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
欧美搡BBBBB摔BBBBB|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
18勿入网站免费永久|
欧美大码毛片在线播放|
菠萝菠萝蜜菠萝菠萝蜜7麻豆|
av最新一级网站在线观看|
免费A片看黄网站WWW下载|
国产成人精品电影不卡|
久久99AV无色码人妻蜜|
成人国产精品影院|
女人被添荫蒂舒服了A片小说|
全黄做爰100分钟视频|
香蕉在线精品视频在线|
95无码人妻精品一区二区三区|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
欧美乱大交AAAA片IF|
中文字幕日韩人妻|
巨胸美女狂喷奶水www网麻豆|
成本人h视频动漫免费 |
污污免费看锕锕锕锕锕锕锕|
久久精品视频久久精品视频|
韩国乱码卡一卡二卡新区网站|
国产女人毛多水多A片视频|
在线精品亚洲观看不卡欧|
影音先锋资源站玖玖网|
精品亚洲国产熟女福利自在线|
最近更新中文字幕完整版视频|
一边添奶一边添p好爽视频|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片免费|
第四色播日韩AV第一页|
精品亚洲中文字幕|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
高潮潮喷无码一区二区三区|
国产亚洲精久久久久久无码妖精|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
18禁外国精品久久久久久|
黄网站免费永久在线观看下载
|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片|
日韩精品久久久肉伦网站|
午夜夫妻试看120国产|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
91在线欧美日韩精品|
91热久久免费频精品99欧美|
成年美女黄网站色大免费视频|
黄片大全免费在线观看|
性啪啪chinese东北女人|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频|
国产精品无码免费在线|
免费全部黄A片免费播放|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
亚洲成年人免费网站|
超碰97成人在线|
免费99精品国产人妻自在线|
动漫AV纯肉无码AV电影网|
99精品人妻无码专区在线视频区
|
青草亚洲国产欧美一区二区|
女人荫蒂被添舒服的A片|
久久爽AV亚洲精品天堂|
蜜桃在线码无精品秘入口九色|
先锋影音伦理在线|
欲香欲色天天综合和网|
少妇大叫又粗又大太爽A片|
欧美性猛交aa一级|
好男人WWW神马社区在线观看|
三人交videosdesexoe|
99亚洲精品成人|
影音先锋av999资源站|
越南女子杂交内射BBWBBW|
最近中文2019字幕第二页|
成年女人色费视频播放|
欧美熟妇另类久久久久久多毛
|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片漫画|
日本不卡视频一区二区|
久爱成欢视频在线观看|
国产色婷婷亚洲999精品小说|
男人猛躁进女人的毛片A片|
朋友娇妻的滋味中文字幕A片|
黑人巨大40cm重口|
91亚洲最新精品|
2014av天堂影音先锋|
国产精品高潮呻吟AV久久床戏|
免费人成网站在线高清|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
最新影片日本巨波霸乳影院|
在线看欧洲一卡二卡三卡残暴|
国产成人综合亚洲A片激情文学|
高中女学生破苞视频免费|
久久伊人久久大香线蕉一区|
两男一女一床一添一摸|
日韩成人伦理在线|
国产又粗又爽又猛的视频A片|
91无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
摸BBB揉BBB揉BBB视频|
国产美女做爰A片免费|
未满十八岁勿入网站WWW|
国产成人永久免费无码观看|
五月丁香六月婷婷网线视频|
日本69色视频在线观看
|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片
|
www成人国产在线观看网站|
久久激情成人国产|
那种视频在线观看亚洲|
巨大乳女人做爰视频在线|
大叫受不了了好爽国产在线|
99精品免费在线视频|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
大量国内自拍AV手机观看|
一级黄色视频在线观看|
日本A一片中国A一片|
999久久久国产综合精品|
久久精品国产99国产精2019|
丝袜熟女脚交足在线一区|
成人a级特黄毛片|
午夜精品久久久久久久99老熟妇
|
国产91精品人妻一区二|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578|
惠民福利亚洲AV无码一区二区乱子仑|
丰满成熟少妇A级毛片|
成人性生交A片免费直播APP|
好吊视频一区二区三区|
免费啪视频在线观看视频日本|
一区二区三区内射美女|
8X亚洲视频久久综合一区|
久久精品视频在线直播6|
91久久综合精品国产丝袜长腿|
97任你碰任你摸任你爽|
a级黄色大片在线观看视频男男|
91麻豆产精品久久久久久粉嫩
|
永久无码日韩A片免费看麻豆精品|
久久精品国产亚洲AV高清色三区|
乱码中字芒果视频一二三多人|
一区二区三区四区国产精品|
窝窝午夜看片http|
欧美日韩一区二区在线视频|
天堂最新版在线中文|
日产一区日产2区日产三区|
91综合国产精品视频|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
精品AV一区二区三区久久|
日本免费一二三区中文|
欧美视频 偷窥自拍视频|
亚洲精品中文字幕制|
A片又大又粗又爽免费视频|
色情美女激情喷水AV|
免费岛国片在线播放|
欧美肉动漫一区二区三区无码|
国产美女高潮福利|
欧美疯狂三P群体交乱免费视频|
污污内射久久一区二区欧美日韩|
办公室制服丝祙在线播放|
国语对白白浆69XX|
91av视频免费在线观看|
丝袜脚夹住上下摩擦榨精|
在线最新av免费费观看|
国产又爽又粗又猛的视频A片|
欧美激情一级精品国产|
四川美女BBBB爽爽毛片|
嫩草国产露脸精品国产软件|
99久酒店在线精品2019|
歪歪爽蜜臀AV久久精品人人槡|
国产成人免费精品|
中文字幕暖暖永久在线视频|
中文无码1234区|
国内高清在线观看视频|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放|
国产国语高清在线视频二区|
草草影院永久线路CCYY|
欧美乱妇欲仙欲死视频免费|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
国产JK白丝AV在线播放|
欧美日韩一级特大黄片|
精品亚洲综合射精|
色偷偷超碰av男人天堂|
日本久久久WWW成人免费毛片丨|
国产美女无遮挡裸体毛片A片|
操老熟女熟妇免费视频|
欧美内射深喉中文字幕|
国产在线观看不卡|
欲妇荡岳丰满少妇A片|
sao虎影院桃红视频在线观看|
中文字幕无码色情网|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
Xx肥妇精品久久久久久久久
|
国产5x社区在线视频|
最近中文2019字幕第二页
|
国产在线精品免费91|
a级男女性高爱潮高清试看|
又粗又硬整进去好爽视频|
国产精品人妻黑人借宿电影
|
先锋影音伦理在线|
色吊丝永久性观看网站|
玩弄秘书的奶又大又软A片视频|
日产黄片中文字幕|
av网站不卡免费在线|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
免费人妻无码不卡中出|
一个人www在线观看免费中文
|
国产女人夜夜春夜夜爽免费看|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578|
新国产美女精品一区二区|
男女做爰猛烈啪啪吃奶动A|
真人做爰视频在40分钟左右|
91精品福利尤物|
妇乱子伦精品小说网|
成人做爰A片免费看黄冈|
色欲AV亚洲午夜精品无码|
国产大尺度吃奶无遮无挡|
黄网站免费线观看免费|
日韩一卡二卡 3卡四卡乱码|
国产1988精品A片|
亚洲精品国产一区二区三
|
被粗大jib捣出了白浆H|
欧美男男gv免费网站观看|
欧美h版在线观看|
BBW.妇女被内射|
99国产精品国产热久久|
国产一区二区三区在线观看网|
99精品人妻无码专区在线视频区
|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
欧美 亚洲 另类 综合网|
最新2021中文字幕无码|
久久成人麻豆午夜电影|
麻豆色情少妇传媒AV一|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫
|
最近中文字幕MV免费高清下载|
小骚妇下面水多要插视频|
极品JK小仙女自慰喷水牛牛影视|
国产网友自拍在线视频|
毛片内射久久久一区|
玩弄丰满少妇高潮A片91|
国内自拍真实伦在线视频|
9久热这里只有国产中文精品国产|
91性爱在线视频|
国产露脸A片国语露对白|
高潮A片揉搓乳尖乱颤视频
|
亚洲国产成在线网站91|
黄网站在线观看高清免费|
啊轻点灬公大JI巴又大又
|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片男男|
欧美搡BBBBB摔BBBBB|
国产毛片又爽又大A片|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
国产高潮抽搐在线观看|
蜜桃人妻无码AV天堂三区|
色噜噜噜一区二区三区|
欧美精品一区二区蜜臀亚洲|
婷婷六月激情综合一区|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合|
日韩精品成人大片|
白天躁晚上躁天天躁21|
亚洲合成久久久久久久综合|
欧美日韩午夜群交多人轮换|
柠檬蜜桃导航500|
无码137片内射在线影院|
国产乱码日产精品BD|
欧美囗交口爆吞精在线视频|
国产精品一区二区三区四区五区|
国产精品AV一区二区三区不卡蜜|
92看看福利午夜影院|
亚洲AV色情成人www|
熟女丰满老熟女熟妇|
美女丝袜一区二区三区|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
国产一国产一本到免费
|
越南女子杂交内射BBWBBW|
99久久国产露脸国语对白|
久在线视频reer6|
国产精品AV国片偷人妻麻豆|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
欧美肥胖裸熟妇的毛发布|
在线视频免费观看爽爽爽|
国产麻豆剧果冻传媒视频免费
|
免费看美女被靠的网站|
乌克兰美女18xxoo在线|
四十如虎的丰满熟妇啪啪|
成人av网址一区二区|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出AVV|
秘书下面太紧拔不出来怎么办|
成人h动漫精品一区二区无码|
最近的2019中文字幕在线|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
亚洲午夜无码毛片AV久久京东热|
99视频这里只有精品国产|
国产免费进入一区二区|
快插我BB好爽舔我视频|
色婷婷AV一区二区三区之红樱桃|
精品午夜伦理一区|
精品国产污网站直接看|
94久久精品午夜|
国产精品污www在线观看|
爽灬好舒服灬别拔出来视频人
|
偷拍自偷 亚洲 欧美20P|
蜜桃BBB蜜桃BBB蜜桃BBB|
真人女性生图片高清黑毛|
欧美激情内射喷水高潮|
色欲天香天天影视综合|
美女被免费网站在线视频app|
未满小14洗澡无码视频网站
|
91大片网站大全|
aV影音先锋毛片子|
国产三级精品三级在线观看|
添女人荫蒂全部过程AV|
日本老妇一级特黄aa大片|
懂色av浪潮av色欲av熟妇|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
欧美产品与亚洲日韩视频|
永久免费看MV网站入口亚洲|
在线视频网站www色|
亚州AV无码乱码色情|
日本无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
丰满熟妇人妻中文字幕|
内射老妇女BBWXOCLOCK|
风间一区二区无码有码|
狂躁女人屁眼爽出白浆的视频网站
|
美女胸18以下禁止看禁网站|
精品无人乱码一区二区三区无限看|
成av人电影在线观看|
4399少妇做受免费A片|
AA片在线观看视频在线播放|
亚洲.欧美.中文字幕在线观看|
成年女人色费视频播放|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
亚洲精品久久久久AV无码|
亚洲国产午夜精品理论片|
国产看真人毛片爱做A片|
99视频久九热精品|
久久精品视频久久精品视频|
国产一国产一本到免费|
色影音先锋av资源网|
国产精品污www在线观看
|
狂处让老二爽18p|
青春热久免费精品视频|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
欧美又粗又大又黄A片|
蜜桃视频在线观看网站|
91日韩中文字幕在线观看|
男女做爰猛烈吃奶摸大胸|
特极西西444WWW大胆无码|
а∨天堂在线中文免费不卡|
无敌神马影院视频观看高清免费|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片俺去也|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
性生生活大片又黄又|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
午夜性做爰A片免费看
|
5个男人躁我一个爽免费视频|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
亚洲jizzjizz中国妇女|
久久婷婷五月综合色丁香|
国产狂喷水潮免费网站www|
亚洲A片成人无码久久精品|
国产V日产∨综合V精品视频麻豆
|
91Porn偷拍熟女在线观看|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产丝袜|
国产精品久人妻精品|
九九99热久久精品在线6|
日本A一片中国A一片|
2019四虎影视最新在线|
大地影院_日本骚妇|
青青草在免费线观曰本|
老女人与小伙子露脸对白|
妇搡BBBB精品一区二区|
国产色情精品一区二区唱戏|
国产乱码卡1卡二卡3卡4卡5|
亚洲图色中文字幕|
中文日韩欧美亚洲|
男人和女人香蕉网线看|
色噜噜2017最新综合|
亚洲va999成人A片在线观看|
天黑黑影院免费观看视频在线播放|
风间一区二区无码有码|
草草影院地址发布页ccyycom|
老熟女肥臀AV老熟女A片|
国产精品色哟哟网站高清|
亚洲精品无码A片一区二区三区|
黄片长版看嘛 直播片|
99精品成人无码A片观看金桔|
一区二区三区在线播放|
无码国产成人777爽死|
亚洲日韩在线中文字幕|
91精品最新国产在线播放|
免费岛国片在线播放|
欧洲精品卡1区2卡三卡四卡|
久久综合色一综合色88|
无码国产成人777爽死|
啊轻点内射在线视频|
亚洲阿v天堂无码在线|
欧美阿v天堂视频在99线|
日本妇人成熟免费中文字幕|
亚洲1卡2卡三卡4卡2021|
国产精品583一区二区免费看|
2019看片w网址|
中文天堂网WWW新版资源在线|
日韩一级无码中文字幕|
国产又大又粗高清观看视频
|
亚洲成 人图片综合网|
亚洲午夜无码毛片AV久久京东热|
嫩BBB搡BBBB榛BBBB|
少妇夹得好紧太爽了A片|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
2018天天拍拍天天爽视频|
扒开腿CAO烂你小SAO货杨爽|
日本精品无码特级毛片|
成片免费观看视频大全|
一区二区三区免费看A片|
男人天堂网2018最新地址|
成人性三级国产在线观看|
四虎永久地址WWW成人无痕|
最新一区二区三区在线影院
|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
男女在线观看啪网站|
亚洲 另类 小说 国产精品|
国产丰满大乳大屁股A片图片|
最近高清中文在线国语视频|
国产精品人妻午夜福利|
国产综合av一区|
人妻中文字幕av无码专区|
精品国产午夜福利在线观看|
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
A片扒开双腿猛进入免费观|
成A人亚洲精V品无码樱花国产|
日韩?V片无码一区二区不卡|
日韩高清特级特黄毛片|
国产a级黄色毛片|
国产乱码日产精品BD|
精品三级无码国产在线观看|
狠狠噜天天噜日日噜久久久电影
|
国精品产露脸偷拍视频|
免费国产美女爽到喷出水来视频
|
99久久人妻无码精品系列性欧美|
久久偷看各类WC女厕嘘嘘偷窃|
国产熟女精品高清在线|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片
|
四十如虎的丰满熟妇啪啪|
女人高潮抽搐潮喷WWW|
日本无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
肥熟女视频一区二区三区国|
羞羞影院午夜男女爽爽影院网站|
在线看无码的免费网站|
huangseajipian|
国产日韩精品SUV|
黄网站色视频大全免费观看|
一区二区三区内射美女|
少妇一级婬片免费放狠狠干狠狠躁
|
性饥渴姓交HDSEX|
国产熟妇高潮叫床视频播放|
亚洲熟妇男女啪啪视频|
久久网正在播中文字幕|
最近日本字幕MV免费观看在线|
欧美荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
国产黄片精品无码在线观看|
日韩精品情欲蜜桃视频JK|
男人猛躁进女人的毛片A片|
欧美国产在线日韩|
中文天堂网WWW新版资源在线|
在线观看亚洲精品国|
91黑料精品国产|
香蕉久久av一区二区三区|
国产91在线播放中文 |
三级国产人成在线亚洲视频观看h|
一级a特黄毛片高清免费|
亚洲精品久久久久久一区|
国产l精品国产亚洲区在线观看|
一本到午夜92版福利|
成人国产精品久久久久久亚洲|
丁香花视频免费播放社区|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片漫画
|
我的初次内射欧美成人影视
|
成人午夜爽A片免费视频|
成人午夜爽A片免费视频|
国产福利高清在线视频|
被粗大jib捣出了白浆H|
菠萝菠萝蜜菠萝菠萝蜜7麻豆|
久久国产人妻一区二区免色戒电影
|
日本爽爽爽爽爽爽免费视频|
爽灬好舒服灬别拔出来视频人|
男人到天堂去a线2019|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片动漫软件|
色欲久久精品AV无码|
男人女人真曰的视频|
av大片在线网站|
偷拍亚洲综合20P|
又硬又粗进去好疼A片麻豆|
福利午夜视频在线|
中文字幕亚洲一区|
福利导航第一福利导航|
被老外添嫩苞添高潮NP|
富婆偷人对白在线观看|
高清无码视频在线观看|
91在线欧美日韩精品|
最近中文字幕在线中文|
最新无码人妻在线视频|
777午夜福利理论电影网|
精品人妻一区二区A片|
波多野结衣美乳人妻hd电影欧美|
又黄又爽吃奶视频在线观看|
99国产精品久久人妻无码|
天堂中文www资源在线|
强硬进入岳A片69|
国产综合在线精品|
伊人激情AV一区二区三区|
最近中文字幕在线中文|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片小说
|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
影音先锋成人色情5566|
A片爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽|
国产又大又粗高清观看视频|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站一丁|
国产中的精品AV一区二区|
国产成人无码精品亚洲|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
aa福利亚洲国内在线精品|
少妇做爰免费视频了|
午夜成人亚洲理伦片在线观看
|
精品无码久久久久久久久国产|
少妇偷拍精品高潮少妇|
国产内射大片99|
女女gay中国免费网站|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
国产JJZZJJZZ视频免费看|
白嫩白嫩美女极品国产在线观看|
综合在线视频精品专区|
91视频精品在线观看 |
第二代国产自在自线|
国产激情久久99久久|
国产精品96久久久久久|
五月色婷婷亚洲男人的天堂|
亚洲一区在线电影|
老头把我添高潮了A片故视频|
无敌神马影院在线观看免费视频
|
国产后式a一视频|
少妇人妻av中文系列久久|
91中文日韩欧美 |
免费无码婬片17com|
国产亚洲精品久久久久久大师|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
成本人h视频动漫免费 |
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
激情综合五月亚洲婷婷|
国产1988精品A片|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师
|
久久久精品免费视频|
亚洲尤码不卡AV麻豆|
强被迫伦姧惨叫国产videos|
激情五月天天婷婷|
新国产美女精品一区二区|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
国产又爽又大又黄A片美女裸体|
国产人妻系列无码专区第二页|
99久久久无码国产精品性|
午夜精品A片一区二区三区|
一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡在线|
亚洲中字幕日产2021草莓|
性色AV一区二区三区咪爱四虎|
两个吃奶一个添下面视频|
成片免费观看视频大全|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
国产白丝JK被疯狂输出视频|
亚洲精品一区二区无码夜色|
韩国无码色情在线播放|
清纯漂亮小美女准备啪啪|
国产又色又爽又黄的|
国产高潮流白浆视频|
高清欧美日韩一区二区 |
亚洲av免费分钟观看|
久久人人玩人妻潮喷内射人人|
wuyueqingsetian|
成人国成人国产SUV|
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
黄 色一 片 级 日本|
成人亚洲天堂一区|
国产又爽又粗又猛的视频A片|
丰满放荡岳乱蜜桃AV|
成年美女拍拍视频免费|
最新女人另类ZOOZ0|
A片好大好紧好爽视频|
99精品成人无码A片观看|
男人躁女人到高潮AV|
欧美激情内射喷水高潮|
不卡高清中文字幕在线播放|
国产精品1区2区3区|
太大太长又硬放进去很爽|
亚洲欧美国产高清|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
日产无码AV在线观看|
国产av网站中文字幕|
看看妇女的B免费看|
青青小草国产在线播放|
91popn在线国产|
91av视频免费在线观看|
欧美性色欧美性A片色欲|
精品国产午夜福利在线观看|
一个人看的www神马视频|
日韩人妻无码精品A片免费不卡
|
50阿姨性生殖视频|
91尤物视频盛宴|
亚洲色欲色欲在线大片|
两老头把我添高潮了A片苏晴|
人妻无码AV中文字久久|
A级毛片内射免费视频|
日本熟妇╳浓密毛HD|
2014av天堂影音先锋|
国产精品人妻无码免费久久久|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
岛国无码免费aⅤ毛片|
抖音WWW视频在线观看|
精品一二三区免费看|
国产JK白丝AV在线播放|
狂处让老二爽18p|
在线毛片片免费观看|
91久久香蕉国产熟女线 |
国产午夜精品视频在线播放|
九九视频在线观看视频6|
最近中文字幕手机大全|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片|
国产成人永久免费无码观看
|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
九九视频在线观看视频6|
欧美成人无码A区视频在线观看|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
最近新免费韩国视频在线观看|
熟岳大屁股疯狂迎合|
国产成人不卡AV在线观看|
特级婬片内谢aaa毛片|
亚洲国产精品一区二区三区在线观看
|
国产人妻XXXX精品HD电影|
亚洲三级在线中文字幕
|
午夜成人亚洲理伦片在线观看|
欧美日韩精品亚洲一区二区|
三人交videosdesexoe|
最近最新中文字幕大全高清8|
色情推油按摩G点高潮无码视频
|
国产天天强奸三级片|
国产一级婬小说A级|
999精品国产人妻无码梦乃爱华|
午夜伦伦电影理论片大片|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
真人做爰48姿势视图片|
91欧美一区二区在线看|
高清国产天堂在线BT免费|
亚洲AV午夜福利精品一区二区app|
亚洲欧美精品午睡沙发|
边摸边吃奶边做爽视频免费|
日本MV高清在线成人高清|
99RE6国产精品99RE在线|
亚洲AV又黄又爽超级A片软件|
三级网站免费观看|
顶级欧美做受xxx000大乳|
灌醉水嫩大学生啪啪嗯啊男女
|
日产国产欧美韩国在线|
丰满少妇夜夜爽爽高潮水|
999久久久成人A片精品免费看|
日韩一卡二卡 3卡四卡乱码|
亚洲乱码卡1卡2新区3|
免费国产一级一级内射|
亚洲午夜精品小说图片专区|
亚洲精品久久久午夜福利电影网|
日韩一区二区免费视频|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
亚洲欧美第一精品网站|
av先锋影音资源男人站|
国产又色又粗又黄又爽免费|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
披按摩高潮A片一区二区三区|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
影音先锋av在资源天堂|
老女人熟女人妻国产|
欧美成人三级经典中文字幕|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
无码国产精品一区二区高潮最大|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合尤物|
日本又黄又爽gif动态图|
国产男人的天堂在线视频|
直接看的成人无码视频网站|
av中文字幕在线观看网址|
成年女人色费视频播放|
亚洲欧美日韩国产|
美国xoxoxoxo性欧美|
99热国产这里只有精品6|
91免费永久在线地址|
中日韩AV亚洲高潮无码|
九九综合VA免费看|
波多野结衣AV一区二区无码 |
大伊香蕉精品视频在线|
最近的中文字幕在线看2019|
中文字幕丰满孑伦无码专区|
欧美国产在线日韩|
亚洲国产欧美日韩另类精品一区二区在线
|
日本阿v手机不卡在线观看视频
|
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
欧美激情合集HB老司机在线|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
影音先锋av色噜噜影院|
中国国语对白高潮A片|
免费高清在线国产视频|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产|
年轻丰满的继牳理伦片中文|
色综合久久88色综合天天6|
影音先锋影院中文无码|
乱码中字芒果视频一二三多人|
伊人成综合网伊人222|
免费观看囯产自偷自拍窥自拍|
试看免看一级a一片|
欧美h版在线观看|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片99A|
99麻豆精品国产人妻无码|
伦理电影v男人天堂|
两个吃奶一个添下面视频|
粉嫩无套白浆第一次jk|
国产精品人妻一区二区三区A|
蜜臀AV99无码精品国产专区
|
大香伊蕉在人线国产最新2005
|
国产一区精选播放022|
色婷婷狠狠97成为人免费|
国产精品美女乱子伦高|
在线成本人视频动漫 www|
国产成人无码网站m3u8|
最新无码人妻在线视频|
亚洲精品乱码8久久久久久日本|
日本XXX免费高清色视频在线观看|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
97人人妻人人看人人澡 |
一级A女人高潮毛片免费男|
亚洲视频无码高清在线|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
亚洲AV无码男男A片在线观看|
女人把腿张开叫男人桶免费视频
|
国产一级婬小说A级|
丰满人妻熟妇乱又伦精品劲|
影音先锋2018av网址|
精品视频在线免费观看|
成人看片黄a在线看|
欧美激情内射喷水高潮|
小雏第一次破苞疼哭|
欧美日韩一区二区在线视频|
大叫受不了了好爽国产在线|
99精品欧美一区蜜桃在线 |
伊人大杳蕉中文在线20|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
黄色网页在线免费观看|
亚洲色熟偷拍视频在线|
内射老妇女BBWXOCLOCK|
日韩二丶三区视频免费|
日本乱妇乱熟乱妇乱色A片|
最近中文字幕视频完整版在线看|
亚洲人成在线播放无码|
成人片黄网站A片免费|
麻豆星空精东天美MV第一页|
成人视频免费在线观看|
国产女仆美女主播一区二区|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
國產午夜亞洲精品一區二區
|
同性男男黄H片在线播放网站|
99精品众筹模特私拍|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
大又大粗又爽又黄少妇毛片|
最近最新中文字幕大全高清8|
入室强伦轩人妻HD|
91一级特黄大片 |
免费岛国片在线播放|
18禁黄网站男男禁片免费观看
|
人妻性爱午夜不卡视频
|
国产精品乱码久久久久久软件|
影音先锋资源站玖玖网|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
日韩无码精品视频|
日日弄天天弄美女BBBB|
中文字幕亚洲欧美日韩2019|
很很鲁在线视频播放影院|
无码丰满熟妇BBBBXXX|
被老外添嫩苞添高潮NP|
国产精品无码一区二区在线欢捆绑
|
欧洲一卡二卡三卡|
性啪啪chinese东北女人|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
真人做爰高潮全过程|
17c人妻无码一区二区三区|
黑寡妇巨大粗爽毛片欧美|
色一情一乱一乱一区99AV|
国产日韩欧美毛片在线|
亚洲一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡网站|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
疼插30分钟一卡二卡三卡四卡
|
国产色欲婬乱视频网站免费|
成人福利国产视频|
我和嫲嫲狂躁了一晚上还住|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
波多野結衣一區二區免費視頻|
日本无码MV免费视频在线|
和黑人高潮了10次A片|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片88|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
久久久视频2019爱|
亚洲精品中文字幕制|
粉嫩小又紧水又多A片|
久久国产精品免费网站|
国产午夜婷婷精品无码A片
|
亚洲 欧美 制服 另类 无码
|
成人免费激情毛片|
日韩少妇内射免费播放|
欧美成人精品区综合A片|
亚洲AV成人无码无在线观看|
不卡人妻无码AV中文系列APP|
亚洲 欧美 制服 另类 无码|
国产真实露脸乱子伦|
国产综合av一区|
精品一卡二卡三卡四卡|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区竹菊影视
|
抖音WWW视频在线观看|
草草影院永久线路CCYY|
aa福利亚洲国内在线精品|
激情自拍另类亚洲|
亚洲AV久久久久久久无码|
久久无码人妻一区二区三区|
九九色网视频天天天操|
99麻豆久久久国产精品免费|
精品久久久爽爽久久久AV|
久久麻豆精亚洲av品国产一区|
日产一线二线三线哺乳|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片精华|
添女人荫蒂全部过程AV|
国产亚洲麻豆精品AA片在线观看|
aV影音先锋毛片子|
真人強奷112分钟|
亚洲精品鲁一鲁一区二区三区|
2018天天弄国产大片|
无遮挡h肉动漫在线观看幽默|
国产一区二区三区在线观看网|
亚洲Av人片在线|
亚洲精品口国自一产A片|
色情.WWW成人天堂|
久草资源在线观看|
麻豆精品一卡2卡三卡4卡免费观看
|
2020最新国产自产精品|
一女被两男吃奶添下A片V图|
在线成本人视频动漫 www|
日产一线二线三线哺乳|
亚洲婷婷六月的婷婷|
邻居少妇被爽到高潮A片|
特极西西444WWW大胆无码|
最近高清中文在线字幕观看|
日产乱码一二三区别免费麻豆
|
超级青草碰碰免费视频|
动漫美女H黄动漫在线观看|
久久中文字幕人妻AV熟女|
91精品少妇色精品一区|
久久人人槡人妻人人玩夜色AV|
中文字幕欧美人乱人精品A片|
国产精品视频在线观看|
a9av红番阁免费观看|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片|
精品亚洲国产成人A片在线观看|
国产JK白丝喷白浆精品视频|
免费啪视频在线观看视频网页|
亚洲区色情区激情区小说公|
无码人妻丰满熟妇A片护士M|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
青草青草久热精品视频在线百度云|
欧美精品一区二区蜜臀亚洲|
啪影院免费线观看视频|
日本B站一卡二卡|
久久国产36精品色熟妇|
亚洲国产aⅴ精品无码|
无遮挡h肉动漫在线观看幽默|
丰满老熟好大bbbxxx|
波多野结衣AV一区二区无码 |
久久伊人久久大香线蕉一区|
久久久久综合网久久
|
亚洲乱码日产一区三区|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
69国产成人精品午夜福中文 |
日韩内射美女片在线观看网站|
黑人大JI巴做爰呻吟视频|
欧美人妻WWW无码国产黄漫|
秋霞无码久久久精品一区二区|
成A人亚洲精V品无码樱花国产|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片|
欧美又大又粗又硬又色A片|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
国产精品1区2区3区|
特黄A又粗又大黄又爽A片|
少妇大叫又粗又大太爽A片|
宅男色影视亚洲人在线|
国产在线精品免费AAA片|
欧美性色欧美性A片色欲|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片免费看|
婷婷五月开心五月色情|
久久久精品激情av日韩|
粉嫩小泬WWW免费视频网站下载|
中文字幕精品AV一区二区五区|
精品无人乱码一区二区三区无限看|
啊轻点内射在线视频|
最近亚洲中文字幕免费av|
欧美日本一区二区三四区
|
国产刺激熟女短视频在线观看|
麻豆高清免费国产一区|
亚洲男人天堂2022|
亚洲精品久久久久久AV伊人
|
国产又黄又爽又色的免费APP|
欧美FREE性黑寡妇|
国产高清国内精品福利色噜噜|
成人网站在线无码高清|
特黄A又粗又大黄又爽A片|
日韩无码精品视频|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合|
伸进护士的小内裤疯狂揉摸|
久久久久综合网久久
|
中文字幕精品AV一区二区五区|
成年人免费视频一区二区
|
激情aa视频试看免费|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
惠民福利国产精品一区二区欧美视频|
色99久久久久高潮综合影院|
19不插片免费视频|
91成人国产麻豆一区二区|
性啪啪chinese东北女人
|
国产综合av一区|
国产AV麻豆一区二区|
国产艳福片内射视频播放|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
粉嫩高潮美女一区二区三|
一本到在线高清观看|
色狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片55|
成人网站 视频免费|
a篇片在线观看快播|
曰韩少妇内射免费播放|
亚洲AV成人影视综合网|
蜜桃人妻无码AV天堂三区
|
久久久国产人妻精品|
av天堂影音先锋在线|
中国无码人妻丰满熟妇啪|
中文字幕黄色av首页网站|
国产夜色精品一区二区|
国产综合色在线视频播放线视
|
亚洲精品久久久久AV无码|
亚洲色无码专区在线观|
2018天天弄国产大片|
无广告观看久久精品99久久香蕉国产全集
|
www.xxx-av.com|
欧美又大又粗无码视频|
美女脱内衣禁黄止18以下免费|
91麻豆产精品久久久久久粉嫩
|
中国亚洲女人69内射少妇|
欧美肥胖裸熟妇的毛发布|
未满十八禁止看床片视频
|
亚洲av无码成人精品区在线播放
|
又硬又粗进去好爽A片春色视频|
久久视频这里只精品18|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
久久视频精品38在线播放|
国产激情久久99久久|
双腿扒开调教羞辱奶头|
国产精品久久久久久久久久久久久久|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
亚洲一区久欠无码A片|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在|
国产精品高潮呻吟久久影视A片|
久久女婷五月综合|
中国亚洲女人69内射少妇|
IJZZIJZZIJZZ教师水多|
17c在线精品无码秘入口|
国产 欧美 首页 精品|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频
|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师|
国产无遮挡又黄又爽在线视频|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠
|
综合久久一区二区三区|
亚洲美女又黄又爽在线观看
|
亚洲一区二区一级视频免费看|
国产狂喷水潮免费网站www|
永久免费无码AV网站在线观看|
欧美黑人精品三级网站|
性色AV久久一区二区|
少妇我被躁爽到高潮A片小说|
免费人妻无码AV不卡在线|
XXX一区二日本视频|
国产亚洲精品AAAAAAA片|
91热久久免费频精品99欧美|
亚洲精品久久久久久一区|
一个人在线观看免费中文www|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套|
亚洲A片无码精品毛片色戒|
国产亚洲va在线电影|
真人女性生图片高清黑毛|
少妇大叫又粗又大太爽A片|
国产艳福片内射视频播放|
真人真实做爰30分钟试看|
91潮喷在线播放|
视频在线观看一区二区三区|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大全集|
亚洲国产精品色情777777|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区色|
啊轻点内射在线视频|
女人爽到高潮潮喷在线观看直播了
|
99RE6国产精品99RE在线|
久久久精品国产AV麻豆|
18禁日韩精品免费观看|
国产人妻人伦又粗又大爽歪歪
|
A级毛片高清免费网站不卡|
最近最新高清中文字幕av|
av最新一级网站在线观看|
好男人影视视频WWW|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
日日弄天天弄美女BBBB|
国产精品久久久久久99人妻绯闻|
高清不卡二卡三卡四卡无卡|
欧美激情综合五月色丁香|
欧美丰满大乳无码少妇|
男人自慰一级看片免费观看|
51国产偷自视频区视频|
亚洲最大成人综合网720P|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
WWW射我里面在线观看|
91综合国产精品视频|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
精品AAAA巨乳|
日韩精品一区二区在线免费看|
女人被添全过程A片免费视频|
98在线精品在线视频|
四平青年电影完整版|
四虎在线永久免费国产精品資源免費看|
亚洲图色中文字幕|
新影音先锋男人色资源网|
国产在线看老王影院入口2021|
亚洲一区二区三区电影在线|
久久国产精品免费网站|
成片免费观看视频大全|
国产亚洲精品久久777777
|
一级无码av护士系列在线观看|
最新日韩欧美中文字幕 |
欧美成a人片免费看久久|
國產午夜亞洲精品不卡電影|
饥渴的40岁熟妇完整版在线|
国产玉足榨精视频在线观看|
欧洲成人4卡5卡6卡7卡|
污的视频带疼痛的叫声在线观看|
精品深夜AV无码一区二区老年
|
亚洲多毛妓女毛茸茸的|
日本AAAA特级毛片|
内射一区二区精品视频在线观看|
丁香花视频免费播放社区|
动漫熟女制服一区二区 |
激情综合成人五月天|
国产啪精品视频免费制服丝袜|
77成年轻人电影网网站|
意大利电影巜豪妇荡乳|
91桃色污无限免费看|
8090碰在线视频97|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区不卡|
av综合网男人的天堂|
欧美精品做人一级爱免费|
恋夜影院支持安卓视频美女|
色噜噜噜一区二区三区|
色欲AV巨乳无码一区二区|
好看的国产精彩视频|
亚洲熟女乱综合一区二区在线|
影音先锋成人电影在线|
韩国一级婬片A片无码肉蒲团|
久久精品免费人成人A片|
中文字幕日韩一区二区不卡|
啦啦啦中文日本免费高清百度|
玩50岁四川熟女A片|
成人做爰A片免费看视频|
少妇性BBB搡BBB爽爽爽毛片|
国产操比视频三级午夜爽 |
亚洲图片综合图区20p|
成人片黄网站A片免费|
搡女人真爽免费视频大全|
欧美精品色婷婷五月综合|
91亚洲老熟女网|
图片区视频区小说区|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片软件|
搡8O老女人老妇人老熟|
高清国产天堂在线BT免费|
边吃奶边狠狠躁日韩A片|
大战熟女丰满人妻AV|
91无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
区产品乱码芒果精品综合|
99在线精品免费视频|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
欧美熟妇乱人伦A片免费高清|
亚洲中字幕日产2021草莓|
美女张开腿黄网站免费下载|
99热久久爱五月天婷婷|
欧美熟妇乱人伦A片免费高清|
久久国产人妻一区二区免色戒电影
|
无码激情做A爰片毛片A片小说|
国产清纯91天堂在线观看|
日本妇人成熟A片一区-老狼|
五月香婷婷俺也去俺也|
免费岛国片在线播放|
着衣爆乳揉みま痴汉电车中文字幕
|
成年人精品免费视频|
5月丁香婷婷网俺来也|
久久精品成人无码A片小说|
琪琪电影网午夜理论片717西瓜|
轻轻一摸就出水13p|
婷婷综合色五月久丁香|
国产寡妇乱子伦一区二区三区。|
亚州AV无码乱码色情|
欧洲一卡2卡3卡4卡免费观看|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
97中文字幕人妻久久精品|
丁香婷婷六月综合缴清|
a在线视频v视频|
国产47页在线观看 |
好大好深我高潮了A片|
国产精品美女WWW爽爽爽视频|
a篇片在线观看快播|
在线精品视频raPPer|
中文字字幕在线中文乱码2019|
69久久无码一区人妻A片|
老熟女肥臀AV老熟女A片|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
天堂免费在线观看亚洲|
欧美全黄a一级一区二区三区视频
欧美日韩国产精选福利片
|
97人妻熟女成人免费视频|
四川美女BBBB爽爽毛片|
美女丝袜一区二区三区|
国产成人国产A∨国片精品白丝美女视频|
色偷偷超碰av男人天堂|
色情美女激情喷水AV|
久久99AV无色码人妻蜜|
女人下边被舔全过视频软件
|
2017秋霞在线观看免费大奶子|
999国产精品欧美一区二区
|
69无人区码一码二码三码区别|
草莓视频APP下载黄色安装|
伊人狠狠色丁香婷婷综合男同|
999热久久这里只有精品|
最近中文字幕大全免费版在线|
2022一本久道久久综合狂躁|
99久久国产综合精品1 |
图片区视频区小说区|
51久久国产露脸精品国产|
五月色婷婷亚洲男人的天堂|
日日碰狠狠躁久久躁7777|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
美女被c视频在线观看|
视频一区国产精戏刘婷30|
无码爽大片日本无码AAA特黄|
99精品国产综合久久麻豆|
影音先锋 影院资源av|
97人人爽人人澡人人妻|
偷拍亚洲制服另类无码专区|
国语对白农村老太婆BBw|
久久伊人五月丁香狠狠色|
国产欧美丝袜另类第三区|
rion美乳弹出来四虎在线观看|
影音先锋成人电影在线|
久久超碰av资源|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
国产狂喷水潮免费网站www|
久久久久亚洲AV无码专区首护士|
日本一卡二卡三卡四卡手机免费观在线|
免费啪视频观免费视频|
91久久嫩草丁香婷婷色伊人|
日本一本二本和三本的视频|
成人国产一区二区精品小说|
国产人妻XXXX精品HD电影|
国产群交轮流内射骚|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
男人吸奶日进去视频|
成人午夜免费无码福利片|
国产在线观看不卡|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
亚洲精品无码一区二区色戒|
黄网站免费线观看免费|
在线永久免费观看黄网站|
国产精品自产拍在线观看55亚洲|
高潮潮喷无码一区二区三区|
欧美一区二区三区不卡免费|
最近日本MV字幕免费高清视频|
亚洲gv天堂gv无码男同|
亚州精品无码久久久久av|
亚洲高清无在码在线电影|
美女裸身无档视频免费|
成人亚洲天堂一区|
玖玖爱这里只有精品视频|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
99视频内射三四|
日本国产精品无码字幕在线观看|
国产中文字幕一区|
天津老熟女高潮A片视频|
少妇人妻丰满做爰XXX|
美女写真福利视频网站|
91精品无人区无豆乱码无人|
一人看片WWW在线视频|
www.008av.com|
亚洲天堂一区二区三区|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出在线|
国产精品日本无码久久一老A|
成人无号精品一区二区三区|
国产偷人爽久久久久久老妇APP|
男人吸奶日进去视频|
西西人体扒开大胆大尺度展露|
国产欧美日韩视频怡春院|
亚洲欧美精品SUV苍井优|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色字幕综合|
少妇无码吹潮久久精品AV|
玩弄丰满奶水的女邻居|
色偷偷资源亚洲在线|
BBW.妇女被内射|
免费男女羞羞的视频网站中文子暮|
9999色艺术中心|
国产成人免费精品|
亚洲欧洲日产国码中学|
中文一卡二卡三卡四卡免费|
国产在线观看91香蕉|
丰满丰满区一区二区二一|
丰满岳跪趴高撅肥臀尤物在线观看|
超碰97久久国产精品牛牛|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
无遮挡h肉动漫在线观看幽默|
久久香蕉超碰97國產精品|
国产精选 第1页-要看tv|
成人免费无码特级毛片A片|
久艾草国产成人综合在线视频|
亚洲欧洲日本无在线码播放|
男女久久久视频2019|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
国产色情AAA级AAA电影|
国产精品久人妻精品|
成年免费大片黄在线观看岛国|
蜜桃av鲁一鲁一鲁一鲁樱花影院|
国产清纯白嫩大学生正在播放|
国产又大又粗又硬又长A片小说|
国产十八熟妇AV成人一区|
小骚妇下面水多要插视频|
顶级欧美做受xxx000大乳|
影音先锋熟女少妇AV资源
|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫|
国产欧美丝袜另类第三区|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
国产AV国产精品白丝JK制服|
亚洲精品无码高潮喷水A片在线
|
WWW成人国产高清内射|
无码人妻欧美丰满熟妇区毛片
|
色欲精品国产AV久久久|
欧美视频 偷窥自拍视频|
国产A∨无码专区亚洲A∨麻豆|
A片试看120分钟做受视频红杏|
国产夜色精品一区二区|
好男人在线视频神马影视WWW|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
97色伦午夜国产亚洲精品 |
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
免费网站观看av片|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产丝袜|
久久精品国产免费中文|
青青草在免费线观曰本|
性生生活大片又黄又|
影音先锋资源AV看片站|
最近2018中文字幕视频免费看|
午夜熟女插插XX免费视频|
亚洲精品久久久午夜福利电影网|
被男人添B超爽视频免费|
免费A级毛片黄A片高清在线播放
|
动漫美女H黄动漫在线观看|
欧美国产在线播放欧美|
国产精品色哟哟网站高清|
久久久国产人妻精品|
77成年轻人电影网网站|
国产精品福利在线播放|
欧洲一卡2卡三卡4卡乱码毛1|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
国产一区精选播放022|
国产亚洲精久久久久久无码妖精|
性一交一乱一美A片图片|
国产清纯白嫩大学生正在播放|
色综合亚洲色综合久久网张柏芝|
国产麻豆剧传媒精品国产AV|
国产一区二三区无码免费|
饥渴难耐的浪荡艳妇在线观看
|
99RE6国产精品99RE在线|
少妇又色又爽又紧的A片|
五月婷婷丁香花综合网|
亚洲乱码一卡二卡四卡乱码新区
|
中文字幕视频一区亚洲欧美|
4484在线观看视频|
末成年美女黄网站色大片连接|
巨大乳女人做爰视频在线|
8090碰在线视频97|
高潮A片揉搓乳尖乱颤视频
|
2019爱久久视频在线12|
av大片在线网站|
天天做天天添天天谢|
国产成熟妇人高潮A片|
小粉嫩精品A片在线视看|
中文日韩欧美亚洲|
少妇把腿扒开让我添69式漫画|
风韵人妻丰满熟妇老熟女|
超级青草碰碰免费视频|
亚洲高清无在码在线电影|
精品卡一卡二卡三免费使用|
欧美成人A片免费无码毛片|
又色又爽的无遮挡免费网址|
91香蕉视频污在线观看|
肉浦团在线观看快播|
亚洲综合AV色婷婷五月蜜臀|
欧美日韩综合无码中文字幕|
欧美乱熟人妻色情影视|
国产又色又爽又刺激的A片|
欧美精品一区二区久久丰满湿润|
一区二区三区A片无码视频不卡|
国产aaav淫片|
欧美粗大特黄AAA片|
草莓AV福利网站导航|
国产午夜精品AV一区二区麻豆|
国产在线观看不卡|
五月色婷婷亚洲男人的天堂
|
欧洲精品无码一区二区三区的视频空间|
av免费无码专区|
91久久无码一区人妻A片蜜桃|
97高潮就出奶水多还在哺乳|
无码人妻久久久午夜一区二区三区|
成人亚洲黄片欧美日韩|
国产V片在线播放免费观看大全|
精品日产乱码卡一卡2卡|
最近韩国日本MV免费观看免费|
A片扒开双腿猛进入免费观|
无遮挡拍拍拍免费观看|
老熟女肥臀AV老熟女A片|
久久久精品免费视频|
黄片欧美一区二区三区|
精品人妻无码一区二区三区手机板|
成年女人免费影院播放|
四虎视频成人版黄A片|
真人做爰视频在40分钟左右|
免费无码又黄又爽又刺激|
免费番肉动漫在线观看|
中日韩AV亚洲高潮无码|
青娱乐国产视频在线分类|
99久久亚洲精品日本无码|
又硬又粗进去爽A片免费|
人妻无码AV中文字久久|
人人妻人人澡人人爽人人老司机|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
肥熟女视频一区二区三区国|
中文字幕乱码免费视频|
亚洲精品中文幕一区二区|
国产粉嫩小泬在线观看泬|
韩国精品福利一区二区|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
无码av在线不卡在线观看|
人妻无码AV中文系统久久免费|
粉嫩av一区二区三区|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
亚洲欧美人高清精品a不卡|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
久了re热在线视频播放6|
嫩草AV久久伊人妇女超级A|
中文字幕 亚洲 有码 在线|
久热这里只精品99re8久|
国产V片在线播放免费观看大全|
国产视频适合在网上看的和出水了|
日韩色情一区二区无码AV|
老妇高潮潮喷到猛进猛出|
美女被免费网站在线视频app|
2019国产精品青青草原|
成人av片无码免费天天看|
强开小婷嫩苞又嫩又紧视频|
亚洲50熟女性视频免费|
无码免费一区二区三区日本A片|
亚洲国产精品一区二区第一页|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
添女人荫蒂全部过程AV|
人妻丰满熟妇av无码久久洗澡|
国产丰满农村妇女一区区|
cijilu在线视频|
泰国两熟女春梦邂逅猛男|
国产欧美日产综合动漫在线观看网站视频
|
99超级碰碰成人香蕉网|
亚洲成人视频一区二区|
中文字幕亚洲精品久久AV|
欧洲精品不卡1卡2卡三卡四卡|
欧美亚洲综合免费|
国产高潮抽搐在线观看
|
1000部免费视频观看|
精品亚洲A∨无码国产一品在线|
色偷偷WWW.8888在线观看|
东京热456大交乱高清视频|
91av国产超碰在线|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
国产精品一区二区 尿失禁|
产福利一区在线观看精品尤物|
越南女子杂交内射BBWBBW|
极品媚黑91黑人在线播放|
又湿又深又爽的A片视频|
国产传媒18精品A片一区|
麻豆AV无码精品一区二区|
亚洲最大天码AV在线观看|
2020最新国产自产精品|
国外人成人色视频在线
|
337p日本欧洲亚洲大胆色噜噜 |
大片国产片日本观看免费视频|
日产一区日产2区日产三区|
极品少妇粉嫩小泬啪啪AV|
日韩色情一区二区无码AV|
影音先锋天堂网资源av|
亚洲乱码AV中文一区二区|
久久视频精品38在线播放|
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA
|
在线毛片片免费观看|
黄 色一 片 级 日本|
一个人看的www的视频中文|
AV国产精品私拍在线观看|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频|
又硬又粗进去好爽A片春色视频
|
丰满熟女人妻中文字幕免费|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
免费无码AV色情在线|
圆产精品久久久久久久久久久新郎
|
男生J桶进女人P又色又爽又黄|
精品亚州aⅤ无码一区|
人妻中文字幕乱人伦在线|
久久久久综合网久久|
A片扒开双腿进入做视频|
www.成人.com|
欧美亚洲色倩在线观看|
国产高潮A片羞羞视频涩涩|
国产内射大片99|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
狠狠色老熟妇老熟女|
国产AV无码熟妇人妻麻豆|
国产yw8825免费观看网站|
丰满少妇大力进入A片中文|
国产精品久久久久久亚洲小说|
不充会员的爽爽影院|
嗯啊开小嫩苞HHH...嗯啊|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
国产在线观看91香蕉|
国产精品乱码久久久久久软件|
天天做天天躁天天躁|
麻豆精品一卡2卡三卡4卡免费观看
|
拍真实国产伦偷精品|
99精品欧美一区蜜桃在线 |
最新国产精品好看的国产精品|
欧洲老妇60一70|
av在线观看网站免费|
国产一区国产二区在线|
亚洲乱码一卡二卡四卡乱码新区
|
性一交一伦一A片免费看|
麻豆果冻传媒在线观看|
久久偷看各类WC女厕嘘嘘偷窃|
www国产亚洲精品久久网站|
免费A片看黄网站WWW|
欧乱色国产精品兔费视频|
2020中文在线一区二区三区|
国语激情对白 VIDEOS|
无码少妇一区二区三区动漫免费看|
久久精品国产亚洲AV高清色三区|
区产品乱码芒果精品综合|
97久久久精品综合88久久|
成人三级理论电影|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片漫|
狂处让老二爽18p|
摸添揉捏胸还添下面视频|
国产成人精品一区二三区熟女在线|
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩18禁|
CAO死你好紧好爽好湿视频男男|
91精品久久久久久综合五月天|
久久精品成人无码A片小说|
99久久精品免费国产一区二区三区
|
2017能在线观看的网站|
91久久综合精品国产丝袜长腿|
国产成人精品男人的天堂网站|
福利午夜视频在线|
欧美粗大特黄AAA片|
亚洲在线一人香蕉免|
国产精品aⅴ久久久久久鸭绿欲|
丰满熟女人妻一区二区三|
成年视频网站在线观看777|
成年人免费在线看黄|
YY6080午夜福利无码理论|
久久五月天激情五月天|
欧美精品久久96人妻无码|
在线看欧洲一卡二卡三卡残暴|
麻豆av一区二区三区|
女人添荫蒂舒服了A片|
最新一本到2019线观看|
亚洲 欧美 制服 另类 无码|
久久久老司机精品网站福利|
亚洲熟妇AV日韩熟妇在线|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片小说|
91精品一区二区在线观看|
色情A片成人免费观看视频|
www色情免费观看日本|
a级毛片无码免费真人久久国|
毛片内射久久久一区|
边啃奶头边躁狠狠躁AV|
大陆老熟女嗷嗷叫AV在线|
从后面挺进去激情视频|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩在线
69一区二三区好的精华
|
中国国语对白高潮A片|
国产成人精品一区二区免费|
污污内射久久一区二区欧美日韩|
成人做爰WWW免费看视频日本
|
无敌神马影院视频观看高清免费|
亚洲av制服自拍诱惑|
男生女生看片视频免费的|
中文无码第3页不卡av|
SM情趣鞭打尿失禁强制高潮女|
日本无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放|
天天影视欲香欲色成人网|
2019天天拍天天爱天天拍|
麻豆星空精东天美MV第一页|
国产亚洲精品AAAAAAA片|
久久久精品国产SM最大网站|
精品成人无码A片观看香草视频|
日韩精品AV一二三区在线|
日韩美女自卫慰黄网站|
黄WWW禁止男女萝卜|
亚洲精品无码一区二区色戒|
羞羞视频网站在线观看18岁无遮挡|
陈红下面又紧又小好爽|
丰满丰满区一区二区二一|
久久成人麻豆精品一牛影视太久|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
强行糟蹋人妻HD中文|
爽灬好舒服灬别拔出来视频人|
日韩插啊免费视频在线观看|
最近中文2019在线观看|
佳佳黑高跟极致踩踏调教视频|
九九影院免费还看视频|
张柏芝精品一区二区三区在线观看|
99久久免费只有精品国产高潮
|
影音先锋中文无码一区|
日本妇人成熟A片一区-老狼|
亚洲国产欧美日韩另类精品一区二区在线
|
安徽妇槡BBBB搡BBBB|
国产精品一区二区不卡蜜臀在线
|
国产国语特级 a毛片|
公交车上双乳被老汉揉搓玩|
人妻少妇精品无码一区二区三区
|
一区二区超碰免费在线观看|
91精品国产高清久久久久久l|
欧美人妻精品久久久久久|
日本无码MV免费视频在线|
国产玉足榨精视频在线观看|
2014手机免费基地旧版懂得|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区不卡|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
青草亚洲国产欧美一区二区|
人妻无码AV中文系统久久免费|
国产偷自久久精品久久|
成人亚洲免费影视|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
91大香蕉国产一区|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片|
91一区二区三区四区五区|
男女无遮挡猛进猛出免费观看视频|
少妇人妻av中文系列久久
|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片漫|
91高清综合一区天天干夜夜操|
chinese国产hdsex水滴|
69无人区乱码一二三四区别|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
最近日本字幕MV在线观看|
亚州日韩精品AV片无码中文|
污污免费看锕锕锕锕锕锕锕|
精品国内片67194|
欧美特级另类xxx|
欧美日韩免费在线|
粗大挺进亲女H小蕾的嫩苞第几集|
AV8888AV色情观看在线|
A片高潮抽搐揉捏奶头视频在线看|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
羞羞影院午夜男女爽爽影院网站|
国产精品高潮呻吟AV久久床戏|
一级黄日本C爱视频|
日本一本道2018无号码|
大陆国产aⅴ国语精品对白|
激情内射亚洲一区二区三区爱妻|
高清国产不卡视频|
亚洲国产成人久久精品导航|
chinese国产hdsex水滴|
欧洲一级毛卡片免费不卡|
中文字幕 亚洲 有码 在线|
91av视频免费在线观看|
欧美特级特黄AAAAA片|
色噜噜狠狠一区二区三区|
成在人线av无码免观看麻豆|
日本一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡高清视频下载
|
又大又紧18P少妇在线观看|
精品无码国产污污污免费|
91国产丝袜在线播放|
少妇被躁到高潮A片免费|
亚洲一区二区三区国产|
成人国产在线观看|
99精品福利视频|
成人无码在线视频区|
又大又黄又爽免费看A片|
影音先锋av在资源天堂|
好大好爽好深舒服死了A片|
少妇又色又爽又紧的A片|
美女被c视频在线观看|
日本A一片中国A一片|
欧美人妻WWW无码国产黄漫|
四川少妇搡BBB搡BBB爽爽爽小说|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
男生女生看片视频免费的|
人妻精品久久无码专区色视蜜臀|
欧洲成人4卡5卡6卡7卡|
军人同性CHINESE69猛男|
欧美区日韩区国产区|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
男女在线观看啪网站|
国产爆初菊一区视频|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
国偷自产aV一区二区三区|
亚洲AV无码乱线观看性色|
日韩好片一区二区在线看|
露营野外帐篷奶头舔齐根没入小说
|
国产欧美又粗又猛又爽|
男插女一起爽的免费樱花小视频|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片秋霞|
午夜精品A片一区二区三区|
亚洲区色情区激情区小说公|
国产国产乱老熟女视频网站97|
国产精品免费AⅤ片在线观看男女|
a亚洲Va欧美va国产综合 |
国产69精品久久久久999小说|
又大又爽又黄A片免费|
中文字幕高清免费日韩视频在线
|
亚洲少妇久久久久|
又黄又粗暴的gif动态图|
国产亚洲精品A片久久久|
色情A片成人免费观看视频|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
10000拍拍18勿入免费看动漫
|
一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡在线|
色老头在线视频免费观看|
亚洲国产成人久久精品导航
|
91中文字字幕人人国产3|
国产女仆美女主播一区二区|
五月综合激情婷婷六月色窝|
成人高清精品视频|
一本道中文字幕av无码|
视频一区二区三区蜜桃麻豆|
亚洲AV成人噜噜无码网站A片|
国产婬A片999片免费网站|
黄色网址在线免费观看|
日本做爰A片AAAA|
欧乱色国产精品兔费视频|
久久久精品国产SM调教网站|
日产乱码一二三区别免费麻豆|
午夜福利精品视频|
很黄又污又色情又爽又猛|
国产精品日本无码久久一|
五十路近親相姦中出し親子|
99国产精品免费一区二区
|
午夜无码熟熟妇丰满人妻|
欧美性猛交aa一级|
精品AAAA巨乳|
91精品国产高清久久久久久l|
无码精品人妻一区二区三刘亦菲|
欧美日韩一级婬片A片吞精怀直播|
又黄又爽又无遮挡在线观看免费|
国产色欲婬乱视频网站免费|
8090碰在线视频97|
亚洲多毛妓女毛茸茸的|
亚洲av免费分钟观看|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
久久久天堂国产精品女人|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
麻花豆传媒剧国产MV入口|
40分钟超爽大片黄|
欧乱色国产精品兔费视频|
日本高清色情高清日本|
午夜欧美日本一区二区三区|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
欧美精品一区二区久久丰满湿润|
亚洲精品国产国语|
亚洲精品久久久久久久蜜桃臀
|
国产亚洲av资源在线观看|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
亚洲女厕所小便bbb|
自怕偷自怕亚洲精品|
三级片中文字幕一区二区|
久久久国产精品无码人妻|
成人a级特黄毛片|
国产精品一区二区亚瑟不卡|
香蕉视频在线看污污|
五月天精品视频在线观看|
99久久人妻无码精品系列性欧美|
成年网站免费视频网站|
亚洲巨乳巨臀在线一区二区BBW|
国色天香精品卡一卡二卡三二百|
中文字幕丰满孑伦无码专区|
边吃奶边狠狠躁日韩A片|
欧美日韩精品电影一区|
教室停电H嗯啊好硬好湿攻守|
女人体a级1963免费|
国产av一区二区三区精华液|
亚洲国产欧美日本视频|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
国产超级a天堂直播在线观看
|
无码中文字幕AV久久专区
|
影音先锋av最新资源网|
99久久人妻无码精品系列蜜桃
|
又大又黄又爽免费看A片|
艾草在线精品视频播放|
九九综合VA免费看|
五月丁香综合啪啪成人|
西西4444www无码大胆|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师|
欧美搡BBBBB摔BBBBB|
国产精品日本无码久久一老A|
邻居少妇被爽到高潮A片|
百度国产精品网友自拍|
四虎视频成人版黄A片|
在线观看的av免费网站|
嫩草欧美曰韩国产大片|
最近中文字幕免费MV视频|
触手侵犯の奶水授乳羞羞漫画动漫|
羞羞影院午夜男女爽爽免费|
丰满少妇大力进入A片中文|
国产清纯美女爆白浆视频|
wuyueqingsetian|
宅男色影视亚洲人在线|
国产精品女A片爽爽免费按摩|
五月丁香激色婷五月天|
无码久久久久久中文字幕视频|
最近中文2019在线观看|
欧美又硬又粗进去好爽A片|
国产亚洲欧美日韩色|
男女作爱在线观看免费网站|
亚洲精品久久久WWW小说|
久久tv中文字幕首页|
日本A片特黄久久免费观看|
欧美叉叉叉BBB网站|
中文字幕乱妇无码AV在线|
免费gv在线观看网址|
另类女人ZOZO人禽交|
a97se亚洲国产综合自在线|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
欧洲一卡二卡三卡|
欧洲一卡2卡三卡4卡网站国色天香|
特级A欧美做爰AAAAA片|
欧美性生交大片免费看|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
91精品国产自产91精品资源|
性色AV爽歪歪啪啪A片|
中国国语对白高潮A片|
久久精品成人无码A片小说|
韩国精品无码少妇在线观看网站|
精品国产一区二区三区久久影院|
亚洲国产aⅴ精品无码|
搡的我好爽视频免费观看|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心
|
国产精品人妻无码免费久久久|
国产又粗又长又大精品A片|
91九色熟女欧美日韩欧美|
国产JJZZJJZZ视频免费看|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区不卡|
亚洲av无码成人精品区在线播放|
亚洲国产卡1卡2卡34卡|
亚洲-av-无限看|
女性爽爽影院免费观看|
大片免免费观看视频播放器在线观看
|
日韩成人伦理在线|
精品亚洲成A人7777在线观看|
免费网站观看av片|
高清成人欧美一区二区三区 |
国产精品人妻黑人借宿电影|
精品卡一卡二卡三免费使用|
欧美成人精精品一区二区三区
|
色婷婷婷丁香亚洲|
亚洲精品一区二区无码夜色|
精品国产亚洲一区二区三区|
国产成人午夜极速观看|
特黄特色大片免费播放器9|
亚洲熟女乱综合一区二区在线
|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
中文无码妇乱子伦视频国产精品亚洲LV粉色
|
又硬又粗进去爽A片免费无码|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片99A|
97成人精品一区二区三区狼人|
黄色网址视频在线播放|
第4色影院午夜在线观看|
91福利视频合集|
亚洲AV爽爽香蕉久久影|
欧美日韩无套内射另类|
91日韩精品在线观看|
色情无码WWW视频无码区小黄鸭|
亚洲AV无码久久蜜桃杨思敏|
伊人狠狠色丁香婷婷综合男同|
少妇的丰满2中文字幕|
适合一男一女看的爱情视频|
强开小婷嫩苞又嫩又紧视频|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区竹菊影视
|
在线精品亚洲观看不卡欧|
国产真实交换配乱婬98视频|
色噜噜2017最新综合|
中文字幕日韩人妻|
最近中文字幕视频完整版在线看|
一道本av免费不卡播放|
圆产精品久久久久久久久久久新郎|
男女又黄又刺激B片免费网站|
蜜桃视频在线观看网站|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
91福利华人在线观看|
国产成人av在线影院 |
粉嫩无套白浆第一次jk|
青青草国产97免费观看|
国产网友自拍在线视频|
国内偷拍亚洲欧洲2018|
影音先锋av色噜噜影院|
午夜福利精品视频|
成人在线观看国产一区|
琪琪电影网www888dvdc|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
百度国产精品网友自拍|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
国产视频久久久久久久一区二区三区|
丰满放荡岳乱蜜桃AV|
塔尔萨之王免费观看西瓜|
拍拍拍无遮挡高清视频在线网站|
成人小视频在线观看 |
少妇的丰满2中文字幕|
99久久婷婷国产综合精品青草欧美成人
|
成人A片产无码免费视频奶头鸭度|
国产成人精品综合久久久久|
久艹视频在线免费观看|
狠狠色很很鲁在线视频|
av天堂影音先锋在线|
中文字幕在线看成电影乱码|
久久中文字幕人妻AV熟女|
99超级碰碰成人香蕉网|
色欲人妻AAAAAAA无码|
色婷婷丁香A片区毛片区女人区|
爱我几何完整版在线观看|
日本乱人伦片中文三区|
亚洲精品婷婷无码成人A片在线
|
免费又黄又爽又色的绿巨人|
国产亚洲精品AV麻豆狂野|
国产极品粉嫩福利姬萌白酱|
成人国产精品视频大全|
亚州日韩精品AV片无码中文|
老头把我添高潮了A片故视频|
国产人妖视频一区二区|
欧美黑人一区二区三区免费A片
|
曰本女人牲交视频视频试看|
啊轻点灬大JI巴又大又粗A片|
亚洲欧洲日韩极速播放|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
av影音先锋天堂网|
50岁的牲欲强老熟女|
国产精品人妻一区二区三区A|
师尊胯羞坐抬臀抖吟迎合视频
|
第四色播日韩AV第一页|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
久久国产精品成人电影院|
影音先锋电影网站色|
看亚洲一级黄色片|
国产欧美日韩另类精彩视频|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片动漫
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA
|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
免播放器无码av网址|
A片好大好紧好爽视频|
四平青年之喋血曼谷免费观看完整|
午夜神马福利电影不卡|
欧美性活一级视频|
亚洲日韩精品一二三四区|
www.啪啪.com|
19不插片免费视频|
WWW射我里面在线观看|
国产亚洲麻豆精品AA片在线观看|
国产在线精品视频二区|
免费人做人爱的视频完整|
久久久国产一区二区三区|
成人特级毛片WWW免费版|
好爽快点我受不了了国产|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
人妻中文无码就熟专区欧美|
一级片视频网站免费看|
中文字乱码电影在线播放|
综合天天久久一区三区乱码|
国产色情精品一区二区唱戏|
最近中文字幕MV免费高清下载|
99久久婷婷国产综合精品青草欧美成人
|
激情综合成人五月天|
最近日本MV字幕免费高清视频|
老司机无码精品A|
极品少妇高潮啪啪无码吴梦梦|
男女啪啪永久免费观看网站|
国产欧美一区二区三区在线看蜜臀|
少妇A级裸片AAAAA八戒|
亚洲欧美日韩国产|
成人黄色网站在线播放|
cijilu在线视频|
在线观看的av免费网站|
青草青草久热精品视频在线百度云|
高潮肉欲少妇A片在线看|
国产一级淫片在线观看|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
AV亚洲欧洲日产国码无码苍井空|
欧美日韩一区二区视频免费观看
|
久久精品国产一区二区三区四区|
丰满女教师中文字幕4|
色欲av亚洲情无码av蜜桃|
大陆老熟女嗷嗷叫AV在线|
99视频这里只有精品国产|
又黄又爽吃奶视频在线观看|
久久精品AV一区二区三|
一本到在线高清观看
|
XXX一区二日本视频|
国产又爽又大又黄A片美女裸体|
精品无人区一码卡二卡三|
影音先锋av网站大全|
成人国产精品无码一区二区三区|
婷婷综合色五月久丁香|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师|
影音先锋av丝袜天堂|
国产成人免费精品|
欲女熟妇国产一区二区|
色妞色视频一区二区三区四区|
国产一级婬小说A级|
男人猛躁进女人毛片A片|
精品国产亚洲一区二区三区|
国产亚洲一卡2卡3卡4卡老狼
|
苍井空三年级片网站|
一本道不卡中中文无码|
欧美精品VIDEOSEX极品|
高中女学生破苞视频免费|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
大片国产片日本观看免费视频|
综合天天久久一区三区乱码|
日本乱人伦片中文三区|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
国产人伦激情在线观看三级
|
成年美女黄网站色大免费视频|
亚洲精品无码苍井空A片|
亚洲jizzjizz中国妇女|
先锋影音av资源站av|
91精品人妻人人做人踫人人爽
|
99久久人妻无码精品系列蜜桃|
91av在线免费观看|
亚洲国产一卡2卡3卡4卡5公司|
女人A级毛片19毛水真多|
18禁止进入黄大全在线|
九九九免费观看视频|
三级久久高清欧美|
一本久到久久亚洲综合|
jijzzizz老师出水喷水多毛|
亚洲AV综合AV一区二区综合|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出AVV
|
91精品一区二区三区无码吞精|
朝桐光日韩一区二区三区|
无人一码二码三码4码免费|
日韩欧美高清在线观看|
国产激情无码久久久久久
|
富婆偷人对白在线观看|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放|
人妻饥渴偷公乱中文字幕|
亲胸揉胸膜下刺激视频在线观看
|
人妻互换HD无码中文在线|
好男人WWW神马社区在线观看|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片软|
秘书下面太紧拔不出来怎么办|
亚洲高清无在码在线电影|
CHINESE叫床对白VIDEOS|
无码精品AV久久久奶水|
掀开奶罩边躁狠狠躁苏玥视频|
亚洲最大天码AV在线观看|
国产精品VA无码区二区|
黄网站色视频大全免费观看|
国产精品久人妻精品老妇|
欧美日韩不卡一区视频在现|
女人与牲囗牲恔视频免费|
亚洲午夜精品AV无码少妇|
变态另类av手机版天堂|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片WWW|
中文字幕电影乱码在线观看|
少妇夹得好紧太爽了A片|
成人久久18秘免费网站|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片动漫软件|
996这里只有精品|
国产色拍拍视频在线|
精品欧美久久三级|
最近最好的中文字幕2019免费|
国产做A爰片久久毛片A片蜜臀|
成在人线av无码免观看麻豆|
国产精品午夜无码AV在线播放
|
那种视频在线观看亚洲|
91精品高清91久久久久久|
欧美丰满少妇a毛片直播|
亚洲-av-无限看|
91精品福利视频|
久爱精品视频在线视频|
蜜月a 免费一区二区三区|
很黄又污又色情又爽又猛|
日韩免费视频一区|
无忧传媒MV国产在线观看|
无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩18禁|
免费亚洲成人久久精品|
手机看片1204免费视频观看|
国产爆初菊一区视频|
免费gv在线观看网址|
97亚洲狠狠色综合久久|
2020最新中文字幕在线|
男人天天在线视频|
а∨天堂在线中文免费不卡|
男女久久久视频2019|
亚洲在线国产日韩欧美|
国产做A爰片久久毛片A片蜜臀|
国产sm激情首页视频在线观看|
午夜无码熟熟妇丰满人妻|
免费番肉动漫在线观看|
9l国产精品久久久久|
宝贝你真湿真紧好爽h视频男男|
国内久经典AAAAA片|
最近中文字幕在线资源3|
青青草免费线观综合网|
陈红下面又紧又小好爽|
成人WWW色情在线观看|
亚洲综合久久无码一区|
少妇高潮喷水惨叫一区|
亚洲精品口国自一产A片|
搡BBBB搡BBB搡18免费观看|
国内露脸少妇精品视频|
免费人成网站在线高清|
特级做A爰片毛片A片免费|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片动漫软件|
9国产熟女视频在线观看|
国产又色又香又爽视频|
搡BBB上海少妇搡BBB3|
国产美女做爰A片免费|
乱换玩3p视频在线视频|
亚洲精品无码一区二区色戒|
国产麻豆剧果冻传媒视频免费|
好吊色欧美一区二区三区视频|
精品久久久久久久无码伊人|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
国产99视频精品免费视频6|
久久国产精品无码观看|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
亚洲男人天堂2022|
最新黄色网址在线观看|
午夜成人亚洲理伦片在线观看|
亚洲综合久久无码一区|
亚洲精品久久久鸭子
|
久热这里只精品99re8久|
国产亲子乱XXXXinin|
麻豆产国品一二三产品区别|
色情五月亚洲中文字幕|
国产精品一级A精品特黄A|
欧美肥胖裸熟妇的毛发布|
91国内免费在线视频 |
青青青爽在线视频观看|
中文人妻熟女波多野结衣|
免费视频在线播放啪|
男生肌肌桶女人屁股|
高清国产激情视频在线观看|
国产精品爽黄69天堂A|
aⅴ国产系列欧美亚洲|
真人做爰视频在40分钟左右|
FREECHINESE东北女人真爽|
a篇片在线观看快播|
国产精品偷窥女厕视频|
黄色网址成人在线观看|
国产69精品久久久久久久久久久久|
午夜亚洲乱码伦小说区69堂
|
亚洲国产精品色情777777|
日产乱码卡一卡2卡三卡四福利|
看毛片看1级片看超级超级片|
美女18禁永久免费观看网站|
91香蕉在线国产 |
小小视频在线观看www|
丝袜熟女脚交足在线一区|
不充会员的爽爽影院
|
国产肥熟女老太老妇A片|
国产日韓无码一区二区三区|
动漫AV纯肉无码AV电影网|
免费gv在线观看网址|
极品少妇粉嫩小泬啪啪AV|
最近更新中文字幕2019国语在线|
亚洲AV无码一区二区A片成人|
国产精品一区二区免费|
蜜臀AV色欲无码A片一区|
美女被免费网站在线视频app|
一级A女人高潮毛片免费男|
丰满人妻在公车被猛烈进入电影|
WWW国产精品内射老熟女|
成人午夜特黄AAAAA片男男|
av手机在线观看网站不卡|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩在线|
色YEYE在线视频观看网站|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
国产成人精品电影不卡|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
99视频在线观看这里只有精品
|
精品人妻无码一区二区三区50|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
人人妻人人澡人人人爽人人DVD|
顶级欧美做受xxx000大乳|
色偷拍亚洲国产大姐|
国产JK白丝喷白浆精品视频|
精品无码国产AV一区二区|
最近中文字幕高清字幕在线视频 |
国产做爰完整版在线观看|
偷拍亚洲制服另类无码专区|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
巨爆乳肉感一区二区三区视频|
很黄又污又色情又爽又猛|
欧美肉体视频一进一出在线|
亚洲AV久久无码精品国产网站|
亚洲精品久久99久久一二三区|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产|
91精品国产午夜福利蜜臀|
996这里只有精品|
真人女性生图片高清黑毛|
亚洲AV综合AV一区二区综合
|
99 精品视频网站|
丝袜熟女脚交足在线一区|
欧美亚洲综合免费|
久久免费精品视频互動交流|
在线观看日韩一区二区视频|
2019年秋霞鲁丝片84|
久久伊人精品毛片|
不卡在线播放一区|
成人网站在线观看免费|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片小说|
蜜臀久久AV无码牛牛影视|
国产中文字幕一区|
国产AV无码熟妇人妻麻豆|
亚洲一区欧洲一区|
99超级碰碰成人香蕉网|
丰满少妇被猛烈进入毛片|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频|
少妇无套内谢久久久久|
小柔在公厕被灌满jing液|
精品精品国产欧美在线|
成人亚洲黄片欧美日韩|
中午日产幕无线码8区|
青青草在现线久观看2019|
日本三级香港三级三级人!妇久|
闷骚的小少妇全程露脸|
成年人视频网站免费|
2018国产偷拍免费视|
无遮挡啪啪摇乳动态图GIF|
欧美又大又粗又硬又色A片|
高潮无遮挡成人A片在线看|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
免费无码又爽又刺激A片软|
一区二区三区免费看A片|
歪歪爽蜜臀AV久久精品人人槡|
AV国産精品毛片一区二区|
91嫩草国产在线无码观看 |
宝贝你真湿真紧好爽h视频男男|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出在线|
欧美FREE性黑寡妇|
国产av网站中文字幕|
欧美牲交A欧美牲交VDO|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
国产精品自产拍在线观看55亚洲|
亚洲50熟女性视频免费|
亚洲AV成人影视综合网|
影888午夜理论不卡|
www国产亚洲精品久久网站|
国产亚洲麻豆精品AA片在线观看
|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫|
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
试看多人做人爱的视频|
男女狂进狂出动态图GIF|
亚洲无人区一码二码三码区别|
少妇中文综合欧美|
国产精品久久久久久99人妻绯闻|
大肉大捧一进一出好爽MBA|
高潮无遮挡成人A片在线看|
女人另类牲交ZOZOZO|
小雪的13又嫩又紧又多视频|
999国产精品欧美一区二区 |
www.黄色免费网站|
日本公妇里乱片A片在线播放保姆|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
se97se成人亚洲网站|
成年人免费在线看黄|
日本成人一区二区三区|
97在线观看视频公开免费|
国产AV麻豆一区二区|
少妇bbb搡bbb搡bbb|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
亚洲成人视频一区二区|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
91精品久久人人妻人人爽人人|
亚洲无码黄色片网站|
丰满多毛少妇做爰视频爽爽和R|
无码人妻AⅤ一区二区三区A片一
|
久久tv中文字幕首页|
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
亚洲精品中文字幕制|
成av人电影在线观看|
超碰97成人免费在线观看|
日日摸夜夜添夜夜添亚洲女人|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片软件|
专干老肥熟女视频网站300部|
亚洲人成人无码.WWW石榴|
国产人妻99精品无码一区二区三区
|
免费费很色视频大片|
欧美黑人添添高潮A片视频|
特黄A又粗又大黄又爽A片|
双性猛男被脔到怀孕txt|
国语激情对白 VIDEOS|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
欧美91精品国产玩人妻|
亲胸揉胸膜下刺激视频在线观看|
中文字幕暖暖永久在线视频
|
亚洲一卡2卡3卡4卡国色天香app
|
国产学生粉嫩无套进入在线小说
|
国产又粗又猛又黄又爽A片|
国产一级特黄高清免费视频|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片秋霞|
免费岛国片在线播放|
a级黄色大片在线观看视频男男|
中文字幕亚洲精品久久AV|
99精品国产亚洲|
国产亚洲国产精品欧美|
少妇人妻偷人精品无码视频新浪|
欧美日韩精品亚洲一区二区|
一本大道一卡二卡入口|
se97se成人亚洲网站|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
欧美乱熟人妻色情影视|
色欲天香天天影视综合|
羞羞漫画破解无线书币|
高清无码国内自拍视频|
国产强被迫伦姧在线观|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
8050午夜二级|
九九视频在线观看视频6|
精品AAAA巨乳|
日韩免费精品视频一区二区三区|
国产精品人妻无码99999|
99国产精品免费一区二区|
欧美性猛交99久久久久99按摩|
天天噜av在线观看|
中文字幕人妻熟女在线|
欧美精品久久久久久无码人妻|
国产欧美日韩专区发布|
特级A欧美做爰AAAAA片
|
在线精品视频raPPer|
色欲AV亚洲午夜精品无码|
大帝a∨无码视频在线播放 |
国产午夜高潮熟女精品AV|
久热久热aV在线青青|
成年网站免费视频网站|
国产精品女A色欲AV色欲老师|
日韩色情一区二区无码AV|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
曰本一本道a东京热播|
欧美荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
色欲AV巨乳无码一区二区|
最近中文字幕大全免费版在线|
无码影片成人网站在线观看|
色情狠久久AV五月综合五月|
亚洲AV一宅男色影视|
国产精成人品2018|
91免费精品国产拍在线|
成人看片黄a在线看|
青青青爽在线视频观看|
亚洲欧美日韩中文在线制服
|
极品吹潮视频大喷潮tv|
最近高清中文在线字幕观看|
成人在无码AV在线观看一|
国产九九精品视频免费播放4互動交流
|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
播五月开心婷婷欧美综合|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区|
丰满少妇被猛烈进入毛片|
欧美特级另类xxx|
91性爱在线视频|
久久午夜无码鲁丝片午夜精品|
日本二本道dvd视频|
久久视频这里有精品21|
天天影视网网色色欲|
国产福利酱国产一区二区|
天堂AV国产夫妇精品自在线|
少妇做爰免费理伦电影|
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
国产精品白丝AV网站|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合尤物|
91精品日韩欧美国产|
2017秋霞在线观看免费大奶子|
91精品国产高清久久久久久l|
亚洲日本精品国产第一区二区|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
97亚洲狠狠色综合久久|
免费无码婬片AAAA片直播表情|
国产中的精品AV一区二区|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站一丁|
秋霞国产日韩91视频|
欧洲精品一卡2卡三卡4卡影视|
久久人人槡人妻人人玩夜色AV|
图片区视频区小说区|
国产精品人成视频免费软件|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
久久中文字幕人妻AV熟女|
天天鲁在视频在线观看|
国产三级激情av|
最近中文字幕MV手机免费高清|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
玩50岁四川熟女A片|
日韩在线看片免费观看软件
|
免费看国产成人无码A片|
免费全部黄A片免费播放软件|
久久免费视频播放中文|
最近日本MV字幕免费观看视频|
色偷偷超碰av男人天堂|
SM情趣鞭打尿失禁强制高潮女|
好爽快点我受不了了国产|
欧美成人A片欲伦艳|
日韩美女欧美精品|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
人妻性爱午夜不卡视频|
有人有片视频吗 免费的|
91大香蕉国产一区|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片软件|
国产一级特黄高清大片多人P一信息网|
国产精品96久久久久久|
女人18毛多水多A片视频|
国产亚洲精品A片久久久|
无码潮喷A片无码高潮漫画
|
先锋影音av最新资源|
免看黄29分钟继续看|
妇搡BBBB精品一区二区|
午夜亚洲一区二区亚洲福利|
黄网站免费永久在线观看下载|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
久艹视频在线免费观看|
日韩人妻精品久久日|
同性男男黄H片在线播放网站|
7777精品伊人久久久大香|
国产看真人毛片爱做A片|
亚洲熟妇男女啪啪视频|
国产高中生三级视频|
香蕉久久国产AV一区二区|
色噜噜2017最新综合|
快播可以看的a网站|
一区二区三区内射美女|
成年美女拍拍视频免费|
国产浓毛大BBWBBW|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
亚洲男人的天堂A片我要看|
四川少妇搡BBB搡BBB爽爽爽小说|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
欧美又大又长又粗又爽A片|
香蕉尹人综合在线观看|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
2019国产精品青青草原|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站仙踪林|
免费啪视频在线看视频|
无码天堂亚洲国产AV久久|
亚洲色欲色欲综合网站|
女人另类牲交ZOZOZO|
奶真大水真多小荡货AV|
国产精品583一区二区免费看|
男生J桶进女人P又色又爽又黄
|
91视频精品在线观看 |
五月丁香综合啪啪成人小说|
内射白嫩少妇超碰|
肉浦团在线观看快播|
国产又粗又长又硬又猛A片|
亚洲久热无码av无码中文字幕|
亚洲无遮挡无码A片在线|
成人国产一区二区精品小说|
成人网站在线进入爽爽爽|
1区2区3区4区产品乱码99|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区竹菊影视
|
AV久久无码AV喷水高潮|
天堂中文www资源在线|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
陈红下面又紧又小好爽|
最近中文字幕视频完整版在线看|
国产色综合色产在线视频|
美女校花被调教出奶水|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
欧美叉叉叉BBB网站|
亚洲国产精品日本无码小说|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片男男
|
91精品一区二区精品视频|
国产精品成人A片在线果冻|
用舌头去添高潮无码AV在线观看|
天堂最新版在线中文|
粉嫩小泬WWW免费视频网站下载|
国产人妻换人妻仑乱电影
|
97高清国语自产拍久久|
亚洲一品AV片观看五月色婷婷|
87福利午夜福利视频|
粗大的内捧猛烈进出视频网|
免费无套内谢少妇毛片A片软件|
草草影院永久线路CCYY|
玖玖爱这里只有精品视频|
国产91精品人妻一区二|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
欧美日韩精品亚洲一区二区|
A欧美爰片久久毛片A片|
风韵丰满优存少妇在线观看|
91久久精品无码一区二区毛片
|
WWW成人国产高清内射|
欧美日韩综合无码中文字幕
|
最近高清中文在线国语视频|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
嫩草AV久久伊人妇女超级A|
一级a一级a爰片免费免三的APP|
国产一区日韩一区二区三区|
国产偷拍在线不卡偷拍|
亚洲无人区码一码二码三码的特点|
3atv精品不卡视频|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
WWW国产精品内射老熟女|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
男女又色又爽又爽视频|
女人爽得直叫免费视频|
精品综合日本国产|
国产欧美网站亚洲成人免费
|
无码又爽又刺激A片涩涩18禁|
色99久久久久高潮综合影院|
又黄又湿免费高清视频|
jlzzzjizzzjlzzz亚洲|
女人在厨房被添高潮全过程A片|
91超碰人妻人人人|
欧美一区二区高清|
玩50岁四川熟女A片|
国产精品A一区二区三区腾讯导航|
日韩精品AV一二三区在线|
午夜精品A片一区二区三区|
久久久久老熟女久久百度淫荡视频|
午夜人妻理论片天堂影院|
无码人妻AⅤ一区二区三区A片一|
98在线精品在线视频|
熟女丰满老熟女熟妇|
又硬又粗进去爽A片免费无码安娜|
最近免费视频中文2019完整版|
多毛熟女HDVido多毛的简介|
日本三级人妻一级二级三级|
成人午夜爽A片免费视频|
护士又紧又深又湿又爽|
欧美群伦性艳史黄94|
国产精品久久久久久爽爽爽床戏|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片WWW|
中文字幕乱码亚洲精品一区|
天天久久尤物视频综合|
乡下妇乱子伦小说|
网址在线观看你懂我意思吧免费的
|
中文在线无码高潮潮喷在线|
夫目前犯人妻av中文字幕|
好爽好紧好大的免费视频国产|
饥渴难耐的浪荡艳妇在线观看|
国产成人无码网站m3u8|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
国产中的精品AV一区二区|
人妻熟女狠狠涩蜜桃|
亚洲福利在线观看|
99国产精品久久人妻无码|
www.xxx-av.com|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
成人做爰69片免费看网站|
思思99在线视频|
美女翘臀强进入系列在线观看|
未满小14洗澡无码视频网站|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片小说|
大陆国产aⅴ国语精品对白|
国产精选 第1页-要看tv|
成人无码A片视频播放|
被男人添B超爽视频免费|
欧美群交在线播放1|
97SE亚洲精品一区|
国产成人永久免费无码观看|
国产在线精品免费AAA片|
草莓视频APP下载黄色安装|
日本五月婷婷手机在线观看|
成人性三级国产在线观看|
99爱免费视频在线看|
91精品久久久久久综合五月天|
女人与牲囗牲恔视频免费|
囯产少妇BBBBBB高潮喷水一|
久久激情成人国产|
国产成人永久免费无码观看|
麻婆豆腐传媒一区二区三区|
先锋影音源资2019|
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
国产V日产∨综合V精品视频麻豆
|
精品無碼人妻一區二區三區品|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色蜜臀v1.5|
国产50岁熟妇露脸|
夜来香AV在线观看|
亚洲一区二区三区国产|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
青青草免费线观综合网|
最新一区二区三区在线影院
|
一边添奶一边添p好爽视频|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
妞干网无缓冲这里只有精品|
97人妻熟女成人免费视频|
91无码人妻一区二区|
久久91精品国产91久|
chinese中国人自拍在线|
亚洲图片综合图区20p|
亚洲多毛妓女毛茸茸的|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
AA片在线观看视频在线播放|
不卡人妻无码AV中文系列APP
|
大香焦在线伊人74|
扒开双腿吃奶呻吟做受视频|
日本69色视频在线观看
|
在线看片免费观看视频|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
亚洲美女综合香蕉片|
欧洲熟妇大荫蒂高潮A片视频|
在线精品亚洲观看不卡欧|
最新国产专区不卡|
日韩视频一区二区有码无码|
成人A片激情免费视频|
国产sm激情首页视频在线观看|
国产熟妇高潮叫床视频播放|
亚洲精品鲁一鲁一区二区三区|
影音先锋av熟女资源网|
影音先锋av在资源天堂|
最新av网站免费在线观看|
999国产精品欧美一区二区 |
台湾四级露性器在线观看|
久久久久亚洲Av无码专区桃色|
色婷婷丁香A片区毛片区女人区|
91麻豆产精品久久久久久粉嫩|
小柔在公厕被灌满jing液|
亚洲国产精品成人久久久软件
|
日本不卡码在线网站|
又大又硬又粗做大爽A片|
欧美整片sss第一页视频|
国产对白精品刺激一区二区|
影音先锋亚洲AV少妇熟女|
精品国产乱码久久久久乱码|
在线最新无码经典无码|
在线观看日本污污ww网站|
成人国产精品影院|
久章草在线视频播放国产|
又爽又高潮的BB视频免费看|
色情免费100部A片看片|
性一交一乱一欲A片|
国产精品1区2区3区|
国产成人不卡AV在线观看|
一女被两男吃奶添下A片V|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
亚洲精品无码高潮喷水A片软|
91州精品一区二区三区|
无码性午夜视频在线观看|
亚洲精品久久久午夜福利电影网|
免费人妻无码不卡中出|
国产真实露脸乱子伦|
4484在线观看视频|
狠狠狠地在啪线香蕉|
多毛熟女HDVido多毛的简介
|
在线午夜福利视频免费|
把腿张开被添得死去活来在线|
男人使劲躁女人过程A片|
男人猛躁进女人毛片A片|
男生肌肌桶女人屁股|
小小视频在线观看www|
午夜精品久久久久久久久日韩欧美|
老太交70years性行为|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
免费无码AV片在线观看潮喷|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片软件
欧洲一卡2卡三卡4卡乱码毛1
|
区产品乱码芒果精品综合|
A片娇妻被交换粗又大又硬
|
五十路近親相姦中出し親子
|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
成人亚洲免费影视|
超碰97久久国产精品牛牛|
青青青视频免费观看2018|
成人AV网站A天堂|
少妇又色又爽又紧的A片|
麻花豆传媒剧国产MV入口|
在线午夜电影63网导航|
精品丰满人妻AV久久久|
啦啦啦中文日本免费高清百度
|
成人啪啪免费无码网站|
无码色情影片视频在线看免费
|
色狠狠色噜噜AV天堂五区|
丰满人妻熟妇乱又伦精品劲|
亚洲一区欧洲一区|
69激情露脸视频|
亚洲视频一区在线|
55大东北熟女啪啪嗷嗷叫|
岛国色情A片无码视频免费看|
不卡久久精品国产亚洲av麻豆|
精品午夜伦理一区|
久久精品视频在线直播6|
影888午夜理论不卡|
SM情趣鞭打尿失禁强制高潮女|
秘书下面太紧拔不出来怎么办
|
三人荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
精品无码国产AV一区二区|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
亚洲人成电影网站在线观看|
巜漂亮的女邻居又紧又爽三级|
91亚洲狠狠色综合久久久久久久
|
朝桐光日韩一区二区三区|
免费一级特黄3大片视频|
最近中文字幕大全免费版在线|
免费一级做a爰片久久毛片潮喷|
好久被狂躁A片视频无码免费视频|
亚洲成α∧人片在线播放无码|
女生奖励自己的声音素材高清版|
日日摸天天添天天添无码蜜臀|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
成年女人免费影院播放|
欧美成人无码A片在线视频QQ群|
国产精品一区二区三区四区五区|
yy6080午夜色情理伦片在线|
国产成人免费爽爽爽视频|
一道本av免费不卡播放|
99久久精品免费观看国产色综合|
亚洲精品gv天堂无码男同娇喘|
欧美亚洲国产小说图片图专区|
国产JK白丝喷白浆精品视频|
无人区AV在线观看|
六月丁香婷婷综合网激情网|
亚洲人成在线播放无码|
92久久精品一区二区|
老女人熟女人妻国产|
日韩高清特级特黄毛片|
自怕偷自怕亚洲精品|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说
999精品国产人妻无码梦乃爱华
|
av一本久道久久综合久久鬼色|
成人A片激情免费视频|
久久精品AV一区二区三|
国产妇少水多毛多高潮A片小说|
99精品欧美一区 |
一级一级特黄女人精品毛片视频|
影音先锋每日最新AV资源网|
综合久久一区二区三区|
男女一对一免费视频|
欧美阿v天堂视频在99线|
嫩BBB槡BBBB槡BBBB18|
性色aV一区二区天美传媒|
亚洲无码黄色片网站|
精品综合久久久久久98|
高清国产在线视频导航 |
欧美人妻精品久久久久久|
亚洲国产一卡2卡3卡4卡5公司|
亚洲AV无码乱线观看性色|
爽爽影院免费观看视频|
女人体a级1963免费|
羞羞漫画破解无线书币|
国产精品色吧国产精品
|
朋友娇妻的滋味中文字幕A片|
51久久国产露脸精品国产|
啊轻点灬大JI巴又大又粗A片|
久久视频这里只精品10|
阴部内射好爽性视频成人|
亚洲乱码一卡二卡四卡乱码新区
|
国产亚洲老牛精品视频|
99国产观看免费视频|
99久久免费只有精品国产高潮
|
久久婷婷五月综合色丁香花|
成av人电影在线观看|
国产特黄级AAAAA片免|
成人精品一區二區激情 |
欧美成人无码A区在线观看免费|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者
|
国产成人精品一区二区免费|
chinese老仑乱|
久久久精品国产AV麻豆|
插插射啊爱视频日A级|
92国产精品综合在线|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小|
92人妻国产一区二区三区|
日韩色情无码免费A片|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套
|
国产清纯美女爆白浆视频|
内谢XXXXX8老|
久久精品视频在线直播6|
免费看毛片的网址|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在|
日韩电影一区二区三区|
94久久国产乱子伦精品免费 |
55夜色66成年视频观看免费|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
天美传媒小甜豆完整视频在线观看|
中文字幕人妻熟女在线|
国产无遮挡A片无码免费软件|
国产一级片内射30岁老熟女
|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578
|
国产经典噜噜在线无码一二三区|
成人av在线播放观看|
少妇高潮呻吟A片免费看软件|
日本亚洲精品无码专区国产|
人妻免费视频公开上传|
性色AV爽歪歪啪啪A片|
麻花豆传媒剧国产入口|
男人天堂2018新在线版|
丰满大姐免费视频16MIN|
国产寡妇乱子伦一区二区三区。|
性色AV一区二区三区咪爱四虎|
亚洲自偷自偷在线制服|
国产成人精品777|
99精品热线在线观看免费视频|
99re视频在线|
荫蒂添的好舒服A片免费|
国产色综合色产在线视频|
国产一级婬小说A级|
国产AV麻豆一区二区|
亚洲一区欧洲一区|
国产十八熟妇AV成人一区
|
久久久久亚洲AV无码AV男人|
人妻丰满熟妇av无码久久洗澡|
黄污色污国产高清无码在线观看|
国产成a人亚洲精品在线观看|
成人乱码一区二区三区A片
|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
国产午夜男女爽爽爽爽爽|
国精品人妻无码一区二区三区性色|
91在线精品你懂的|
歪歪爽蜜臀AV久久精品人人槡|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色蜜臀v1.5|
黑人二十厘米进入A片|
伊人久久丁香色婷婷啪啪|
亚洲av片不卡无码久东京搔|
内射高潮享受视频在线观看|
在线观看免费av网站|
国产偷国产偷亚州清高APP|
99久久99热这里只有精品|
午夜无码影院在线|
又爽又高潮的BB视频免费看|
最新国产精品自拍不卡|
精品免费国产一区二区三区四区五
|
国产av一区二区三区精华液
|
青青草免费线观综合网|
亚洲是图 夜夜撸|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
国产偷国产偷亚州清高APP|
狠狠噜天天噜日日噜久久久电影|
久久人人爽人人爽人人片AV不|
又黄又湿免费高清视频|
国产精品美女WWW爽爽爽视频|
好吊视频一区二区三区|
日本无码国产在线婷婷直播|
波多野结衣亚洲一二三|
男人J桶进女人下部无遮挡A片|
男人都懂的www网站免费观看|
草莓视频成年人 |
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
岳的大肥屁熟妇五十路99|
欧美疯狂三P群体交乱免费视频
|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
97国产露脸精品国产麻豆|
久久久精品理论A级A片|
男女啪啪永久免费观看网站|
日韩色情无免费高清在线视频|
50岁老熟女高潮喷水|
粗大猛烈进出高潮免费视频日本|
少妇搡BBBB搡BBBB毛多多|
国产精品视频一区二区三区不卡|
YY6080午夜福利无码理论
|
又色又爽又高潮免费视频观看|
亚洲日韩国产AV无码无码精品|
国产精品日本无码久久一老A|
久久人人爽人人人爽成人AV
|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片免费|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放
|
一本加勒比HEZYO东京热高清播放|
波多野结衣AV在线观看|
丰满少妇又爽又紧又丰满在线观看|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
精品深夜AV无码一区二区老年|
久久免费看少妇高潮A片小说图片|
免费观看欧美成人AA片爱我多深|
成年妇女观看在线视频|
无套内射无矿码免费看黄|
亚洲精品伦理熟女国产一区二区|
好爽好深好猛好舒服视频上|
好大好爽快点大JI巴视频|
欧美精品久久96人妻无码|
泰国两熟女春梦邂逅猛男|
色情WWW成人片WWW222|
少妇午夜精品福利一区二区三区蜜桃
|
五月丁香国产在线视频|
老师办公室娇喘浪吟女学生漫画|
拔萝卜视频免费看高清|
欧美性A片又大又长|
欧洲老妇60一70|
国产精品人成在线观看1一|
无广告观看久久精品99久久香蕉国产全集
|
宅男宅女做a天堂|
色99久久久久高潮综合影院|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
欧美人妻无码A级视频|
日韩高清一区二区三区不卡|
成人国产精品无码一区二区三区|
四平青年之喋血曼谷免费观看完整|
久久女婷五月综合|
高潮肉欲少妇A片在线看|
vr专区自拍无码中文字幕精品|
亚洲国产精品无码乱码三区红酒|
亚洲AV久久无码精品国产网站|
99视频久九热精品|
99国产精品免费一区二区|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
国产精品系列在线一区|
免费看少妇高潮A片特黄
|
日韩一区二区三区免费视频|
糖心LOGO在线观看视频|
成年人视频网站免费|
中文字幕欧美人乱人精品A片|
成片免费观看视频大全|
日本无码MV免费视频在线|
亚洲尤码不卡AV麻豆|
成年妇女观看在线视频|
影音先锋影院中文无码|
小柔在教室伦流澡到高潮视频|
龙欲h粗喘强占公妇H|
野花视频免费观看2019|
亚洲国产精品无码乱码三区红酒|
久久99热人妻偷产国产|
免费高清在线国产视频|
梦寻桃花源免费观看|
无码免费一区二区三区日本A片|
最近的中文字幕在线MV|
欧美性狂猛AAAAAA|
成AV免费大片黄在线观看|
真实国产乱子伦对白视频37P|
人妻中文字幕av无码专区|
中文字幕丰满孑伦无码精品|
四虎影成人Av在线观看|
国产后式a一视频|
国产高清色情在线观看APP|
91丝袜白浆高潮潮喷在线观看|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
美女裸身无档视频免费|
秋霞成人国产理论A片|
亚洲AV无码乱码国产麻豆穿越|
天天影视亚洲综合网|
poronovideos人初重口|
国产清纯91天堂在线观看|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片|
成人WWW色情在线观看|
欧美牲交A欧美牲交VDO|
www.成人.com|
人妻熟女狠狠涩蜜桃|
恋夜影院支持安卓视频美女|
www.日日夜夜撸|
在线永久免费观看黄网站|
草莓视频成年人 |
亚洲AV嫩草AV极品A片|
a在线视频播放免费视频完整版|
末成年毛片在线播放|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
2022一本久道久久综合狂躁|
乌克兰女人大白屁股ASS|
老头把我添高潮了A片视频|
东北旺仔系列xvideos|
AV国産精品毛片一区二区|
屁屁影院最新地址入口|
蜜臀AV99无码精品国产专区|
特极西西444WWW大胆无码|
公交车上扒开嫩J挺进去|
动漫熟女制服一区二区 |
99精产国品一二三产品香蕉|
国产国语特级 a毛片|
91超碰人妻人人人|
色欲av亚洲情无码av蜜桃|
成人自拍网站在线观看|
欧美群交在线播放1|
精品综合日本国产|
成在人线av无码免观看麻豆|
午夜精品人妻无码一区二区三区
|
国产一级特黄a大片99|
男人猛躁进女人毛片A片|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片|
成人激情综合网影院在线观看|
亚洲天天一色综合AV|
少妇成熟A片无码专区小说
|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
91久久人澡人人添人人爽|
无码人妻久久一区二区三区免费|
色情成人影音先锋电影|
欧美又粗又大又黄A片在|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
国产吧在线视频中文字幕|
精品卡1卡二卡三卡乱码|
国产三区在线成人AV|
亚洲国产货青视觉盛宴|
亚洲天堂av一本道无码|
91亚洲狠狠色综合久久久久久久
|
91在线精品你懂的|
日韩雏女无套内射11P|
玩弄了裸睡少妇人妻野战|
五月丁香六月婷婷网线视频|
囯产精品一区二区三区线|
丰满岳跪趴高撅肥臀|
奇米影视第四色av首页|
免费高清在线国产视频|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
男生肌肌桶女人屁股|
无套内射无矿码免费看黄|
久久无码人妻一区二区三区|
搡8O老女人老妇人老熟|
五月丁香综合啪啪成人小说|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
粉嫩小又紧水又多A片|
国产精品人妻黑人借宿电影|
99精品国产综合久久麻豆|
色情成人影音先锋电影|
风韵人妻丰满熟妇老熟女|
无遮挡啪啪摇乳动态图GIF|
huan色大片电影百度影音|
蜜臀久久AV无码牛牛影视|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
亚洲无码在线观看免费|
天美传媒小甜豆免费观看|
国产成人精品不卡久久久|
天天看片视频免费观看|
拔萝卜视频免费看高清|
丰满人妻老熟妇伦人精品|
中文字幕乱码 电影在线观看|
国内自拍真实伦在线视频|
日韩无码一区二区三区四区|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
内射干少妇亚洲69XXX|
亚洲人成小说网站色|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说色噜噜|
成人免费无码特级毛片A片|
欧美黑人精品三级网站|
国产高潮A片羞羞视频涩涩|
全黄做爰100分钟视频|
丁香五月综合缴情在线观看|
极品吹潮视频大喷潮tv|
日本成人一区二区三区|
亚洲区色情区激情区小说公|
japanesevideo喷潮|
亚洲AV成人影视综合网|
秋霞成人国产理论A片|
久久久久久久999|
精品无人区一码卡二卡三|
亲胸揉胸膜下刺激视频在线观看|
香蕉久久av一区二区三区|
国产亚洲精品久久777777|
欧美又黄又粗暴免费视频|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
成人毛片100免费观看|
国产三级激情av|
成人做爰WWW免费看视频日本|
XXX波多野结衣苍井空|
a在线视频播放免费视频完整版|
很很鲁在线视频播放影院|
欧美又色又爽又黄的A片18禁|
亚洲欧美第一精品网站|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
新婚人妻不戴套国产精品
|
白丝校花被狂揉大胸羞羞动漫|
欧美成人精精品一区二区三区|
快播可以看的a网站|
2020最新国产自产精品|
免费看毛片的网址|
最新国语对白超清偷拍|
女教师杨雪的性荡生活|
人妻无码AV一区二区三区|
最新欧美精品一区二区视频|
亚洲精品中文幕一区二区|
91一区二区三区四区五区|
99精品久久久久久久久久综合|
国产爆初菊一区视频|
免费无套内谢少妇毛片A片软件|
亚洲乱码AV中文一区二区|
人妻精品久久无码专区色视蜜臀|
www成人国产在线观看网站|
五月婷婷在线人妻精品视频|
久久AV无码乱码A片无码|
中文字幕高清免费日韩视频在线
|
免费啪视频在线看视频|
亚洲精品无码苍井空A片|
国产V日产∨综合V精品视频麻豆
|
午夜熟女插插XX免费视频|
免费无码又黄又爽又刺激|
中文字字幕在线中文乱码2019|
国产乱人伦无无码视频|
婷婷四月开心色房播播|
人妻内射一区二区在线视频|
先锋影音源资2019|
无人区卡一卡二卡老狼网站|
97在线观看视频公开免费|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
色AV亚洲AV永久无码精品软件
|
偷拍自偷 亚洲 欧美20P|
欧美黑人一区二区三区免费A片
|
人插女人免费视频久久|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
亚洲欧美国产高清|
亚洲成年人免费网站|
日本老头4569gay|
有人有片视频吗 免费的|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产丝袜|
日韩MV欧美MV中文无码|
男人和女人香蕉网线看|
丰满人妻老熟妇伦人精品|
国产又黄又猛又粗又爽的A片漫|
美国一级大黄一区免费无码|
8x8国产人妻精品一区二区|
无人区AV在线观看|
久久视频在线视频观看 99|
91日韩精品在线观看|
欧美性猛交XXXXX拉换交大3|
成 人影片 免费观看10分钟|
成人国产精品久久久久久亚洲|
人妻AV无码一区二区三区蜜臀|
亚洲精品国产国语|
欧美激情一区二区三区四区|
国产色综合色产在线视频|
asian极品呦女xx农村|
影音先锋av网站大全|
在线观看高清黄网站免费|
国产又色又爽又刺激的A片|
天黑黑影院免费观看视频在线播放|
成人免费激情毛片|
女人另类牲交ZOZOZO|
成人三级理论电影|
亚洲国产精品一区二区第一页|
成A人亚洲精V品无码樱花国产|
真人女人无遮挡内谢免费视频%|
亚洲中文字幕熟女久久
|
激情自拍另类亚洲|
视频一区国产第一页|
午夜夫妻试看120国产|
欧美日韩综合无码中文字幕|
少妇又大又粗又硬啪啪|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
91桃色污无限免费看|
国产真实乱子伦清晰对白|
久久久精品国产SM调教网站|
免费又黄又爽又色的绿巨人|
17c人妻无码一区二区三区|
激情综合成人五月天|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
国产精品久久久AV色欲A|
久久99AV无色码人妻蜜|
国产精品久久人妻互换毛片|
欧美一级黃色A片免费看蜜桃|
99操在线观看国产视频|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
国产成+人欧美+综合在线观看|
欧美ideosgratis暴力|
亚洲中文字幕在线观看|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
2020美女视频黄频大全视频|
成人黄色国产视频|
大陆极品少妇内射AAAAA|
影音先锋资源av天堂|
国产无遮挡又黄又爽又色又刺激|
一本道免费高清视频ccd|
y1111111丰满少妇毛片|
小柔跪趴撅着给人玩弄H视频|
拍在线2018国产爽在|
色偷拍亚洲国产大姐|
日本一卡2卡三卡4卡无卡免费网站|
www.日韩av.com|
不卡在线播放一区|
国内精品视频在线播放一区|
日韩人体做爰大胆337P|
亚洲AV无码乱线观看性色|
高中女学生破苞视频免费
|
一面亲上边一面膜带揉胸|
精品人妻一区二区A片|
好大好爽快点大JI巴视频
|
成人无码免费A片免费看软件|
色偷拍亚洲国产大姐|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
国产厨房一区二区三区
|
麻豆星空精东天美MV第一页|
亚洲AV无码一区二区A片成人|
免费永久在线观看黄网站|
中文字幕欧美一区|
亚洲A片无码秘色多多|
成人无码www免费视频欧美|
男生J桶进女人P又色又爽又黄
|
8x8x福利在钱视频|
国产一区二区三区四区精品AV|
av三级国产a级水|
色情.WWW成人天堂|
办公室的超薄丝袜人妻献身 |
久久精品久久精品久久精品|
国产成人精品不卡久久久|
亚洲成α∧人片在线播放无码|
亚洲人美女肛交真人全程|
草莓视频中文字幕|
国产人成视频在线观看|
999国产精品欧美一区二区 |
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
999在线免费视频|
欧美全黄a一级一区二区三区视频
欧美日韩国产精选福利片
|
99久久精品免费国产一区二区三区
|
在线观看黄A片免费AV软件|
y1111111丰满少妇毛片|
中文字幕欧美人乱人精品A片|
亚洲成年人免费网站|
成人无码www免费视频欧美|
亚洲乱码AV中文一区二区|
小SAO货张开腿CAO死你A片|
亚洲国产精品一区二区三区在线观看|
HEZYO加勒比久久爱综合|
2017男人天堂手机在线|
国产精品aⅴ久久久久久鸭绿欲
|
日日躁夜夜躁夜夜揉人人视频|
亚洲99精品A片久久久久久|
av免费无码专区|
国产综合久久久777777|
最近最好的中文字幕2019免费|
免费黄色录像一集AV一集片|
欧美日韩精品一区二区三区不卡|
国产中文字字幕乱码无限|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
丁香花视频资源在线观看|
99爱免费视频在线看|
男人天堂2018在线观看97|
国色天香精品卡一卡二卡三二百|
丰满成熟少妇A级毛片|
色狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片55|
美女翘臀强进入系列在线观看|
国产又色又粗又黄又爽免费|
人妻激情偷乱一区二区三区|
国产真实交换配乱婬98视频|
亚洲久悠悠色悠在线播放|
欧美特级特黄a大片免费|
午夜色情A片成人免费视频下载|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在线观看|
欧美激情一区二区三区不卡|
色噜噜狠狠一区二区三区|
又硬又粗进去好爽A片春色视频|
欧美肉动漫一区二区三区无码|
国产强被迫伦姧在线观|
最好免费观看高清视频直播小说|
亚洲精品伦理熟女国产一区二区|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
777片理伦片在线观看|
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
国产免费进入一区二区|
中文字幕一区二区三区视|
色情成人免费视频激情在线观看|
99久久精品免费观看国产色综合|
网站情侣色情网网站|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
日韩免费视频一区|
好看的国产精彩视频|
果冻传媒国产仙踪林|
成年人午夜激情黄色视频|
国产熟女真实乱精品视频|
av综合网男人的天堂|
黄片长版看嘛 直播片|
特黄做愛又硬又大A片视频|
无码人妻欧美丰满熟妇区毛片|
亚洲成AV人片一区二区梦乃|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
日韓最新视頻一區二區三|
多人做人爱免费视频试看|
AV久久无码AV喷水高潮|
欧美一道本一区二区三区|
又大又硬又粗做大爽A片|
爆乳JK美女脱内衣裸体网站
|
久久婷婷五月综合色精品|
少妇内射高潮福利炮|
嫩BBB搡BBBB榛BBBB|
免费无码AV色情在线|
亚洲精品无码苍井空A片|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片88|
美女内射毛片在线看|
亚洲国产熟妇无码日韩|
国产成人av免费手机麻豆 |
国产91对白刺激露脸在线观看|
亚洲欧美一区二区三区久久|
久久人人做人人妻人人玩精品AV|
91桃色污无限免费看|
师尊胯羞坐抬臀抖吟迎合视频|
成人免费又大又爽A片视频|
亚洲不卡在线观看|
2019最新国产不卡a国内2018|
天天做天天躁天天躁|
男人天堂网2018最新地址|
国产精品VA无码区二区|
亚洲一区在线电影|
2022一本久道久久综合狂躁
|
精品国语自产拍在线观看|
国产精品丝袜一区二区|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
欧美成人无码A区在线观看免费|
欧美无人区码卡二卡3卡4|
日本亚洲精品无码专区国产|
国语对白农村老太婆BBw|
无码影片成人网站在线观看|
最新av网站免费在线观看
|
午夜精品成人一区二区视频|
一区二区三区免费版在线|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
麻豆精品一区二区综合AV|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
综合久久一区二区三区|
亚洲 暴爽 AV人人爽日日碰|
农村嫖妓一区二区三区|
亚洲AV无码一区二区A片成人|
国产精品久久久久久久AV大片|
免费一级做a爰片久久毛片潮喷|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
亚洲精品美女av在线|
大香伊在人线国产中国|
性一交一乱一美A片69|
男女又黄又刺激B片免费网站|
日本一本道2018无号码|
AV8888AV色情观看在线|
欧美一级黃色A片免费看蜜桃|
91在线精品你懂的|
国产女13黄A片AAA片视频|
不卡久久精品国产亚洲av麻豆|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套|
亚洲精品美女av在线|
国产精选 第1页-要看tv|
精品一卡二卡三卡四卡网站|
精品国产乱码久久久久久下载|
2015影音先锋色撸撸|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
欧美日韩精品一区二区三区高清视频
|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫
|
色婷婷激婷婷深爱五月小蛇|
青娱乐国产视频在线分类|
欧洲亚洲精品A片久久99果冻
|
99麻豆久久久国产精品免费|
AV免费网站在线观看
|
成人黄色小视频在线观看|
狠狠色老熟妇老熟女|
乱伦小说与照片电影一区二区三区|
色情无码永久免费网站APP|
亚洲一区美女视频|
欧美AAAA级A片又粗又硬|
免费A级毛片黄A片高清在线播放
|
日韩高清特级特黄毛片|
69无人区乱码一二三四区别|
9久热这里只有国产中文精品国产|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在线观看|
av三级国产a级水|
精品日韩一卡2卡三卡4卡乱码
|
窝窝午夜看片http|
国产熟妇久久精品亚洲熟女图片|
欧洲精品无码一区二区三区的视频空间|
人人妻人人澡人人爽人人老司机|
成人免费大片黄在线观下载|
很很鲁在线视频播放影院|
欧美整片sss第一页视频|
国产精品人妻无码免费久久久|
亚洲精品国偷拍电影自产在线|
精品久久久久久久无码伊人
|
男女狂进狂出动态图GIF|
不卡精品国产夜色|
国产国语高清在线视频二区|
亚洲国产欧美日本视频|
亚洲图色中文字幕|
国产1988精品A片|
欲妇荡岳丰满少妇A片|
91精品福利尤物|
亚洲福利在线观看|
亚洲欧美日韩国产精品一区二区|
国产啪精品视频免费制服丝袜
|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
国产又色又爽又刺激的A片|
a国产在线v的不卡视频视频免费 |
99久久精品免费看国产免费粉嫩|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站仙踪林|
99精品免费在线视频|
无码潮喷A片无码高潮软件|
国产高清色情在线观看APP|
荫蒂添的好舒服A片免费|
狠狠噜天天噜日日噜久久久电影
|
中文日韩欧美亚洲|
中文人妻熟女波多野结衣|
日韩A片中文字幕视频免费|
欧美阿v天堂视频在99线|
乳荡麻麻肉欲500合集|
国产精品高潮呻吟AV久久床戏
|
成人精品视频99在线观看免费|
丁香啪啪综合成人亚洲|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
国产精品大陆在线观看|
奴色虐aV一区二区三区|
久久伊人久久大香线蕉一区|
亚洲最大成人综合网720P|
成av人电影在线观看|
国产成人精品综合久久久久
|
欧美一级特黄aaaaaa在线看首页|
亚洲无码视频免费观看|
国产精品久久久久国产A级|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
巨爆乳肉感一区二区三区视频|
精品日产1区2卡三卡麻豆|
三上悠亚网站在线观看一区二区|
18国产成人在线|
欧美亚洲国产精品久久第一页|
美女禁止的网站免费|
欧美顶级又粗又大又黑A片黑寡妇
欧美性色欧美性A片色欲
|
最新欧美精品一区二区视频|
国产做A爱片久久毛片A片小说|
亚洲AV无码国产精品色字幕综合|
国产十八熟妇AV成人一区|
未满小14洗澡无码视频网站|
中文字幕精品无码一区二区|
久久精品视频在线直播6
|
一本色道88久久亚洲精品|
日日摸天天添天天添无码蜜臀|
se97se成人亚洲网站|
201一本道在线在线观看|
成人免费视频caoporn|
亚洲夜夜夜无代码|
一区二区三区在线视频观看|
91精品一区二区三区无码吞精|
入室强伦轩人妻HD|
中文无码妇乱子伦视频国产精品亚洲LV粉色
|
同性男男黄H片在线播放网站|
国产亚洲欧洲人人网|
成 人 黄 色 视 频网址大全|
国产女人乱人伦精品一区二区|
变态Sm天堂无码专区|
香蕉AV777XXX色综合一区|
爱爱好爽好大好紧视频|
2019四虎最新地址免费观看
|
成年人视频网站免费|
两老头把我添高潮了A片苏晴|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片漫画|
狼狼躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
婷婷五月色综合人妻|
黄色小网站在线观看|
久久久久亚洲Av无码专区桃色|
国语对白白浆69XX|
国产精品无码人妻在线|
免费无码AV片在线观看潮喷|
最近免费视频中文2019完整版|
骚片AV蜜桃精品一区|
美女老黄一区二区|
久亚洲AV无码专区A片|
搡女人真爽免费视频大全|
国产无遮挡又黄又爽又色又刺激|
在线观看日韩一区二区视频|
国产乱码一卡一卡2卡三卡四|
成人特级裸体AAA毛片 |
女人十八毛片水真多啊|
丁香啪啪综合成人亚洲|
国产精品久久丫毛片A片软件|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
来啊mm影院亚洲mm影院|
九九九免费观看视频|
人妻性奴波多野结衣无码|
清纯漂亮小美女准备啪啪|
乌克兰美女18xxoo在线|
99国精产品一区二区三区A片|
免费无码婬片AAAA片直播表情|
亚洲精品AV一区午夜福利|
欧美产品与亚洲日韩视频|
精品国产人妻国语|
国产午夜男女爽爽爽爽爽|
国产色欲婬乱视频网站免费
|
国产xxxxxx久色视频在|
欧美精品色婷婷五月综合|
成人av网址一区二区|
欧美一区二区三区不卡免费|
国产做爰又粗又大免费看|
最近韩国日本MV免费观看免费|
美女翘臀强进入系列在线观看|
亚洲国产精品无码乱码三区红酒|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
很黄很黄地在床视频女|
粗大的内捧猛烈进出视频网|
91九色熟女欧美日韩欧美
|
国产又爽又黄又不遮挡视频|
女人一级A片免费播放|
97无码欧美熟妇人妻蜜桃天美|
亚洲综合AV色婷婷五月蜜臀|
国产无码在线观看黄色|
影音先锋2018av网址|
国内偷拍亚洲欧洲2018|
亚洲成人视频一区二区|
77成年轻人电影网网站|
国产又色又爽又黄的|
10周岁女全身裸无遮挡网站|
免费人做人爱的视频完整|
国产精品583一区二区免费看|
中文字幕日韩一区二区不卡|
J8又粗又硬又大又爽又长A片|
成人免费网站又大又黄又粗
|
欲妇荡岳丰满少妇A片24小时|
天美传媒小甜豆完整视频在线观看
|
亚欧成人毛片一区二区三区四区|
日产一区日产2区日产三区|
国产又粗又猛又爽在线视频|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
蜜臀AV色欲A片无码一区|
欧美特级另类xxx|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
亚洲精品国产一区二区三|
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
国产又粗又长又硬又猛A片|
亚洲一区在线电影|
成 人 黄 色 视 频网址大全|
国产 亚洲 综合 在线观看|
女人爽到高潮潮喷叫床69|
国产婬A片999片免费网站|
影音先锋中文无码一区|
91精品一区二区三区无码吞精|
熟妇人妻系列AV无码一区二区|
五月色播先锋在线丁香|
91性爱在线视频|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
琪琪电影午夜理论片YY6080|
泰国两熟女春梦邂逅猛男|
18禁止进入黄大全在线|
苍井空激烈的120|
男人用嘴添女人免费视频A片|
18勿入网站免费永久|
久久久久亚洲AV无码专区首护士|
99精品视频久久精品|
五月色丁香婷婷网蜜臀AV|
97精品国产高清在线看入口|
在线午夜福利视频免费|
猫咪av最新永久网址无码|
丝袜脚夹住上下摩擦榨精|
日本爽爽爽爽爽爽在线观看免
|
蜜臀色欲AV无人A片一区|
成人小视频在线观看 |
91AV在线视频网址|
日韩一区二区三区无码影院
|
老湿地在线观看一区二区三区
|
欧美黑人一区二区三区免费A片
|
国产免费进入一区二区|
99在线观视频免费观看|
亚洲一区二区三区电影在线|
欧美亚洲综合在线|
欧美乱大交AAAA片IF|
亚洲AV无码男男A片在线观看|
日本一本道2018无号码|
边啃奶头边躁狠狠躁AV|
超久久人人爱免费|
波多野结衣亚洲一二三
|
色YEYE网址在线观看|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
日韩一级无码中文字幕|
试看免看一级a一片|
午夜dj在线观看免费完整高清神马|
影音先锋2017av资源|
嗯灬啊灬把腿张开灬A片MBA
|
小14萝视频裸体视频|
欧美又大又长又粗又爽A片|
偷拍自偷 亚洲 欧美20P|
亚洲精品无码色情AV在线观看|
四虎成人午夜影视亚州精品|
中文字幕日韩精品有码视频|
国产福利视频一区二区|
A片爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽|
欧美一区二区三区成人A片|
欧美荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
日本爽爽爽爽爽爽免费视频|
免费网站观看av片|
成全影视在线观看国语|
欧美激情一级精品国产|
成人av在线播放观看|
国产内射大片99|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
亚洲精品一区二区成人|
影音先锋秋霞在线影院|
国产乱对白刺激视频|
欧美又黄又粗暴免费视频|
少妇高潮毛片色欲AVA片|
亚洲色噜噜狠狠站欲八|
成人精品视频99在线观看免费|
玩弄丰满奶水的女邻居|
性色AV爽歪歪啪啪A片|
先锋影音avt天堂影院|
亚洲AV又黄又爽超级A片软件|
午夜精品久久久内射近拍高清|
国产乱码免费卡1卡二卡3卡四卡|
边摸边吃奶边做爽视频免费|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
爱咲れいら无码一区二区|
10000拍拍18勿入免费看动漫|
男人的天堂在线无码高清|
777片理伦片在线观看|
欧美疯狂三P群体交乱免费视频|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
圆产精品久久久久久久久久久新郎|
50岁老熟女高潮喷水|
无码中文字幕热热久久|
91国产自产精品a|
国产乱妇无码大黄AA片|
日韩中文字幕资源站|
最近中文字幕免费MV视频|
性一交一乱一美A片图片|
欧美日韩不卡一区视频在现|
免费啪视频在线观看视频日本|
亚洲欧洲日本无在线码播放|
精品AAAA巨乳|
中国字字幕在线播放2019
|
宝贝你真湿真紧好爽h视频男男|
一本到在线高清观看|
成人乱码一区二区三区AV66|
免费人成网站在线高清|
五十六十老熟妇激情A片|
护士又紧又深又湿又爽|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套
|
亚洲日韩AV在线中日综合|
欧美无人区码卡二卡3卡4|
精品国产卡一卡2卡3卡|
国产真实乱子伦清晰对白|
亚洲成AV人片一区二区梦乃|
百度国产精品网友自拍|
亚洲av免费分钟观看|
92久久精品一区二区|
疯狂少妇2做爰中文字幕|
精品无码久久久久久国产牛牛影视
|
男女作爱在线观看免费网站|
粉嫩无套白浆第一次jk|
日产一线二线三线哺乳|
狂野猛交ⅩXXX吃奶免费视频|
国产又硬又粗进去好爽A片软件|
av黄在线观免费网站|
国产成人精品综合久久久久|
精品丰满人妻AV久久久|
91一级特黄大片 |
日产乱码一二三区别免费麻豆|
亚洲精品日韩一区二区电影|
91精品久久人人妻人人爽人人|
黑寡妇巨大粗爽毛片欧美|
影音先锋影院中文无码|
美女禁止的网站免费|
强硬进入岳A片69视频|
一区二区三区内射美女|
国产成人亚洲欧美一级在线|
免费番肉动漫在线观看|
人妻含泪让粗大挺进|
国产裸体精品免费观看|
色狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片55|
色综合久久88色综合天天6|
99精品国产福久|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片小说天美|
www.黄色免费网站|
91极品女神私人尤物在线播放|
影音先锋2017av资源|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠|
大片国产片日本观看免费视频|
午夜无码片在线观看影院|
欧洲内射XXX高清|
真人真实做爰30分钟试看|
国产精品久久久久久爽爽爽床戏|
男人天堂影院WWW94|
國產午夜亞洲精品一區二區|
A片免费观看一区二区三区|
欧美产品与亚洲日韩视频|
蜜月a 免费一区二区三区|
亚洲欧洲日韩极速播放|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
无码精品AV久久久奶水|
18精品久久久无码午夜福利 |
一本av高清一区二区三区|
狼狼躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
亚洲国产aⅴ精品无码|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合|
国产内射大片99|
成人A片产无码免费视频奶头鸭度
一女被两男吃奶添下A片V图
|
国产成人av在线影院 |
播五月开心婷婷欧美综合|
中文字幕人成乱码熟女免费69|
中国字字幕在线播放2019|
日本无码国产在线婷婷直播|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
欧美搡BBBBB摔BBBBB|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
18勿入网站免费永久|
欧美大码毛片在线播放|
菠萝菠萝蜜菠萝菠萝蜜7麻豆|
av最新一级网站在线观看|
免费A片看黄网站WWW下载|
国产成人精品电影不卡|
久久99AV无色码人妻蜜|
成人国产精品影院|
女人被添荫蒂舒服了A片小说|
全黄做爰100分钟视频|
香蕉在线精品视频在线|
95无码人妻精品一区二区三区|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
欧美乱大交AAAA片IF|
中文字幕日韩人妻|
巨胸美女狂喷奶水www网麻豆|
成本人h视频动漫免费 |
污污免费看锕锕锕锕锕锕锕|
久久精品视频久久精品视频|
韩国乱码卡一卡二卡新区网站|
国产女人毛多水多A片视频|
在线精品亚洲观看不卡欧|
影音先锋资源站玖玖网|
精品亚洲国产熟女福利自在线|
最近更新中文字幕完整版视频|
一边添奶一边添p好爽视频|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片免费|
第四色播日韩AV第一页|
精品亚洲中文字幕|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
高潮潮喷无码一区二区三区|
国产亚洲精久久久久久无码妖精|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
18禁外国精品久久久久久|
黄网站免费永久在线观看下载
|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片|
日韩精品久久久肉伦网站|
午夜夫妻试看120国产|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
91在线欧美日韩精品|
91热久久免费频精品99欧美|
成年美女黄网站色大免费视频|
黄片大全免费在线观看|
性啪啪chinese东北女人|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频|
国产精品无码免费在线|
免费全部黄A片免费播放|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类|
亚洲成年人免费网站|
超碰97成人在线|
免费99精品国产人妻自在线|
动漫AV纯肉无码AV电影网|
99精品人妻无码专区在线视频区
|
青草亚洲国产欧美一区二区|
女人荫蒂被添舒服的A片|
久久爽AV亚洲精品天堂|
蜜桃在线码无精品秘入口九色|
先锋影音伦理在线|
欲香欲色天天综合和网|
少妇大叫又粗又大太爽A片|
欧美性猛交aa一级|
好男人WWW神马社区在线观看|
三人交videosdesexoe|
99亚洲精品成人|
影音先锋av999资源站|
越南女子杂交内射BBWBBW|
最近中文2019字幕第二页|
成年女人色费视频播放|
欧美熟妇另类久久久久久多毛
|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片漫画|
日本不卡视频一区二区|
久爱成欢视频在线观看|
国产色婷婷亚洲999精品小说|
男人猛躁进女人的毛片A片|
朋友娇妻的滋味中文字幕A片|
黑人巨大40cm重口|
91亚洲最新精品|
2014av天堂影音先锋|
国产精品高潮呻吟AV久久床戏|
免费人成网站在线高清|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在线古代|
最新影片日本巨波霸乳影院|
在线看欧洲一卡二卡三卡残暴|
国产成人综合亚洲A片激情文学|
高中女学生破苞视频免费|
久久伊人久久大香线蕉一区|
两男一女一床一添一摸|
日韩成人伦理在线|
国产又粗又爽又猛的视频A片|
91无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
摸BBB揉BBB揉BBB视频|
国产美女做爰A片免费|
未满十八岁勿入网站WWW|
国产成人永久免费无码观看|
五月丁香六月婷婷网线视频|
日本69色视频在线观看
|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片
|
www成人国产在线观看网站|
久久激情成人国产|
那种视频在线观看亚洲|
巨大乳女人做爰视频在线|
大叫受不了了好爽国产在线|
99精品免费在线视频|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
大量国内自拍AV手机观看|
一级黄色视频在线观看|
日本A一片中国A一片|
999久久久国产综合精品|
久久精品国产99国产精2019|
丝袜熟女脚交足在线一区|
成人a级特黄毛片|
午夜精品久久久久久久99老熟妇
|
国产91精品人妻一区二|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578|
惠民福利亚洲AV无码一区二区乱子仑|
丰满成熟少妇A级毛片|
成人性生交A片免费直播APP|
好吊视频一区二区三区|
免费啪视频在线观看视频日本|
一区二区三区内射美女|
8X亚洲视频久久综合一区|
久久精品视频在线直播6|
91久久综合精品国产丝袜长腿|
97任你碰任你摸任你爽|
a级黄色大片在线观看视频男男|
91麻豆产精品久久久久久粉嫩
|
永久无码日韩A片免费看麻豆精品|
久久精品国产亚洲AV高清色三区|
乱码中字芒果视频一二三多人|
一区二区三区四区国产精品|
窝窝午夜看片http|
欧美日韩一区二区在线视频|
天堂最新版在线中文|
日产一区日产2区日产三区|
91综合国产精品视频|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
精品AV一区二区三区久久|
日本免费一二三区中文|
欧美视频 偷窥自拍视频|
亚洲精品中文字幕制|
A片又大又粗又爽免费视频|
色情美女激情喷水AV|
免费岛国片在线播放|
欧美肉动漫一区二区三区无码|
国产美女高潮福利|
欧美疯狂三P群体交乱免费视频|
污污内射久久一区二区欧美日韩|
办公室制服丝祙在线播放|
国语对白白浆69XX|
91av视频免费在线观看|
丝袜脚夹住上下摩擦榨精|
在线最新av免费费观看|
国产又爽又粗又猛的视频A片|
欧美激情一级精品国产|
四川美女BBBB爽爽毛片|
嫩草国产露脸精品国产软件|
99久酒店在线精品2019|
歪歪爽蜜臀AV久久精品人人槡|
国产成人免费精品|
中文字幕暖暖永久在线视频|
中文无码1234区|
国内高清在线观看视频|
懂色Av一区二区三区四区在线播放|
国产国语高清在线视频二区|
草草影院永久线路CCYY|
欧美乱妇欲仙欲死视频免费|
18禁美女久久久久久久|
国产JK白丝AV在线播放|
欧美日韩一级特大黄片|
精品亚洲综合射精|
色偷偷超碰av男人天堂|
日本久久久WWW成人免费毛片丨|
国产美女无遮挡裸体毛片A片|
操老熟女熟妇免费视频|
欧美内射深喉中文字幕|
国产在线观看不卡|
欲妇荡岳丰满少妇A片|
sao虎影院桃红视频在线观看|
中文字幕无码色情网|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
Xx肥妇精品久久久久久久久
|
国产5x社区在线视频|
最近中文2019字幕第二页
|
国产在线精品免费91|
a级男女性高爱潮高清试看|
又粗又硬整进去好爽视频|
国产精品人妻黑人借宿电影
|
先锋影音伦理在线|
色吊丝永久性观看网站|
玩弄秘书的奶又大又软A片视频|
日产黄片中文字幕|
av网站不卡免费在线|
久久综合老色鬼网站|
免费人妻无码不卡中出|
一个人www在线观看免费中文
|
国产女人夜夜春夜夜爽免费看|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578|
新国产美女精品一区二区|
男女做爰猛烈啪啪吃奶动A|
真人做爰视频在40分钟左右|
91精品福利尤物|
妇乱子伦精品小说网|
成人做爰A片免费看黄冈|
色欲AV亚洲午夜精品无码|
国产大尺度吃奶无遮无挡|
黄网站免费线观看免费|
日韩一卡二卡 3卡四卡乱码|
国产1988精品A片|
亚洲精品国产一区二区三
|
被粗大jib捣出了白浆H|
欧美男男gv免费网站观看|
欧美h版在线观看|
BBW.妇女被内射|
99国产精品国产热久久|
国产一区二区三区在线观看网|
99精品人妻无码专区在线视频区
|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
欧美 亚洲 另类 综合网|
最新2021中文字幕无码|
久久成人麻豆午夜电影|
麻豆色情少妇传媒AV一|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片漫
|
最近中文字幕MV免费高清下载|
小骚妇下面水多要插视频|
极品JK小仙女自慰喷水牛牛影视|
国产网友自拍在线视频|
毛片内射久久久一区|
玩弄丰满少妇高潮A片91|
国内自拍真实伦在线视频|
9久热这里只有国产中文精品国产|
91性爱在线视频|
国产露脸A片国语露对白|
高潮A片揉搓乳尖乱颤视频
|
亚洲国产成在线网站91|
黄网站在线观看高清免费|
啊轻点灬公大JI巴又大又
|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片男男|
欧美搡BBBBB摔BBBBB|
国产毛片又爽又大A片|
亚洲精品AV无码喷奶水糖心|
国产高潮抽搐在线观看|
蜜桃人妻无码AV天堂三区|
色噜噜噜一区二区三区|
欧美精品一区二区蜜臀亚洲|
婷婷六月激情综合一区|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合|
日韩精品成人大片|
白天躁晚上躁天天躁21|
亚洲合成久久久久久久综合|
欧美日韩午夜群交多人轮换|
柠檬蜜桃导航500|
无码137片内射在线影院|
国产乱码日产精品BD|
欧美囗交口爆吞精在线视频|
国产精品一区二区三区四区五区|
国产精品AV一区二区三区不卡蜜|
92看看福利午夜影院|
亚洲AV色情成人www|
熟女丰满老熟女熟妇|
美女丝袜一区二区三区|
黄瓜香蕉草莓18岁可以做吗|
国产一国产一本到免费
|
越南女子杂交内射BBWBBW|
99久久国产露脸国语对白|
久在线视频reer6|
国产精品AV国片偷人妻麻豆|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
欧美肥胖裸熟妇的毛发布|
在线视频免费观看爽爽爽|
国产麻豆剧果冻传媒视频免费
|
免费看美女被靠的网站|
乌克兰美女18xxoo在线|
四十如虎的丰满熟妇啪啪|
成人av网址一区二区|
A片粗大的内捧猛烈进出AVV|
秘书下面太紧拔不出来怎么办|
成人h动漫精品一区二区无码|
最近的2019中文字幕在线|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
亚洲午夜无码毛片AV久久京东热|
99视频这里只有精品国产|
国产免费进入一区二区|
快插我BB好爽舔我视频|
色婷婷AV一区二区三区之红樱桃|
精品午夜伦理一区|
精品国产污网站直接看|
94久久精品午夜|
国产精品污www在线观看|
爽灬好舒服灬别拔出来视频人
|
偷拍自偷 亚洲 欧美20P|
蜜桃BBB蜜桃BBB蜜桃BBB|
真人女性生图片高清黑毛|
欧美激情内射喷水高潮|
色欲天香天天影视综合|
美女被免费网站在线视频app|
未满小14洗澡无码视频网站
|
91大片网站大全|
aV影音先锋毛片子|
国产三级精品三级在线观看|
添女人荫蒂全部过程AV|
日本老妇一级特黄aa大片|
懂色av浪潮av色欲av熟妇|
欧美日韩亚洲综合视频|
欧美产品与亚洲日韩视频|
永久免费看MV网站入口亚洲|
在线视频网站www色|
亚州AV无码乱码色情|
日本无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
丰满熟妇人妻中文字幕|
内射老妇女BBWXOCLOCK|
风间一区二区无码有码|
狂躁女人屁眼爽出白浆的视频网站
|
美女胸18以下禁止看禁网站|
精品无人乱码一区二区三区无限看|
成av人电影在线观看|
4399少妇做受免费A片|
AA片在线观看视频在线播放|
亚洲.欧美.中文字幕在线观看|
成年女人色费视频播放|
亚洲 自拍色综合图区|
亚洲精品久久久久AV无码|
亚洲国产午夜精品理论片|
国产看真人毛片爱做A片|
99视频久九热精品|
久久精品视频久久精品视频|
国产一国产一本到免费|
色影音先锋av资源网|
国产精品污www在线观看
|
狂处让老二爽18p|
青春热久免费精品视频|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
欧美又粗又大又黄A片|
蜜桃视频在线观看网站|
91日韩中文字幕在线观看|
男女做爰猛烈吃奶摸大胸|
特极西西444WWW大胆无码|
а∨天堂在线中文免费不卡|
无敌神马影院视频观看高清免费|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片俺去也|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
性生生活大片又黄又|
小发廊妓女很紧在线播放|
午夜性做爰A片免费看
|
5个男人躁我一个爽免费视频|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
亚洲jizzjizz中国妇女|
久久婷婷五月综合色丁香|
国产狂喷水潮免费网站www|
亚洲A片成人无码久久精品|
国产V日产∨综合V精品视频麻豆
|
91Porn偷拍熟女在线观看|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产丝袜|
国产精品久人妻精品|
九九99热久久精品在线6|
日本A一片中国A一片|
2019四虎影视最新在线|
大地影院_日本骚妇|
青青草在免费线观曰本|
老女人与小伙子露脸对白|
妇搡BBBB精品一区二区|
国产色情精品一区二区唱戏|
国产乱码卡1卡二卡3卡4卡5|
亚洲图色中文字幕|
中文日韩欧美亚洲|
男人和女人香蕉网线看|
色噜噜2017最新综合|
亚洲va999成人A片在线观看|
天黑黑影院免费观看视频在线播放|
风间一区二区无码有码|
草草影院地址发布页ccyycom|
老熟女肥臀AV老熟女A片|
国产精品色哟哟网站高清|
亚洲精品无码A片一区二区三区|
黄片长版看嘛 直播片|
99精品成人无码A片观看金桔|
一区二区三区在线播放|
无码国产成人777爽死|
亚洲日韩在线中文字幕|
91精品最新国产在线播放|
免费岛国片在线播放|
欧洲精品卡1区2卡三卡四卡|
久久综合色一综合色88|
无码国产成人777爽死|
啊轻点内射在线视频|
亚洲阿v天堂无码在线|
欧美阿v天堂视频在99线|
日本妇人成熟免费中文字幕|
亚洲1卡2卡三卡4卡2021|
国产精品583一区二区免费看|
2019看片w网址|
中文天堂网WWW新版资源在线|
日韩一级无码中文字幕|
国产又大又粗高清观看视频
|
亚洲成 人图片综合网|
亚洲午夜无码毛片AV久久京东热|
嫩BBB搡BBBB榛BBBB|
少妇夹得好紧太爽了A片|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
2018天天拍拍天天爽视频|
扒开腿CAO烂你小SAO货杨爽|
日本精品无码特级毛片|
成片免费观看视频大全|
一区二区三区免费看A片|
男人天堂网2018最新地址|
成人性三级国产在线观看|
四虎永久地址WWW成人无痕|
最新一区二区三区在线影院
|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
男女在线观看啪网站|
亚洲 另类 小说 国产精品|
国产丰满大乳大屁股A片图片|
最近高清中文在线国语视频|
国产精品人妻午夜福利|
国产综合av一区|
人妻中文字幕av无码专区|
精品国产午夜福利在线观看|
亚洲人大战欧洲人A片|
欧美囗交荫蒂互慰|
A片扒开双腿猛进入免费观|
成A人亚洲精V品无码樱花国产|
日韩?V片无码一区二区不卡|
日韩高清特级特黄毛片|
国产a级黄色毛片|
国产乱码日产精品BD|
精品三级无码国产在线观看|
狠狠噜天天噜日日噜久久久电影
|
国精品产露脸偷拍视频|
免费国产美女爽到喷出水来视频
|
99久久人妻无码精品系列性欧美|
久久偷看各类WC女厕嘘嘘偷窃|
国产熟女精品高清在线|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片
|
四十如虎的丰满熟妇啪啪|
女人高潮抽搐潮喷WWW|
日本无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
肥熟女视频一区二区三区国|
羞羞影院午夜男女爽爽影院网站|
在线看无码的免费网站|
huangseajipian|
国产日韩精品SUV|
黄网站色视频大全免费观看|
一区二区三区内射美女|
少妇一级婬片免费放狠狠干狠狠躁
|
性饥渴姓交HDSEX|
国产熟妇高潮叫床视频播放|
亚洲熟妇男女啪啪视频|
久久网正在播中文字幕|
最近日本字幕MV免费观看在线|
欧美荫蒂添的好舒服A片|
国产黄片精品无码在线观看|
日韩精品情欲蜜桃视频JK|
男人猛躁进女人的毛片A片|
欧美国产在线日韩|
中文天堂网WWW新版资源在线|
在线观看亚洲精品国|
91黑料精品国产|
香蕉久久av一区二区三区|
国产91在线播放中文 |
三级国产人成在线亚洲视频观看h|
一级a特黄毛片高清免费|
亚洲精品久久久久久一区|
国产l精品国产亚洲区在线观看|
一本到午夜92版福利|
成人国产精品久久久久久亚洲|
丁香花视频免费播放社区|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片漫画
|
我的初次内射欧美成人影视
|
成人午夜爽A片免费视频|
成人午夜爽A片免费视频|
国产福利高清在线视频|
被粗大jib捣出了白浆H|
菠萝菠萝蜜菠萝菠萝蜜7麻豆|
久久国产人妻一区二区免色戒电影
|
日本爽爽爽爽爽爽免费视频|
爽灬好舒服灬别拔出来视频人|
男人到天堂去a线2019|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片动漫软件|
色欲久久精品AV无码|
男人女人真曰的视频|
av大片在线网站|
偷拍亚洲综合20P|
又硬又粗进去好疼A片麻豆|
福利午夜视频在线|
中文字幕亚洲一区|
福利导航第一福利导航|
被老外添嫩苞添高潮NP|
富婆偷人对白在线观看|
高清无码视频在线观看|
91在线欧美日韩精品|
最近中文字幕在线中文|
最新无码人妻在线视频|
777午夜福利理论电影网|
精品人妻一区二区A片|
波多野结衣美乳人妻hd电影欧美|
又黄又爽吃奶视频在线观看|
99国产精品久久人妻无码|
天堂中文www资源在线|
强硬进入岳A片69|
国产综合在线精品|
伊人激情AV一区二区三区|
最近中文字幕在线中文|
国产又粗又猛又爽又黄A片小说
|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
影音先锋成人色情5566|
A片爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽爽|
国产又大又粗高清观看视频|
国产精品久久人妻无码网站一丁|
国产中的精品AV一区二区|
国产成人无码精品亚洲|
亚洲另类欧美在线电影|
aa福利亚洲国内在线精品|
少妇做爰免费视频了|
午夜成人亚洲理伦片在线观看
|
精品无码久久久久久久久国产|
少妇偷拍精品高潮少妇|
国产内射大片99|
女女gay中国免费网站|
波多野结衣乳巨码无在线578|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
国产JJZZJJZZ视频免费看|
白嫩白嫩美女极品国产在线观看|
综合在线视频精品专区|
91视频精品在线观看 |
第二代国产自在自线|
国产激情久久99久久|
国产精品96久久久久久|
五月色婷婷亚洲男人的天堂|
亚洲一区在线电影|
老头把我添高潮了A片故视频|
无敌神马影院在线观看免费视频
|
国产后式a一视频|
少妇人妻av中文系列久久|
91中文日韩欧美 |
免费无码婬片17com|
国产亚洲精品久久久久久大师|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
成本人h视频动漫免费 |
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
激情综合五月亚洲婷婷|
国产1988精品A片|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师
|
久久久精品免费视频|
亚洲尤码不卡AV麻豆|
强被迫伦姧惨叫国产videos|
激情五月天天婷婷|
新国产美女精品一区二区|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
国产又爽又大又黄A片美女裸体|
国产人妻系列无码专区第二页|
99久久久无码国产精品性|
午夜精品A片一区二区三区|
一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡在线|
亚洲中字幕日产2021草莓|
性色AV一区二区三区咪爱四虎|
两个吃奶一个添下面视频|
成片免费观看视频大全|
国产色情18一20岁片A片下载|
国产白丝JK被疯狂输出视频|
亚洲精品一区二区无码夜色|
韩国无码色情在线播放|
清纯漂亮小美女准备啪啪|
国产又色又爽又黄的|
国产高潮流白浆视频|
高清欧美日韩一区二区 |
亚洲av免费分钟观看|
久久人人玩人妻潮喷内射人人|
wuyueqingsetian|
成人国成人国产SUV|
国产男女做爰高清全过小说|
黄 色一 片 级 日本|
成人亚洲天堂一区|
国产又爽又粗又猛的视频A片|
丰满放荡岳乱蜜桃AV|
成年美女拍拍视频免费|
最新女人另类ZOOZ0|
A片好大好紧好爽视频|
99精品成人无码A片观看|
男人躁女人到高潮AV|
欧美激情内射喷水高潮|
不卡高清中文字幕在线播放|
国产精品1区2区3区|
太大太长又硬放进去很爽|
亚洲欧美国产高清|
97久久国产露脸精品国产|
日产无码AV在线观看|
国产av网站中文字幕|
看看妇女的B免费看|
青青小草国产在线播放|
91popn在线国产|
91av视频免费在线观看|
欧美性色欧美性A片色欲|
精品国产午夜福利在线观看|
一个人看的www神马视频|
日韩人妻无码精品A片免费不卡
|
50阿姨性生殖视频|
91尤物视频盛宴|
亚洲色欲色欲在线大片|
两老头把我添高潮了A片苏晴|
人妻无码AV中文字久久|
A级毛片内射免费视频|
日本熟妇╳浓密毛HD|
2014av天堂影音先锋|
国产精品人妻无码免费久久久|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
岛国无码免费aⅤ毛片|
抖音WWW视频在线观看|
精品一二三区免费看|
国产JK白丝AV在线播放|
狂处让老二爽18p|
在线毛片片免费观看|
91久久香蕉国产熟女线 |
国产午夜精品视频在线播放|
九九视频在线观看视频6|
最近中文字幕手机大全|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片|
国产成人永久免费无码观看
|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
九九视频在线观看视频6|
欧美成人无码A区视频在线观看|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
最近新免费韩国视频在线观看|
熟岳大屁股疯狂迎合|
国产成人不卡AV在线观看|
特级婬片内谢aaa毛片|
亚洲国产精品一区二区三区在线观看
|
国产人妻XXXX精品HD电影|
亚洲三级在线中文字幕
|
午夜成人亚洲理伦片在线观看|
欧美日韩精品亚洲一区二区|
三人交videosdesexoe|
最近最新中文字幕大全高清8|
色情推油按摩G点高潮无码视频
|
国产天天强奸三级片|
国产一级婬小说A级|
999精品国产人妻无码梦乃爱华|
午夜伦伦电影理论片大片|
99无人区码一码二码三码...|
真人做爰48姿势视图片|
91欧美一区二区在线看|
高清国产天堂在线BT免费|
亚洲AV午夜福利精品一区二区app|
亚洲欧美精品午睡沙发|
边摸边吃奶边做爽视频免费|
日本MV高清在线成人高清|
99RE6国产精品99RE在线|
亚洲AV又黄又爽超级A片软件|
三级网站免费观看|
顶级欧美做受xxx000大乳|
灌醉水嫩大学生啪啪嗯啊男女
|
日产国产欧美韩国在线|
丰满少妇夜夜爽爽高潮水|
999久久久成人A片精品免费看|
日韩一卡二卡 3卡四卡乱码|
亚洲乱码卡1卡2新区3|
免费国产一级一级内射|
亚洲午夜精品小说图片专区|
亚洲精品久久久午夜福利电影网|
日韩一区二区免费视频|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
亚洲欧美第一精品网站|
av先锋影音资源男人站|
国产又色又粗又黄又爽免费|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
披按摩高潮A片一区二区三区|
2024中文字幕在线高清|
影音先锋av在资源天堂|
老女人熟女人妻国产|
欧美成人三级经典中文字幕|
成年人免费视频一区二区|
无码国产精品一区二区高潮最大|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合尤物|
日本又黄又爽gif动态图|
国产男人的天堂在线视频|
直接看的成人无码视频网站|
av中文字幕在线观看网址|
成年女人色费视频播放|
亚洲欧美日韩国产|
美国xoxoxoxo性欧美|
99热国产这里只有精品6|
91免费永久在线地址|
中日韩AV亚洲高潮无码|
九九综合VA免费看|
波多野结衣AV一区二区无码 |
大伊香蕉精品视频在线|
最近的中文字幕在线看2019|
中文字幕丰满孑伦无码专区|
欧美国产在线日韩|
亚洲国产欧美日韩另类精品一区二区在线
|
日本阿v手机不卡在线观看视频
|
国产精品免费大片一区二区|
欧美激情合集HB老司机在线|
狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片|
影音先锋av色噜噜影院|
中国国语对白高潮A片|
免费高清在线国产视频|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片|
国产人妻人伦精品1国产|
年轻丰满的继牳理伦片中文|
色综合久久88色综合天天6|
影音先锋影院中文无码|
乱码中字芒果视频一二三多人|
伊人成综合网伊人222|
免费观看囯产自偷自拍窥自拍|
试看免看一级a一片|
欧美h版在线观看|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片99A|
99麻豆精品国产人妻无码|
伦理电影v男人天堂|
两个吃奶一个添下面视频|
粉嫩无套白浆第一次jk|
国产精品人妻一区二区三区A|
蜜臀AV99无码精品国产专区
|
大香伊蕉在人线国产最新2005
|
国产一区精选播放022|
色婷婷狠狠97成为人免费|
国产精品美女乱子伦高|
在线成本人视频动漫 www|
国产成人无码网站m3u8|
最新无码人妻在线视频|
亚洲精品乱码8久久久久久日本|
日本XXX免费高清色视频在线观看|
免费AV岛国大片在线观看|
97人人妻人人看人人澡 |
一级A女人高潮毛片免费男|
亚洲视频无码高清在线|
欧美成人猛片AAAAAAA|
亚洲AV无码男男A片在线观看|
女人把腿张开叫男人桶免费视频
|
国产一级婬小说A级|
丰满人妻熟妇乱又伦精品劲|
影音先锋2018av网址|
精品视频在线免费观看|
成人看片黄a在线看|
欧美激情内射喷水高潮|
小雏第一次破苞疼哭|
欧美日韩一区二区在线视频|
大叫受不了了好爽国产在线|
99精品欧美一区蜜桃在线 |
伊人大杳蕉中文在线20|
国产第一页浮力影院入口|
黄色网页在线免费观看|
亚洲色熟偷拍视频在线|
内射老妇女BBWXOCLOCK|
日韩二丶三区视频免费|
日本乱妇乱熟乱妇乱色A片|
最近中文字幕视频完整版在线看|
亚洲人成在线播放无码|
成人片黄网站A片免费|
麻豆星空精东天美MV第一页|
成人视频免费在线观看|
国产女仆美女主播一区二区|
手机午夜福利1000视频|
國產午夜亞洲精品一區二區
|
同性男男黄H片在线播放网站|
99精品众筹模特私拍|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
大又大粗又爽又黄少妇毛片|
最近最新中文字幕大全高清8|
入室强伦轩人妻HD|
91一级特黄大片 |
免费岛国片在线播放|
18禁黄网站男男禁片免费观看
|
人妻性爱午夜不卡视频
|
国产精品乱码久久久久久软件|
影音先锋资源站玖玖网|
精品日韩人妻一区二区欧美|
日韩无码精品视频|
日日弄天天弄美女BBBB|
中文字幕亚洲欧美日韩2019|
很很鲁在线视频播放影院|
无码丰满熟妇BBBBXXX|
被老外添嫩苞添高潮NP|
国产精品无码一区二区在线欢捆绑
|
欧洲一卡二卡三卡|
性啪啪chinese东北女人|
波多野结衣国产区42部|
真人做爰高潮全过程|
17c人妻无码一区二区三区|
黑寡妇巨大粗爽毛片欧美|
色一情一乱一乱一区99AV|
国产日韩欧美毛片在线|
亚洲一卡二卡三卡四卡无卡网站|
日本又色又爽又黄的A片视频免费|
疼插30分钟一卡二卡三卡四卡
|
国产色欲婬乱视频网站免费|
成人福利国产视频|
我和嫲嫲狂躁了一晚上还住|
国产又粗又黄又爽又硬|
波多野結衣一區二區免費視頻|
日本无码MV免费视频在线|
和黑人高潮了10次A片|
丰满少妇猛烈进入A片88|
最近更新2019中文字幕国语|
久久久视频2019爱|
亚洲精品中文字幕制|
粉嫩小又紧水又多A片|
久久国产精品免费网站|
国产午夜婷婷精品无码A片
|
亚洲 欧美 制服 另类 无码
|
成人免费激情毛片|
日韩少妇内射免费播放|
欧美成人精品区综合A片|
亚洲AV成人无码无在线观看|
不卡人妻无码AV中文系列APP|
亚洲 欧美 制服 另类 无码|
国产真实露脸乱子伦|
国产综合av一区|
精品一卡二卡三卡四卡|
乱码丰满人妻一二三区竹菊影视
|
抖音WWW视频在线观看|
草草影院永久线路CCYY|
aa福利亚洲国内在线精品|
激情自拍另类亚洲|
亚洲AV久久久久久久无码|
久久无码人妻一区二区三区|
九九色网视频天天天操|
99麻豆久久久国产精品免费|
精品久久久爽爽久久久AV|
久久麻豆精亚洲av品国产一区|
日产一线二线三线哺乳|
国产又粗又黄又爽的A片精华|
添女人荫蒂全部过程AV|
国产亚洲麻豆精品AA片在线观看|
aV影音先锋毛片子|
真人強奷112分钟|
亚洲精品鲁一鲁一区二区三区|
2018天天弄国产大片|
无遮挡h肉动漫在线观看幽默|
国产一区二区三区在线观看网|
亚洲Av人片在线|
亚洲精品口国自一产A片|
色情.WWW成人天堂|
久草资源在线观看|
麻豆精品一卡2卡三卡4卡免费观看
|
2020最新国产自产精品|
一女被两男吃奶添下A片V图|
在线成本人视频动漫 www|
日产一线二线三线哺乳|
亚洲婷婷六月的婷婷|
邻居少妇被爽到高潮A片|
特极西西444WWW大胆无码|
最近高清中文在线字幕观看|
日产乱码一二三区别免费麻豆
|
超级青草碰碰免费视频|
动漫美女H黄动漫在线观看|
久久中文字幕人妻AV熟女|
91精品少妇色精品一区|
久久人人槡人妻人人玩夜色AV|
中文字幕欧美人乱人精品A片|
国产精品视频在线观看|
a9av红番阁免费观看|
国产美女被爽到高潮免费A片|
精品亚洲国产成人A片在线观看|
国产JK白丝喷白浆精品视频|
免费啪视频在线观看视频网页|
亚洲区色情区激情区小说公|
无码人妻丰满熟妇A片护士M|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
青草青草久热精品视频在线百度云|
欧美精品一区二区蜜臀亚洲|
啪影院免费线观看视频|
日本B站一卡二卡|
久久国产36精品色熟妇|
亚洲国产aⅴ精品无码|
无遮挡h肉动漫在线观看幽默|
丰满老熟好大bbbxxx|
波多野结衣AV一区二区无码 |
久久伊人久久大香线蕉一区|
久久久久综合网久久
|
亚洲乱码日产一区三区|
麻豆专媒体一区二区|
69国产成人精品午夜福中文 |
日韩内射美女片在线观看网站|
黑人大JI巴做爰呻吟视频|
欧美人妻WWW无码国产黄漫|
秋霞无码久久久精品一区二区|
成A人亚洲精V品无码樱花国产|
五十路丰满老熟女人妻图片|
欧美又大又粗又硬又色A片|
国产丰满老熟妇乱XXX|
国产精品1区2区3区|
特黄A又粗又大黄又爽A片|
少妇大叫又粗又大太爽A片|
宅男色影视亚洲人在线|
国产在线精品免费AAA片|
欧美性色欧美性A片色欲|
欧美又粗又深又猛又爽A片免费看|
婷婷五月开心五月色情|
久久久精品激情av日韩|
粉嫩小泬WWW免费视频网站下载|
中文字幕精品AV一区二区五区|
精品无人乱码一区二区三区无限看|
啊轻点内射在线视频|
最近亚洲中文字幕免费av|
欧美日本一区二区三四区
|
国产刺激熟女短视频在线观看|
麻豆高清免费国产一区|
亚洲男人天堂2022|
亚洲精品久久久久久AV伊人
|
国产又黄又爽又色的免费APP|
欧美FREE性黑寡妇|
国产高清国内精品福利色噜噜|
成人网站在线无码高清|
特黄A又粗又大黄又爽A片|
日韩无码精品视频|
亚洲图片欧美在线97色色|
狠狠色丁香婷婷综合|
伸进护士的小内裤疯狂揉摸|
久久久久综合网久久
|
中文字幕精品AV一区二区五区|
成年人免费视频一区二区
|
激情aa视频试看免费|
亚洲av无码专区亚洲av影音先锋|
惠民福利国产精品一区二区欧美视频|
色99久久久久高潮综合影院|
19不插片免费视频|
91成人国产麻豆一区二区|
性啪啪chinese东北女人
|
国产综合av一区|
国产AV麻豆一区二区|
国产艳福片内射视频播放|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
粉嫩高潮美女一区二区三|
一本到在线高清观看|
色狠狠躁日日躁夜夜躁A片55|
成人网站 视频免费|
a篇片在线观看快播|
曰韩少妇内射免费播放|
亚洲AV成人影视综合网|
蜜桃人妻无码AV天堂三区
|
久久久国产人妻精品|
av天堂影音先锋在线|
中国无码人妻丰满熟妇啪|
中文字幕黄色av首页网站|
国产夜色精品一区二区|
国产综合色在线视频播放线视
|
亚洲精品久久久久AV无码|
亚洲色无码专区在线观|
2018天天弄国产大片|
无广告观看久久精品99久久香蕉国产全集
|
www.xxx-av.com|
欧美又大又粗无码视频|
美女脱内衣禁黄止18以下免费|
91麻豆产精品久久久久久粉嫩
|
中国亚洲女人69内射少妇|
欧美肥胖裸熟妇的毛发布|
未满十八禁止看床片视频
|
亚洲av无码成人精品区在线播放
|
又硬又粗进去好爽A片春色视频|
久久视频这里只精品18|
AA片免费观看视频中国|
特黄AAAAA免费A片毛多水多|
久久视频精品38在线播放|
国产激情久久99久久|
双腿扒开调教羞辱奶头|
国产精品久久久久久久久久久久久久|
国产凸凹视频熟女A片|
亚洲国产视频a在线观看|
亚洲一区久欠无码A片|
国产极品JK白丝喷白浆在|
国产精品高潮呻吟久久影视A片|
久久女婷五月综合|
中国亚洲女人69内射少妇|
IJZZIJZZIJZZ教师水多|
17c在线精品无码秘入口|
国产 欧美 首页 精品|
一进一出下面喷白浆九瑶视频
|
欧美激情肉欲高潮无码鲁大师|
国产无遮挡又黄又爽在线视频|
成人性做爰AAA片免费看不忠
|
综合久久一区二区三区|
亚洲美女又黄又爽在线观看
|
亚洲一区二区一级视频免费看|
国产狂喷水潮免费网站www|
永久免费无码AV网站在线观看|
欧美黑人精品三级网站|
性色AV久久一区二区|
少妇我被躁爽到高潮A片小说|
免费人妻无码AV不卡在线|
XXX一区二日本视频|
国产亚洲精品AAAAAAA片|
91热久久免费频精品99欧美|
亚洲精品久久久久久一区|
一个人在线观看免费中文www|
真实国产熟睡乱子伦对白无套|
亚洲A片无码精品毛片色戒|
国产亚洲va在线电影|
真人女性生图片高清黑毛|
少妇大叫又粗又大太爽A片|
国产艳福片内射视频播放|
真人真实做爰30分钟试看|
91潮喷在线播放|
视频在线观看一区二区三区|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大全集|
亚洲国产精品色情777777|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区色|
啊轻点内射在线视频|
女人爽到高潮潮喷在线观看直播了
|
99RE6国产精品99RE在线|
久久久精品国产AV麻豆|
18禁日韩精品免费观看|
国产人妻人伦又粗又大爽歪歪
|
A级毛片高清免费网站不卡|
最近最新高清中文字幕av|
av最新一级网站在线观看|
好男人影视视频WWW|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
日日弄天天弄美女BBBB|
国产精品久久久久久99人妻绯闻|
高清不卡二卡三卡四卡无卡|
欧美激情综合五月色丁香|
欧美丰满大乳无码少妇|
男人自慰一级看片免费观看|
51国产偷自视频区视频|
亚洲最大成人综合网720P|
无套内谢少妇毛片A片小说作者|
WWW射我里面在线观看|
91综合国产精品视频|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
精品AAAA巨乳|
日韩精品一区二区在线免费看|
女人被添全过程A片免费视频|
98在线精品在线视频|
四平青年电影完整版|
四虎在线永久免费国产精品資源免費看|
亚洲图色中文字幕|
新影音先锋男人色资源网|
国产在线看老王影院入口2021|
亚洲一区二区三区电影在线|
久久国产精品免费网站|
成片免费观看视频大全|
国产亚洲精品久久777777
|
一级无码av护士系列在线观看|
最新日韩欧美中文字幕 |
欧美成a人片免费看久久|
國產午夜亞洲精品不卡電影|
饥渴的40岁熟妇完整版在线|
国产玉足榨精视频在线观看|
欧洲成人4卡5卡6卡7卡|
污的视频带疼痛的叫声在线观看|
精品深夜AV无码一区二区老年
|
亚洲多毛妓女毛茸茸的|
日本AAAA特级毛片|
内射一区二区精品视频在线观看|
丁香花视频免费播放社区|
动漫熟女制服一区二区 |
激情综合成人五月天|
国产啪精品视频免费制服丝袜|
77成年轻人电影网网站|
意大利电影巜豪妇荡乳|
91桃色污无限免费看|
8090碰在线视频97|
精品无码人妻一区二区三区不卡|
av综合网男人的天堂|
欧美精品做人一级爱免费|
恋夜影院支持安卓视频美女|
色噜噜噜一区二区三区|
色欲AV巨乳无码一区二区|
好看的国产精彩视频|
亚洲熟女乱综合一区二区在线|
影音先锋成人电影在线|
韩国一级婬片A片无码肉蒲团|
久久精品免费人成人A片|
中文字幕日韩一区二区不卡|
啦啦啦中文日本免费高清百度|
玩50岁四川熟女A片|
成人做爰A片免费看视频|
少妇性BBB搡BBB爽爽爽毛片|
国产操比视频三级午夜爽 |
亚洲图片综合图区20p|
成人片黄网站A片免费|
搡女人真爽免费视频大全|
欧美精品色婷婷五月综合|
91亚洲老熟女网|
图片区视频区小说区|
亚洲精品久久无码AV片软件|
搡8O老女人老妇人老熟|
高清国产天堂在线BT免费|
边吃奶边狠狠躁日韩A片|
大战熟女丰满人妻AV|
91无码人妻精品一区二区蜜桃|
区产品乱码芒果精品综合|
99在线精品免费视频|
国产免费又色又爽粗视频|
欧美熟妇乱人伦A片免费高清|
亚洲中字幕日产2021草莓|
美女张开腿黄网站免费下载|
99热久久爱五月天婷婷|
欧美熟妇乱人伦A片免费高清|
久久国产人妻一区二区免色戒电影
|
无码激情做A爰片毛片A片小说|
国产清纯91天堂在线观看|
日本妇人成熟A片一区-老狼|
五月香婷婷俺也去俺也|
免费岛国片在线播放|
着衣爆乳揉みま痴汉电车中文字幕
|
成年人精品免费视频|
5月丁香婷婷网俺来也|
久久精品成人无码A片小说|
琪琪电影网午夜理论片717西瓜|
轻轻一摸就出水13p|
婷婷综合色五月久丁香|
国产寡妇乱子伦一区二区三区。|
亚州AV无码乱码色情|
欧洲一卡2卡3卡4卡免费观看|
国产精品扒开腿做爽爽爽A片小说|
97中文字幕人妻久久精品|
丁香婷婷六月综合缴清|
a在线视频v视频|
国产47页在线观看 |
好大好深我高潮了A片|
国产精品美女WWW爽爽爽视频|
a篇片在线观看快播|
在线精品视频raPPer|
中文字字幕在线中文乱码2019|
69久久无码一区人妻A片|
老熟女肥臀AV老熟女A片|
亚洲天天网综合自拍图片专区|
天堂免费在线观看亚洲|
欧美全黄a一级一区二区三区视频
欧美日韩国产精选福利片
|
97人妻熟女成人免费视频|
四川美女BBBB爽爽毛片|
美女丝袜一区二区三区|
国产成人国产A∨国片精品白丝美女视频|
色偷偷超碰av男人天堂|
色情美女激情喷水AV|
久久99AV无色码人妻蜜|
女人下边被舔全过视频软件
|
2017秋霞在线观看免费大奶子|
999国产精品欧美一区二区
|
69无人区码一码二码三码区别|
草莓视频APP下载黄色安装|
伊人狠狠色丁香婷婷综合男同|
999热久久这里只有精品|
最近中文字幕大全免费版在线|
2022一本久道久久综合狂躁|
99久久国产综合精品1 |
图片区视频区小说区|
51久久国产露脸精品国产|
五月色婷婷亚洲男人的天堂|
日日碰狠狠躁久久躁7777|
亚洲精品无码成人A片在|
美女被c视频在线观看|
视频一区国产精戏刘婷30|
无码爽大片日本无码AAA特黄|
99精品国产综合久久麻豆|
影音先锋 影院资源av|
97人人爽人人澡人人妻|
偷拍亚洲制服另类无码专区|
国语对白农村老太婆BBw|
久久伊人五月丁香狠狠色|
国产欧美丝袜另类第三区|
rion美乳弹出来四虎在线观看|
影音先锋成人电影在线|
久久超碰av资源|
欧美性A片又硬又粗又大暴力|
国产狂喷水潮免费网站www|
久久久久亚洲AV无码专区首护士|
日本一卡二卡三卡四卡手机免费观在线|
免费啪视频观免费视频|
91久久嫩草丁香婷婷色伊人|
日本一本二本和三本的视频|
成人国产一区二区精品小说|
国产人妻XXXX精品HD电影|
国产群交轮流内射骚|
成人性生交片无码免费看|
男人吸奶日进去视频|
成人午夜免费无码福利片|
国产在线观看不卡|
无人区码卡二卡1卡2卡在线|
亚洲精品无码一区二区色戒|
黄网站免费线观看免费|
在线永久免费观看黄网站|
国产精品自产拍在线观看55亚洲|
高潮潮喷无码一区二区三区|
欧美一区二区三区不卡免费|
最近日本MV字幕免费高清视频|
亚洲gv天堂gv无码男同|
亚州精品无码久久久久av|
亚洲高清无在码在线电影|
美女裸身无档视频免费|
成人亚洲天堂一区|
玖玖爱这里只有精品视频|
91精品国产丝袜白色高跟鞋分类
|
99视频内射三四|
日本国产精品无码字幕在线观看|
国产中文字幕一区|
天津老熟女高潮A片视频|
少妇人妻丰满做爰XXX|
美女写真福利视频网站|
91精品无人区无豆乱码无人|
一人看片WWW在线视频|
www.008av.com|
亚洲天堂一区二区三区|